Automation makes ISO 27001 compliance faster, simpler, and more reliable for private cloud environments. Instead of relying on manual processes, which are time-consuming and prone to errors, automated tools streamline evidence collection, monitor security configurations in real time, and ensure continuous audit readiness.
Key takeaways:
- Why it matters: With 98% of businesses reporting cloud-data breaches by late 2025 and average breach costs reaching £3.6 million, ISO 27001 compliance is critical for protecting sensitive data.
- Manual challenges: Manual compliance wastes resources, increases errors, and struggles to keep up with constantly changing cloud environments.
- Automation benefits: Tools like Hyperproof, Process Street, and Scrut Automation reduce compliance time by up to 30%, enforce secure configurations, and provide centralised dashboards for instant insights.
- How it works: Automation integrates controls like access management, encryption, and logging into your cloud workflows, ensuring compliance is maintained without disrupting operations.
Key ISO 27001 Controls for Private Cloud Environments
Cloud-Specific Risks and Controls
Even in private cloud setups, the shared responsibility model remains a key principle. As Microsoft explains:
In any cloud deployment, you always own your data and identities and are responsible for protecting them[4].
While your cloud provider handles the physical infrastructure's security, the responsibility for safeguarding your data, identities, and configurations lies squarely with you. ISO 27001:2022 Control A.5.23 underscores the need for well-defined policies to manage cloud services effectively [4].
The risks in these environments are significant. Cyber attackers often exploit cloud misconfigurations and weak security controls. One persistent issue is configuration drift, where manual changes over time stray from established secure baselines. Automation tools can mitigate this risk by regularly resetting security settings - like Azure Local environments that refresh configurations every 90 minutes [2].
These measures highlight the importance of automation in maintaining compliance and security.
Access Control, Encryption, and Monitoring
Addressing cloud-specific risks calls for a focused approach to access control, encryption, and continuous monitoring. Here’s how these areas are covered under ISO 27001:
Access control (Controls 8.2, 8.3, and 8.5) is critical for managing privileged accounts and enforcing secure authentication. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a must, and automated systems can quickly identify over-privileged accounts or disabled MFA. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Privileged Identity Management (PIM) further ensure that users operate under the principle of least privilege [2][4].
Cryptography (Control 8.24) ensures data security through robust encryption. BitLocker XTS-AES 256-bit protects data at rest, while TLS 1.3 and SMB encryption safeguard data in transit. Automation plays a role here, too, by monitoring key rotation and enforcing HTTPS across web services, ensuring encryption remains consistently applied [2].
Continuous monitoring (Control 8.15) enables detailed tracking of activities within your environment. Solutions like Microsoft Sentinel integrate with SIEM platforms to ensure audit logs are always active. Automated detectors verify log sinks and check VPC flow logs, providing critical forensic data. This is especially important given that the average data breach takes 241 days to resolve [4].
| ISO 27001 Control | Automation | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| 8.20 Network Security | Datacentre firewalls & software load balancers | Blocks lateral movement within the private cloud [2] |
| 8.24 Cryptography | BitLocker & TLS 1.3 enforcement | Secures data against theft or interception [2] |
| 8.15 Logging | SIEM integration & log verification | Ensures forensic evidence is available for investigations [2] |
| 8.9 Configuration Management | Drift control & policy enforcement | Prevents manual changes from undermining security [2][4] |
Automation Tools and Techniques for ISO 27001 Compliance
Tools for Compliance Automation
The market for compliance automation offers a variety of platforms designed to simplify ISO 27001 processes. For instance, Hyperproof provides an ISO 27001 template library and automates evidence collection, which has been shown to reduce compliance time significantly. Byron Thomas from Glance Networks shared:
With Hyperproof, we reduced time spent on ISO 27001 compliance processes by 30%[5].
Scrut Automation stands out with over 100 integrations and more than 75 auditor-ready policy templates [1]. If you need rapid deployment, Anitian's SecureCloud platform is impressive - it can deploy over 15 pre-configured security tools around an application in just one day [6]. It also features DriftDefend, which identifies and corrects compliance drift in real time.
Another notable tool is Process Street, which employs Cora
, an AI compliance agent that automates risk identification and scoring. For organisations with specific data residency needs in regions like the UK, US, or EU, it offers private cloud deployment options [7]. Meanwhile, Orca Security links security risks such as malware or misconfigurations directly to ISO 27001 Annex A controls, providing automated pass/fail results across VMs, containers, and serverless functions [3].
These tools lay the foundation for integrating compliance automation into your existing workflows, particularly in cloud environments.
Integrating Automation into Cloud Management
Rather than treating compliance as an isolated task, it’s more effective to embed it directly into your cloud workflows. A popular approach is Policy as Code (PaC), where governance rules are written as executable code (using formats like Rego or YAML). This ensures compliance standards are automatically enforced across platforms like Kubernetes, OpenStack, and VMware. This method addresses potential challenges by maintaining continuous compliance.
In CI/CD pipelines, tools like conftest or the Kyverno CLI validate infrastructure-as-code manifests during pull requests, catching non-compliant configurations early in the development process. For Kubernetes-based private clouds, tools like OPA Gatekeeper and Kyverno act as admission controllers, intercepting API requests to block non-compliant resources in real time.
Continuous Controls Monitoring (CCM) takes compliance a step further by replacing annual audits with frequent scans - sometimes hourly or daily. Mike Caldwell, Senior Programme Manager of GRC at Outreach, demonstrated this at scale by setting up five compliance programmes in just a few months. His team linked nearly 1,000 controls to 1,500 pieces of automated evidence [5]. Additionally, a GitOps workflow stores policies in version control, enabling peer reviews and maintaining a clear audit trail for governance changes.
When standard tools fall short, custom solutions can bridge the gap.
Custom Automation Solutions from Hokstad Consulting

Not every organisation’s needs can be met by off-the-shelf platforms, especially for private cloud environments. Hokstad Consulting specialises in creating custom automation solutions tailored to specific infrastructure requirements, whether on-premises, hybrid, or fully private.
Their expertise in DevOps transformation and custom development allows them to design workflows that integrate seamlessly with your existing systems. This includes building policy-as-code frameworks, automated evidence collection pipelines, and continuous monitoring systems that align directly with ISO 27001 Annex A controls. For organisations requiring advanced AI-driven compliance detection or bespoke automation, Hokstad Consulting’s technical expertise ensures compliance is maintained without disrupting daily operations.
Customised automation solutions make it possible to transition from manual processes to a more proactive, efficient compliance approach.
Step-by-Step Guide to Automating ISO 27001 Compliance
Step 1: Conduct a Risk Assessment and Define Responsibilities
Start by creating a detailed inventory of all your private cloud assets - this includes virtual machines, containers, storage, and identities. Automation begins with this thorough asset inventory to ensure every component is covered by effective controls [3]. Once your infrastructure is mapped, use a risk assessment to identify which Annex A controls apply [2].
It's also critical to establish clear boundaries of responsibility. While cloud providers handle independent audits of their infrastructure, your organisation is still accountable for the compliance of the services and workloads you deploy on their platforms [2]. Clearly document these shared responsibilities, especially in hybrid setups where some infrastructure remains on-premises.
With your assets mapped and responsibilities outlined, you can move on to securing configurations.
Step 2: Set Up Configuration Baselines
Define secure-by-default configurations based on CIS Benchmarks. Use Infrastructure as Code (IaC) scanning to catch misconfigurations early in the development process, often referred to as 'Shift Left' security [3][2]. This ensures that potential issues are addressed before deployment.
Automate drift control to maintain configuration consistency and enable encryption by default for both data-at-rest and data-in-transit [2][9]. Once these secure baselines are in place, continuous monitoring becomes the next focus.
Step 3: Implement Continuous Monitoring and Auditing
Replace the traditional annual audit approach with continuous monitoring, running daily or even hourly scans. Automate malware and vulnerability scanning across all resources, including virtual machines, containers, and serverless functions [3]. Set up real-time alerts for network activity, ensuring you monitor all protocols and ports. Be sure to flag weak protocols like FTP or outdated TLS versions for immediate action [3][10].
Centralise your logs using tools like a syslog event forwarder or SIEM solutions such as Microsoft Sentinel. This automated collection of activity logs is vital for meeting ISO 27001's logging and monitoring requirements [2].
Once monitoring is operational, focus on automating evidence collection to simplify compliance reporting.
Step 4: Automate Evidence Collection and Reporting
Use centralised dashboards to display compliance outcomes for all cloud assets. Link failed compliance checks - such as Annex A.9.2.3 for privileged access - directly to specific risks, like a user not having MFA enabled. Provide clear instructions for remediation [3].
Automation tools can pull data directly from cloud services, HR platforms, and ticketing systems via APIs, eliminating the need for manual screenshots or log downloads [8][12]. This creates a Compliance HQ
that maintains an audit-ready state year-round, saving time and effort when audits arise.
Step 5: Establish Regular Review and Improvement Processes
To close the compliance loop, schedule regular reviews to validate and refine your automated controls. Set up notifications for expert review, as human judgement is still essential for interpreting complex regulatory issues, even when AI flags anomalies in logs or configuration drift [8]. Use automation tools to track progress over time, showing that vulnerabilities have been addressed [3].
Incorporate posture templates tailored to ISO 27001, with detectors for issues like disabled audit logging, unrestricted API keys, or unrotated KMS keys [11]. Regularly review and update your automation rules to keep up with evolving threats and technology changes. This ensures your compliance processes remain effective and aligned with current standards.
Need help optimizing your cloud costs?
Get expert advice on how to reduce your cloud expenses without sacrificing performance.
Doing Compliance with Automation: an ISO 27001 Case Study
Benefits of Automating ISO 27001 Compliance
::: @figure 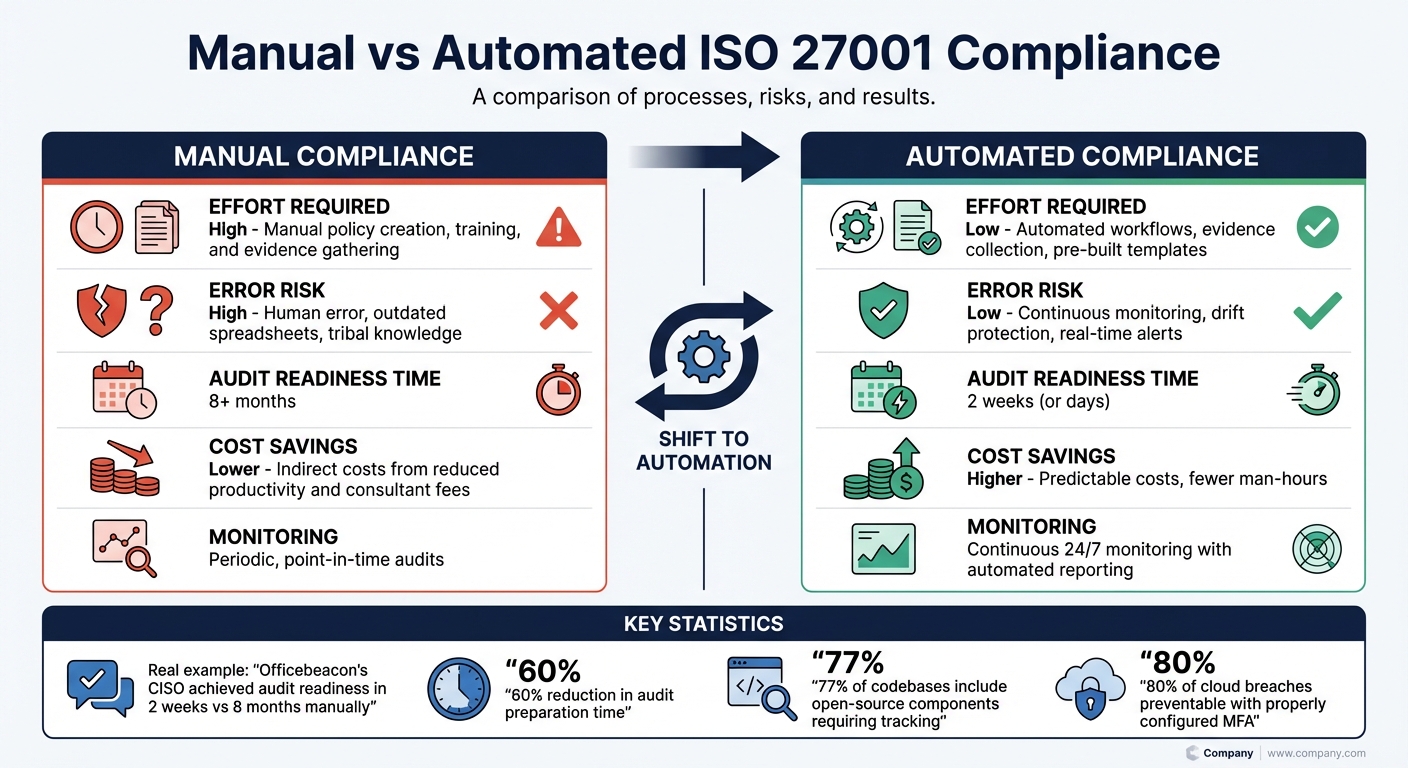 {Manual vs Automated ISO 27001 Compliance: Time, Cost, and Efficiency Comparison}
:::
{Manual vs Automated ISO 27001 Compliance: Time, Cost, and Efficiency Comparison}
:::
Manual vs Automated Compliance Comparison
Manual compliance is a labour-intensive process, while automation simplifies and accelerates it. Teams managing compliance manually often spend months drafting policies, collecting evidence from various systems, and preparing for audits. In contrast, automation can drastically reduce this timeline. For example, in August 2024, Officebeacon's CISO Anil achieved ISO 27001 audit readiness in just 2 weeks using automation, compared to the 8 months it would have taken manually [13].
Given that 77% of codebases include open-source components [14], automation plays a crucial role in tracking vulnerabilities and reducing errors. Here's a quick comparison of the two approaches:
| Feature | Manual Compliance Process | Automated Compliance Process |
|---|---|---|
| Effort Required | High; involves manual policy creation, training, and evidence gathering [13] | Low; uses automated workflows, evidence collection, and pre-built templates [13] |
| Error Risk | High; susceptible to human error, outdated spreadsheets, and reliance on tribal knowledge[13][15] |
Low; offers continuous monitoring, drift protection, and real-time alerts [6][2] |
| Audit Readiness Time | Typically over 8 months [13] | Achievable in 2 weeks or even a few days [13][6] |
| Cost Savings | Lower; indirect costs due to reduced productivity and consultant fees [13] | Higher; predictable costs with fewer man-hours required [13] |
| Monitoring | Periodic, point-in-time audits [13] | Continuous 24/7 monitoring with automated reporting [6] |
Long-Term Cost and Efficiency Gains
Beyond the immediate benefits, automation provides significant long-term cost savings and efficiency improvements. Organisations using automated compliance tools report a 60% reduction in audit preparation time [17]. The National Cyber Security Centre highlights that over 80% of cloud account breaches could be avoided with properly configured Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), which automation enforces consistently.
Cloud automation mitigates \[runaway cloud bills\] by providing greater control and visibility across cloud environments, facilitating efficient resourcing and management and alleviating the burden of repetitive tasks from IT teams.- IBM [16]
Automation not only simplifies compliance but also helps control cloud-related expenses. As private cloud infrastructures grow, automated policies adapt seamlessly without the need for extra staff. With configuration drift detection every 90 minutes [2], organisations maintain compliance as new resources are added. This always-ready
state eliminates the frantic rush typical of manual compliance processes, freeing up security teams to focus on strategic improvements rather than tedious evidence collection.
Conclusion
Key Points Recap
Automating ISO 27001 compliance can shift private cloud management from being a time-consuming, reactive chore to a streamlined, proactive process. By replacing annual audits with continuous monitoring, security settings can be refreshed as often as every 90 minutes to address unauthorised changes automatically [2][9]. Automated platforms also simplify the audit process, generating documentation instantly and reducing evidence collection time from months to mere days [6].
The advantages go beyond just saving time. Automation removes the risks tied to manual spreadsheet updates and scattered email chains by linking controls directly to system configurations [1]. This allows security teams to focus on tackling strategic risks rather than getting bogged down in administrative tasks. Additionally, centralised dashboards offer a unified view of compliance across multi-cloud environments, eliminating the need to juggle multiple monitoring tools [3].
As Scrut Automation highlights:
Automation replaces fragmented, manual efforts with a system that continuously maps controls to real configurations, flags misalignments in real time, and generates audit-ready evidence on demand.- Scrut Automation [1]
These capabilities set the stage for tailored, practical implementations that fit your organisation's needs.
How Hokstad Consulting Can Help
Achieving the full potential of automated ISO 27001 compliance requires more than just selecting the right software - it calls for expertise in adapting these tools to your specific private cloud setup. Hokstad Consulting specialises in crafting custom solutions, guiding organisations through the intricacies of ISO 27001’s 114 controls spread across 14 domains [3]. Their DevOps transformation services integrate security directly into deployment pipelines, embedding compliance into your infrastructure from the ground up.
Whether you're working with hybrid systems, private clouds, or multi-cloud environments, Hokstad Consulting offers more than compliance. Their cloud cost engineering and migration strategies ensure your automation solutions not only meet regulatory standards but also boost operational efficiency and cut costs. With expertise in AI strategy and agents, they enhance monitoring capabilities, while their retainer-based support model ensures you have ongoing assistance as your infrastructure evolves. Visit hokstadconsulting.com to discover how customised automation can revolutionise your ISO 27001 compliance approach.
FAQs
How can automation help with ISO 27001 compliance in private cloud environments?
Automation makes achieving ISO 27001 compliance in private cloud environments much simpler. By reducing human errors, it ensures that security and governance policies are applied consistently while providing real-time control monitoring. This transforms compliance from a reactive, manual process into a proactive, automated system.
Here’s how automation helps:
- Continuous monitoring: Automated tools keep an eye on compliance metrics 24/7, instantly flagging any issues for quick resolution.
- Simplified audits: With up-to-date records and evidence maintained automatically, the time and effort needed to prepare for audits is significantly reduced.
- Greater efficiency: Repetitive compliance tasks, like control testing, are completed faster and with greater accuracy.
By adopting automation, organisations can maintain secure and compliant private cloud environments while cutting down on time and resources.
What automation tools can help with ISO 27001 compliance in private clouds?
Automation tools can make achieving ISO 27001 compliance much easier in private cloud environments by simplifying workflows and ensuring constant oversight. For instance, cloud security platforms can automate compliance checks, deliver real-time security insights, and enable quick deployment. These tools help organisations stay on top of security requirements without the need for extensive manual intervention.
Another valuable resource is policy as code solutions like Open Policy Agent (OPA) and Kyverno. These tools allow compliance rules to be seamlessly integrated into CI/CD pipelines, ensuring governance policies are automatically enforced during both development and deployment stages.
By using these technologies, organisations can cut down on manual tasks, reduce the risk of errors, and maintain steady alignment with ISO 27001 standards - all while boosting overall efficiency in their operations.
Why is continuous monitoring essential for staying compliant?
Keeping a close eye on your systems is essential for staying compliant. Continuous monitoring allows organisations to spot and fix misconfigurations, security gaps, and any departures from regulatory standards as they happen. This real-time vigilance helps reduce the chances of data breaches, hefty fines, or interruptions to operations.
By actively identifying and resolving potential problems, organisations can keep their private cloud environments secure, dependable, and in line with ISO 27001 standards.
