Cloud patch compliance auditing ensures systems across cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and GCP stay updated and meet regulatory standards. Automated tools simplify this task, offering real-time monitoring, compliance reporting, and remediation features. This article outlines the top seven tools for cloud patch compliance, comparing their features, strengths, and use cases.
Key Takeaways:
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint and Intune: Best for organisations using Azure and Microsoft ecosystems. Offers 450+ compliance assessments and seamless integration with Azure Policy.
- AWS Systems Manager Patch Manager: Ideal for AWS-heavy environments with hybrid support. Provides user-defined patch baselines and centralised compliance reporting.
- Azure Update Manager and Azure Policy: Focused on Azure-native workloads with automated patching and compliance tracking through Azure Policy.
- Google Cloud OS Patch Management: Tailored for GCP workloads, with real-time compliance dashboards and flexible patch scheduling.
- Qualys Patch Management: Multi-cloud tool with a vulnerability-centric approach, supporting over 950 compliance policies.
- Automox Cloud-Native Patch Management: A lightweight, cloud-native solution offering zero-touch automation and Worklets for custom tasks.
- ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus: Budget-friendly, supports 1,100+ apps, and provides automated patching with compliance reporting for GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
Quick Comparison:
| Tool | Best For | Key Features | Pricing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Defender + Intune | Azure-focused environments | 450+ compliance assessments, Secure Score, Azure Policy integration | Included in Microsoft plans |
| AWS Systems Manager Patch | AWS-heavy environments | Patch baselines, integration with AWS Security Hub, lifecycle hooks | Free (AWS resources billed) |
| Azure Update Manager | Azure-native workloads | Policy-driven compliance, automated patching with maintenance windows | Azure VMs free; £5/server |
| Google Cloud OS Patch | GCP-native workloads | Real-time compliance dashboards, flexible scheduling, pre/post-patch scripts | GCP resource costs apply |
| Qualys Patch Management | Multi-cloud environments | CVSS-based reporting, 950+ compliance policies, TruRisk prioritisation | Subscription-based |
| Automox | Cloud-native automation | Zero-touch patching, custom Worklets, AI scripting assistant | Subscription-based |
| ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus | Budget-conscious organisations | 1,100+ supported apps, GDPR/HIPAA/PCI DSS compliance, Test and Approve feature | From £0.80/endpoint/month |
These tools cater to different needs, from single-cloud setups to multi-cloud environments. Choose based on your platform, compliance requirements, and automation needs.
::: @figure 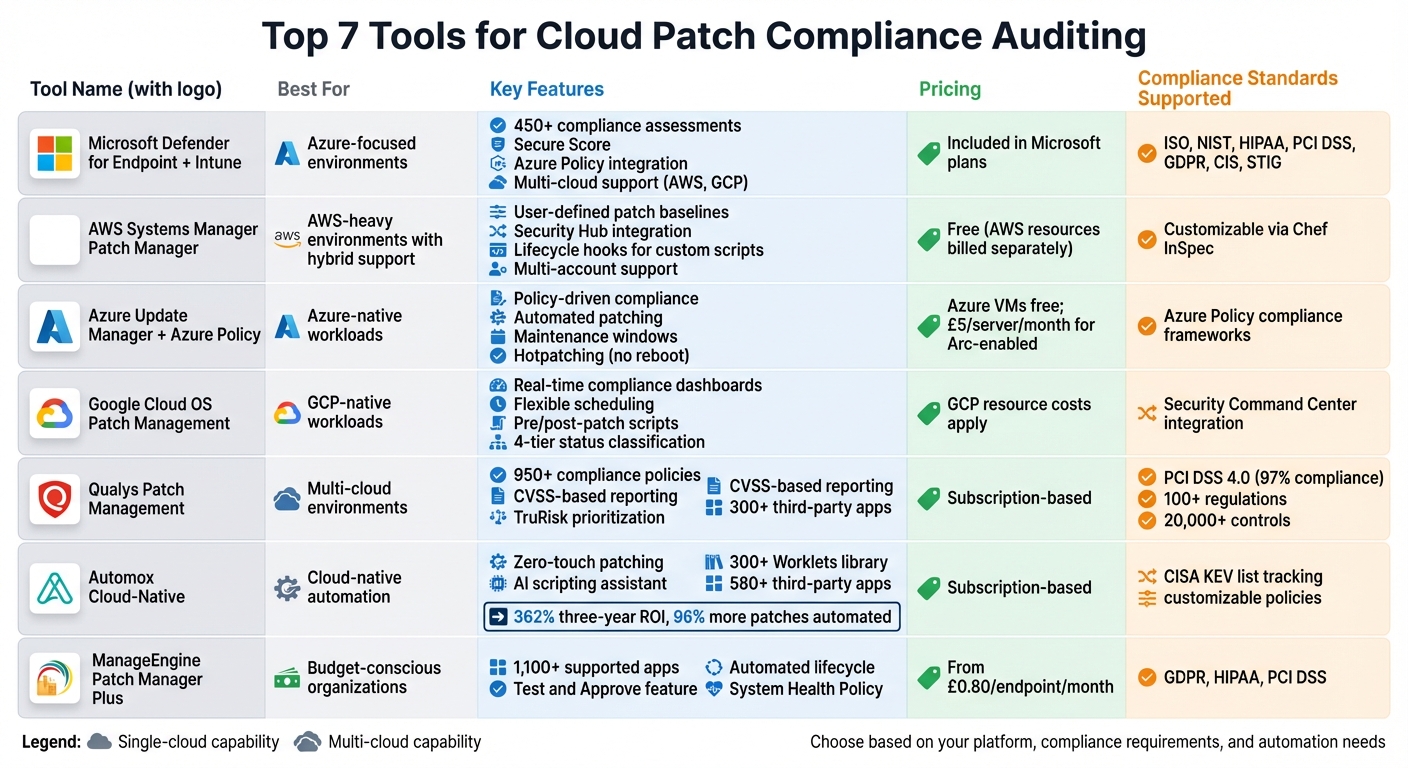 {Cloud Patch Compliance Tools Comparison: Features, Pricing, and Best Use Cases}
:::
{Cloud Patch Compliance Tools Comparison: Features, Pricing, and Best Use Cases}
:::
1. Microsoft Defender for Endpoint and Intune
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint and Intune combine endpoint protection with device management, offering a unified platform to manage patch compliance across Azure, AWS, GCP, and on-premises systems. Let’s dive into how its broad cloud and operating system support accommodates varied infrastructures.
Cloud and OS Coverage
This platform keeps an eye on resources across major cloud providers while supporting a wide range of operating systems, including Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, iOS, and even network devices. With Azure Arc, workloads on AWS and GCP can be managed as if they were native to Azure, making it easier to maintain visibility and control in multicloud environments.
Compliance Reporting
Defender goes beyond basic patch tracking with extensive compliance features. It offers over 450 built-in assessments covering standards like ISO, NIST, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR. It also evaluates systems against benchmarks such as CIS and STIG to ensure they are secure. A 2024/2025 Forrester study found that organisations using Defender for Cloud achieved a 117% return on investment within three years, with a payback period of less than six months [4]. Additionally, the Microsoft Secure Score for Devices helps organisations focus on the most critical security improvements by assessing actual risk exposure.
Automation and Remediation Features
The platform simplifies remediation with one-click actions via the Defender portal, which integrates seamlessly with Intune to create tasks. Defender for Servers Plan 2 automatically scans for missing updates and provides security recommendations when vulnerabilities are identified. To handle configuration drift and patching at scale, Azure Policy’s deployIfNotExists
feature can automate remediation across multiple subscriptions. The Quick Fix
option also ensures regular update checks through Azure Update Manager, keeping systems consistently up to date.
2. AWS Systems Manager Patch Manager
AWS Systems Manager Patch Manager is a tool designed to handle patching across AWS environments, including hybrid and multicloud setups. It works seamlessly with Amazon EC2 instances, edge devices, on-premises servers, and virtual machines, offering compatibility with Windows Server, macOS, and various Linux distributions [3][5][6]. For Linux systems, administrators can set up trusted repositories to ensure updates are sourced only from approved locations [5]. This integration with AWS tools provides better visibility into patching across different infrastructures.
Compliance Reporting
Patch Manager uses Patch Baselines
, which are user-defined lists of approved, rejected, and required patches, to assess compliance [3]. It generates detailed snapshots that highlight compliance status, missing patches, and their severity levels [3][8]. These reports are accessible via the AWS console, AWS CLI, or can be exported as .csv files for further analysis [2][3][8]. For organisations needing a historical view, enabling SSM:PatchCompliance resource recording in AWS Config allows for a full audit trail of compliance changes [1][2].
Integration Capabilities
Patch Manager integrates with AWS Security Hub to provide a centralised compliance view and with AWS CloudTrail for logging patching operations, ensuring a robust audit trail [2][3][6]. Through AWS Organizations, you can deploy patching policies across an enterprise from a centralised location [3][6]. It also supports compliance scans via Chef InSpec [1][2]. With Amazon EventBridge, you can monitor compliance events and trigger automated workflows when issues are detected [2].
Automation and Remediation Features
The platform simplifies patch management through Patch Policies, which automate patch schedules and baselines across multiple AWS accounts and regions using a configuration wizard [3][6]. Maintenance Windows allow you to schedule patching tasks during specific timeframes to minimise disruptions to critical operations [3][5]. With Lifecycle Hooks in SSM documents, you can run custom scripts before and after patching - for example, to perform health checks or restart services [3][7]. Auto-approval rules streamline the process by automatically approving patches after a set delay [3][5]. For non-compliant nodes, remediation can be handled using Run Command, State Manager, or Amazon EventBridge [2]. While the Compliance tool itself is free, costs may apply for the underlying AWS resources, such as S3 storage [2].
3. Azure Update Manager and Azure Policy
Azure Update Manager (AUM) offers a centralised way to manage patch compliance across various environments, including Azure virtual machines, on-premises servers, and multicloud platforms like AWS and GCP [12][13]. It works seamlessly with both Windows and Linux servers, while client systems rely on Intune for updates [10][14]. Non-Azure systems can also be managed through Azure Arc, enabling AUM to handle management and auditing tasks [13][14]. This flexibility ensures a broad range of systems can be effectively managed.
Cloud and OS Coverage
AUM supports multiple operating systems, including Windows Server versions with Extended Security Updates for Windows Server 2012 and 2012 R2. It also integrates with package managers like apt and yum for major Linux distributions [11][12][14]. Beyond standard virtual machines, it can manage VMware environments, System Center Virtual Machine Manager (SCVMM) machines, and Azure Local clusters [13]. Azure VMs require only the standard VM agent, while Arc-enabled servers need the Azure Arc agent [13]. These features are designed to support compliance reporting through Azure Policy.
Compliance Reporting
All compliance and update data is stored in Azure Resource Graph, allowing administrators to build tailored compliance reports and dashboards using Azure Workbooks [9][14]. Azure Policy provides a clear overview of compliance, helping administrators identify resources that don’t meet patching requirements. It also allows for detailed analysis of configuration drifts. Unlike older solutions, this approach eliminates the need for Log Analytics or Azure Automation [12][13].
Integration Capabilities
Azure Policy simplifies management by automating periodic assessments and recurring update schedules across resource groups or subscriptions [9][13]. The platform checks for pending updates every 24 hours as part of its periodic assessments [10][13][14]. Machines can be dynamically grouped by subscription, resource group, location, or tags, enabling automatic association with maintenance schedules [12][13]. For instance, any new resource tagged with Environment: Production
is automatically included in patch compliance policies without requiring manual setup. Azure Policy can also fix non-compliant resources by installing missing extensions or enabling settings such as Periodic Assessment
automatically [15].
Automation and Remediation Features
Automatic VM Guest Patching ensures that Security
and Critical
patches are applied to Azure virtual machines as soon as they are available [13][14]. For supported Windows Server Azure VMs, hotpatching allows critical security updates to be installed without restarting the system, significantly reducing downtime [13][14]. The platform supports pre- and post-update events via webhooks or Azure Functions, making it easier to manage tasks like service shutdowns or health checks [9]. Maintenance schedules can be customised to align with specific update windows, including synchronisation with Patch Tuesday
[12][14]. Azure VMs benefit from this service at no extra cost, while Azure Arc-enabled servers are priced at £5 per server per month (based on a 31-day month) [12][14].
4. Google Cloud OS Patch Management
Google Cloud OS Patch Management, part of VM Manager, is tailored specifically for managing Google Cloud Compute Engine VM instances [16][17]. It supports Windows systems through the Windows Update Agent and several Linux distributions, including Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), Rocky Linux, CentOS, Debian, Ubuntu, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES), and openSUSE. However, there are some limitations: SLES does not support patch compliance reporting, and while Rocky Linux provides basic reporting, it lacks severity-based classifications [16].
Cloud and OS Coverage
The service relies on distribution-specific tools for updates: RHEL and CentOS use yum upgrade, Debian and Ubuntu use apt upgrade, and SLES uses zypper update. Each operating system taps into its default vulnerability data source, such as Red Hat Security Data for RHEL or the Ubuntu CVE Tracker for Ubuntu. To keep compliance information up to date, the OS Config agent refreshes inventory data every 10 minutes. For organisations looking for more control over patch baselines, Google suggests using a local repository or Windows Server Update Service (WSUS) instead of depending solely on public sources [16].
Compliance Reporting
A unified dashboard classifies VM patch statuses into four categories: Critical (Red), Important/Security (Orange), Other (Yellow), and Up-to-date (Green), offering a clear, real-time overview of patch compliance across both Windows and Linux environments [16]. Integration with the Security Command Center's Audit Manager simplifies regulatory compliance by automatically generating audit evidence [19]. While patch jobs are limited to individual projects, administrators can consolidate compliance data from multiple projects. Dashboard updates generally occur about 30 minutes after a patch job starts [18]. This centralised reporting aligns with the dashboards offered by other leading cloud patch tools, ensuring a streamlined approach to compliance.
Integration Capabilities
Google Cloud OS Patch Management enhances its core features with various integration options. It works seamlessly with the OS Config API, Google Cloud Console, and the gcloud CLI, making it accessible for day-to-day operations. Teams can also use Infrastructure as Code tools like Terraform to manage patches consistently across projects [17]. For added security, the platform integrates with VPC Service Controls to enforce strict boundaries. Virtual machines in private VPCs without public IPs can still access external update sources through Cloud NAT or proxy services. For compliance auditing, assigning the roles/osconfig.patchJobViewer role is recommended, as it provides read-only access without execution permissions [18].
Automation and Remediation Features
The platform offers flexible patch scheduling options, including on-demand, one-time, and recurring schedules with custom maintenance windows [16][18]. The patch installation deadline
feature ensures critical updates are applied by a specific date [16]. Pre- and post-patch scripts, stored locally or in Cloud Storage, can automate tasks like shutting down applications or performing health checks. Administrators can target specific instances for patch deployment using filters such as labels, zones, or name prefixes (e.g., 'env=prod'). Rollout strategies include zone-by-zone or concurrent updates, with disruption budgets in place to minimise the number of VMs taken offline at the same time [18]. To avoid conflicts and ensure accurate reporting, Google advises disabling native Windows automatic updates during the patch management process [18].
5. Qualys Patch Management
Expanding on the automation and compliance tools mentioned earlier, Qualys Patch Management delivers extensive vulnerability and patch control across multi-cloud environments. As a key component of the Qualys Vulnerability Management, Detection and Response (VMDR) platform, it supports platforms like AWS, Azure, GCP, and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure [20]. It simplifies patch compliance for Windows, Linux, macOS, and even mobile systems like Android and iOS/iPadOS. All of this is managed through a single lightweight Cloud Agent, which handles data collection and patch deployment across on-premises systems, endpoints, and cloud environments [20].
Cloud and OS Coverage
In AWS, Qualys offers Transparent Orchestration
and supports the Graviton-ready ARM architecture, which helps reduce costs while maintaining strong security [24]. Take the example of Children's Mercy Kansas City: they deployed Cloud Agents across 13,000 assets, gaining vulnerability insights every four hours without needing system reboots. The platform also supports over 300 third-party applications, with its Cloud Agent now running on more than 110 million assets globally [20].
Compliance Reporting
Qualys provides a unified dashboard that gives a complete view of all assets, automatically linking detected vulnerabilities to the patches required to fix them. The platform supports over 950 policies, 20,000 controls, and 100 regulations, achieving 97% compliance with PCI DSS 4.0 standards [22]. It also integrates seamlessly with tools like AWS Security Hub, and organisations using it have reported resolving security tickets 60% faster thanks to bidirectional integrations with ITSM tools such as ServiceNow and JIRA [20].
Integration Capabilities
The platform offers built-in integrations with leading cloud providers, delivering near-instant visibility - just two seconds - across hybrid environments [25]. It works with CMDB and ITSM tools to automate ticketing and asset updates. For environments with strict internet restrictions, the Gateway Service ensures Cloud Agent deployment within locked-down networks [21]. In one real-world example, Qualys demonstrated continuous patching and system monitoring even during major operational disruptions.
Automation and Remediation Features
Qualys' zero-touch patching system has been shown to boost patch rates by as much as 90% [20]. The TruRisk engine helps prioritise patches by factoring in business importance and real-time threat data, leading to a 40% reduction in Mean Time to Remediation and an 85% drop in overall vulnerabilities [23]. Moreover, the QFlow tool - a no-code workflow builder - allows teams to automate complex tasks without requiring programming skills.
Cintas Security Operations Manager Tom Scheffler highlighted the simplicity of this system:
Previously, we used SCCM, which was a challenge because you had to tell it what to do. Qualys scans it, finds it, patches it. That's it.[20]
This approach has not only saved labour costs but also improved workforce efficiency and planning.
Need help optimizing your cloud costs?
Get expert advice on how to reduce your cloud expenses without sacrificing performance.
6. Automox Cloud-Native Patch Management
Automox stands out by eliminating the need for on-premises infrastructure. As a cloud-native solution, it patches devices automatically as soon as they connect - no VPN required [30][31]. It works seamlessly with Windows, macOS, and Linux, covering physical, virtual, and cloud-based endpoints, including those hosted on AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform [26]. Its lightweight agent can be deployed and start patching in under 30 minutes [28], making it a practical choice for fast-paced cloud environments. Currently, Automox manages over 1,250,077 endpoints [26].
Cloud and OS Coverage
Automox's capabilities go beyond operating system updates. It supports patching for over 580 third-party applications, including popular tools like Adobe, Chrome, Slack, Zoom, and Firefox [26]. This unified approach allows IT teams to oversee clients, servers, virtual machines, containers, and cloud instances - all from a single console. Thanks to its cloud-native design, Automox is not tied to specific locations or domains, enabling organisations to patch devices for remote workers and distributed teams without complex network setups [30][31].
Compliance Reporting
Automox offers a real-time dashboard that provides visibility into critical metrics like CVE exposure, Mean Time to Remediate (MTTR), and policy outcomes. It also flags high-risk threats, such as those identified in CISA's Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) list, helping organisations prioritise their response [29]. The platform includes more than 20 prebuilt reports covering areas like device health, patch status, and vulnerability exposure, with options to export reports in PDF, CSV, or XLSX formats [29].
Jonathan Sibray, Senior Director at the University of Colorado Law School, shared his experience:
We needed a solution that was cloud-based, served our multi-OS environment, and gave us the right mix of automation and control needed to configure/customise a variety of end users. Automox just worked[27].
By combining robust reporting with automation, Automox simplifies the process of staying compliant and secure.
Automation and Remediation Features
Automox takes automation to the next level with its Worklets - reusable PowerShell and Bash script blocks that fully automate patching tasks [30][31]. IT teams can choose from a library of over 300 pre-made Worklets for tasks like software deployment and configuration enforcement [31]. For custom needs, the Ask Otto AI assistant helps draft scripts, removing the need for in-depth coding expertise [30][26]. The FixNow feature allows immediate action on selected devices, with real-time progress updates [31].
The results speak for themselves: Automox delivers a 362% three-year ROI, automates 96% more patches, and reduces patching errors by 65% [30].
7. ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus
Rounding out the top seven, ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus offers a streamlined approach to patch compliance with powerful automation tools tailored for modern cloud environments. This platform supports Windows, macOS, and Linux systems, as well as over 850 third-party applications like Adobe, Java, and WinRAR [32]. Available as a cloud-native SaaS or deployable on cloud infrastructure (such as AWS instances), it ensures patch management across various network setups - LAN, WAN, DMZ, and even remote work-from-home setups - without needing a VPN [32]. Pricing starts at under £0.80 per endpoint monthly for the Professional Edition, with the Enterprise Edition starting at a similar rate [32].
Cloud and OS Coverage
Patch Manager Plus goes beyond basic operating system updates, handling patches for servers, laptops, and workstations - all from a single console [32]. For AWS users, the platform recommends using an Elastic IP Address to maintain stable communication between agents and servers [34]. Its compatibility spans over 1,100 applications, ensuring IT teams can maintain compliance across physical, virtual, and cloud-based endpoints [32].
Compliance Reporting
The platform employs a System Health Policy to categorise endpoints into categories like Healthy, Vulnerable, or Highly Vulnerable. It provides detailed reports through one-click templates, automated tasks, and real-time dashboards [36][37]. The entire remediation process - from detection to automated deployment - is meticulously logged, offering a clear record of how non-compliant systems were brought back into compliance [37]. Additionally, it supports adherence to international standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS by keeping systems updated and generating audit-ready reports [35].
Integration Capabilities
Patch Manager Plus integrates seamlessly with vulnerability scanners like Tenable.io and Tenable.sc, simplifying detection and remediation workflows [39]. It also connects with ServiceDesk Plus to enhance IT service management [38]. User reviews reflect its reliability, with ratings of 4.6/5 on both Capterra and G2, 4.4/5 on Gartner Peer Insights, and 4.5/5 on Software Advice [32]. These integrations and features make it an essential tool for automated patch deployment.
Automation and Remediation Features
The Automated Patch Management (APM) feature takes care of the entire patch lifecycle, including vulnerability database updates, endpoint scanning, patch downloads, deployment, and status reporting [38]. Its 'Test and Approve' function allows patches to be tested on a smaller group before full deployment [33]. For systems that fail initial deployment due to inactivity or connectivity issues, the platform automatically re-scans and re-attempts deployment [33].
Patrick Brown, an IT Support Specialist at Empower Media Marketing, highlighted its benefits:
Our biggest challenge was going to every machine in the company to run the update. Being able to automate patch deployment, this tool saves a lot of time and is worth the money.[39]
For organisations like Gupshup, which rely heavily on Linux servers, the platform has been described as a lifesaver
for maintaining server security through automated patch and package deployment. Users have reported reducing patching time by up to 90% [32].
Feature Comparison Table
Here’s a detailed side-by-side comparison of key features for patch compliance auditing across various tools, highlighting their strengths and capabilities.
| Tool | Cloud & OS Coverage | Compliance Reporting | Integration Capabilities | Automation Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Defender for Endpoint and Intune | Azure, on-premises; Windows Server, Windows Desktop [5] | Policy-based configuration with real-time security dashboards | Deep integration within the Microsoft ecosystem; limited external integrations | Automated security policies via Windows Update for Business |
| AWS Systems Manager Patch Manager | AWS, on-premises, hybrid, multicloud; Windows Server, Linux (Amazon Linux, RHEL, Ubuntu), macOS [3][5] | User-defined patch baselines with snapshot exports [3][8]; integrates with Amazon Athena and QuickSight [2] | Chef InSpec for compliance profiles [2]; Hybrid Activations for edge devices [3][5] | Patch policies via Quick Setup, including auto-approval rules and lifecycle hooks for custom scripts [3]; no additional charges [2] |
| Azure Update Manager and Azure Policy | Azure, hybrid; Windows, Linux | Policy-driven compliance with Azure Monitor integration | Native Azure services; limited external integrations | Scheduled patching with maintenance windows; automated Update Management |
| Google Cloud OS Patch Management | Google Cloud, hybrid; Linux, Windows | GCP-native compliance dashboards with Cloud Monitoring | Integration with Cloud Security Command Centre | Automated patch deployment schedules; OS Config agent-based management |
| Qualys Patch Management | Multi-cloud, on-premises; Windows, Linux, macOS | Vulnerability-focused reporting with CVSS scoring | Qualys Cloud Platform integration; SIEM connectors | Automated patch testing and deployment workflows |
| Automox Cloud-Native Patch Management | Cloud-native SaaS; Windows, macOS, Linux | Real-time compliance dashboards with policy-based grouping | REST API for custom integrations; PSA/RMM tool connections | Zero-touch automation with worklet-based custom scripting |
| ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus | Cloud-native SaaS or cloud-deployed (AWS); Windows, macOS, Linux; 1,100+ applications [32] | System Health Policy categorisation (Healthy, Vulnerable, Highly Vulnerable) [36][37]; GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS compliance reports [35] | Integrates with Tenable.io, Tenable.sc, and ServiceDesk Plus [38][39] | Automated Patch Management lifecycle [38]; Test and Approve functionality; automatic re-deployment for failed patches [33] |
Each tool has its own strengths depending on your organisation's needs:
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint and Intune is ideal for Windows-focused environments with its seamless integration into the Microsoft ecosystem.
- AWS Systems Manager Patch Manager offers extensive flexibility, supporting diverse platforms and custom patch baselines, and it doesn’t incur extra charges beyond resource usage.
- Azure Update Manager and Azure Policy work well for Azure-native workloads, with robust policy-driven compliance.
- Google Cloud OS Patch Management excels in managing GCP-native workloads, offering automated schedules and integration with Google’s security tools.
- Qualys Patch Management stands out with its vulnerability-centric approach and CVSS-based reporting.
- Automox prioritises simplicity with cloud-native, zero-touch automation.
- ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus is a budget-friendly option (under £0.80 per endpoint monthly [32]) that supports over 1,100 applications and offers compliance with frameworks like GDPR and HIPAA.
When choosing a tool, consider whether you need multi-cloud support, extensive integration options, or adherence to specific compliance standards. Each solution brings unique capabilities to help maintain continuous, real-time patch compliance in complex environments.
Conclusion
Choosing the right patch compliance tool depends on your cloud environment, operating systems, and specific compliance needs. For single-cloud setups, cloud-native options like AWS Systems Manager Patch Manager and Azure Update Manager are excellent choices. They integrate seamlessly with their respective platforms and only charge for the core resources you use [2]. These tools are particularly effective if you need provider-specific features, such as lifecycle hooks for running custom scripts.
For organisations managing multi-cloud or hybrid environments, cross-platform solutions provide a unified view. These tools often come with built-in frameworks to help meet UK compliance standards like GDPR and ISO 27001. While they usually require a subscription, they simplify compliance efforts by offering pre-configured frameworks tailored to regulatory requirements.
To strengthen your patch compliance strategy, consider combining tools. Use cloud-native solutions for granular, provider-specific control, and cross-platform tools for broad visibility across diverse environments. This dual approach ensures both deep integration where it’s needed and comprehensive oversight. Keep in mind that patch compliance reports are typically snapshots of a single point in time. To maintain historical records for audits, services like AWS Config can continuously log data, preventing the loss of previous scans [8][1].
For UK organisations, regular audits and proper log storage are non-negotiable. Look for tools that support multi-account and multi-region configurations, integrate with SIEM and ITSM systems, and allow you to define custom compliance metrics [2][1]. It’s also important to establish a responsibility matrix to clarify which compliance controls are managed by your organisation and which are the responsibility of the cloud provider. Using consistent resource tagging will further help with cost allocation and compliance tracking.
Schedule compliance audits at least twice a year and ensure audit logs are stored within compliant jurisdictions. A well-planned combination of tools, backed by regular evaluations and audits, lays the foundation for a scalable and compliant patch management strategy.
FAQs
What should I consider when choosing a cloud patch compliance tool?
When choosing a cloud patch compliance tool, there are a few critical factors to keep in mind. First, the tool should support regulatory compliance by aligning with frameworks like GDPR, ISO 27001, or PCI DSS. It’s also important that it can generate detailed, audit-ready reports to simplify compliance checks.
Next, look for automation and integration features. Automated patching policies, multi-region scanning, and seamless integration with cloud-native services like AWS Config or Security Hub can save time and reduce manual effort.
Strong visibility and reporting capabilities are another must-have. Tools with real-time dashboards and historical tracking allow you to quickly spot and address compliance issues. If your organisation operates across different platforms, multi-cloud support is essential for managing workloads across AWS, Azure, GCP, or even on-premise systems.
Finally, consider factors like scalability, ease of use, and cost-effectiveness. The tool should be capable of handling large-scale operations without exceeding your budget or creating unnecessary complexity.
Hokstad Consulting can help you evaluate these considerations and develop a tailored solution to enhance your patch compliance processes and overall cloud strategy.
How do these tools work with cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and GCP?
AWS offers native tools like Systems Manager Compliance and Patch Manager, which work effortlessly with managed nodes through the Systems Manager API, EventBridge, and Security Hub. These tools help track and report on patch compliance within AWS environments, ensuring smooth operations.
For organisations managing resources across multiple cloud platforms, Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) tools come into play. These tools connect with AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) using platform-specific APIs or lightweight agents. They continuously scan resources and compile compliance data into a single, easy-to-navigate dashboard. This makes it simpler to keep track of compliance across various cloud providers.
By leveraging these integrations, organisations can effectively manage patch compliance, whether they rely on a single-cloud setup or operate within a multi-cloud environment.
What are the advantages of using a multi-cloud patch management tool instead of a single-cloud solution?
Using a multi-cloud patch management tool gives you a centralised view of all your cloud environments. This means you can audit, fix, and report on patch compliance across platforms like AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and private clouds - all from one interface. It eliminates coverage gaps often found with provider-specific tools and ensures your entire infrastructure, including newly added resources, is under continuous and consistent monitoring.
By defining policies just once and applying them across all providers, these tools cut down on administrative work, making it easier to meet regulations like GDPR and ISO 27001. They also lower the chances of missing critical patches. In comparison, single-cloud solutions often rely on separate tools or manual processes for each provider, which can result in fragmented reporting, duplicated efforts, and increased operational costs. Consolidating patch management with a multi-cloud tool not only simplifies operations but also enhances coverage and helps save costs.
