Vulnerability scanning is a process that helps identify security issues in systems and applications, ensuring organisations meet compliance standards like PCI DSS and ISO/IEC 27001. By automating security checks, businesses can detect risks such as outdated software, weak encryption, and exploitable vulnerabilities. This approach not only mitigates potential threats but also simplifies audit preparation and ensures adherence to regulatory requirements.
Key takeaways:
- Automated Scanning: Identifies vulnerabilities quickly, reducing manual effort.
- Compliance Integration: Aligns with standards like PCI DSS, ISO 27001, and UK GDPR.
- Cost Efficiency: Early detection prevents expensive post-deployment fixes.
- CI/CD Pipeline Integration: Embeds security checks into development workflows.
- Audit Support: Provides documented evidence for regulatory reviews.
To stay compliant, businesses should integrate vulnerability scanning into their processes, focusing on frequent scans and automated controls to block insecure code from deployment. This proactive approach helps manage risks effectively while maintaining operational security.
Compliance Benefits of Vulnerability Scanning
Automating Industry Standards Compliance
Automated vulnerability scanning simplifies meeting regulatory requirements. Many modern scanning tools come with custom checks tailored to align with widely recognised information security standards or your organisation's specific control framework [1]. For example, in the context of ISO 27001, vulnerability scanning plays a key role in fulfilling the monitoring and improving
mandates of an Information Security Management System (ISMS). This enables organisations to routinely assess compliance and address technical vulnerabilities as they arise [6].
The National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) emphasises:
Automated scanning should be viewed as a cost-effective way of finding and managing common security issues, without needing to employ specialist security testers [1].
For businesses processing card payments, PCI DSS v4.0 requires external vulnerability scans (ASV scans) at least every three months and after any major changes to the IT environment [7]. Additionally, critical or high-severity patches must be applied within 30 days of their release [7]. By integrating scans into your CI/CD pipeline, you can enforce automated controls that halt builds if vulnerabilities exceed acceptable thresholds, ensuring only compliant code is deployed [5].
Reducing Security Risks and Preparing for Audits
Beyond automation, vulnerability scanning enhances security and simplifies audit preparation. Regular scans provide the documented evidence auditors need to confirm your systems are being managed securely. Maintaining a vulnerability register - which tracks details such as vulnerability identification, severity (using CVSS), and remediation actions - creates a clear and traceable audit trail [3][2]. Automated tools also generate logs and detailed reports, which are invaluable during compliance audits, while meeting scan frequency requirements helps demonstrate ongoing security efforts [2].
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) rates vulnerabilities on a scale from 0.0 to 10.0, with Critical
issues (9.0-10.0) posing the highest risks to financial and reputational stability [2]. This risk-based approach shows auditors that your organisation prioritises addressing the most severe threats.
By addressing vulnerabilities proactively and simplifying audit processes, organisations can also realise measurable cost efficiencies.
Cost Savings from Early Detection
Detecting vulnerabilities early is far more economical. Automated scans can perform thousands of checks in a fraction of the time it would take to conduct manual testing. Continuous scanning reduces response and recovery times, minimising system downtime and protecting your organisation's financial health [8][4].
Catching vulnerabilities before they reach production helps avoid the steep costs of post-deployment fixes. The NCSC underscores this point:
The benefits of speed and automation make it far more economical to perform vulnerability scanning against a target than testing it manually [1].
Effective vulnerability management not only prevents breaches that could result in financial or reputational damage [2][4] but also flags issues like expired vendor support or missing licences. Unsupported systems are considered vulnerabilities that can lead to direct financial losses [2]. By identifying these risks early in the development cycle, organisations can avoid the much higher costs associated with emergency patches, regulatory penalties, and breach recovery efforts.
What Is The Purpose Of Automated Vulnerability Scans?
Types of Vulnerability Scans and Their Compliance Impact
::: @figure 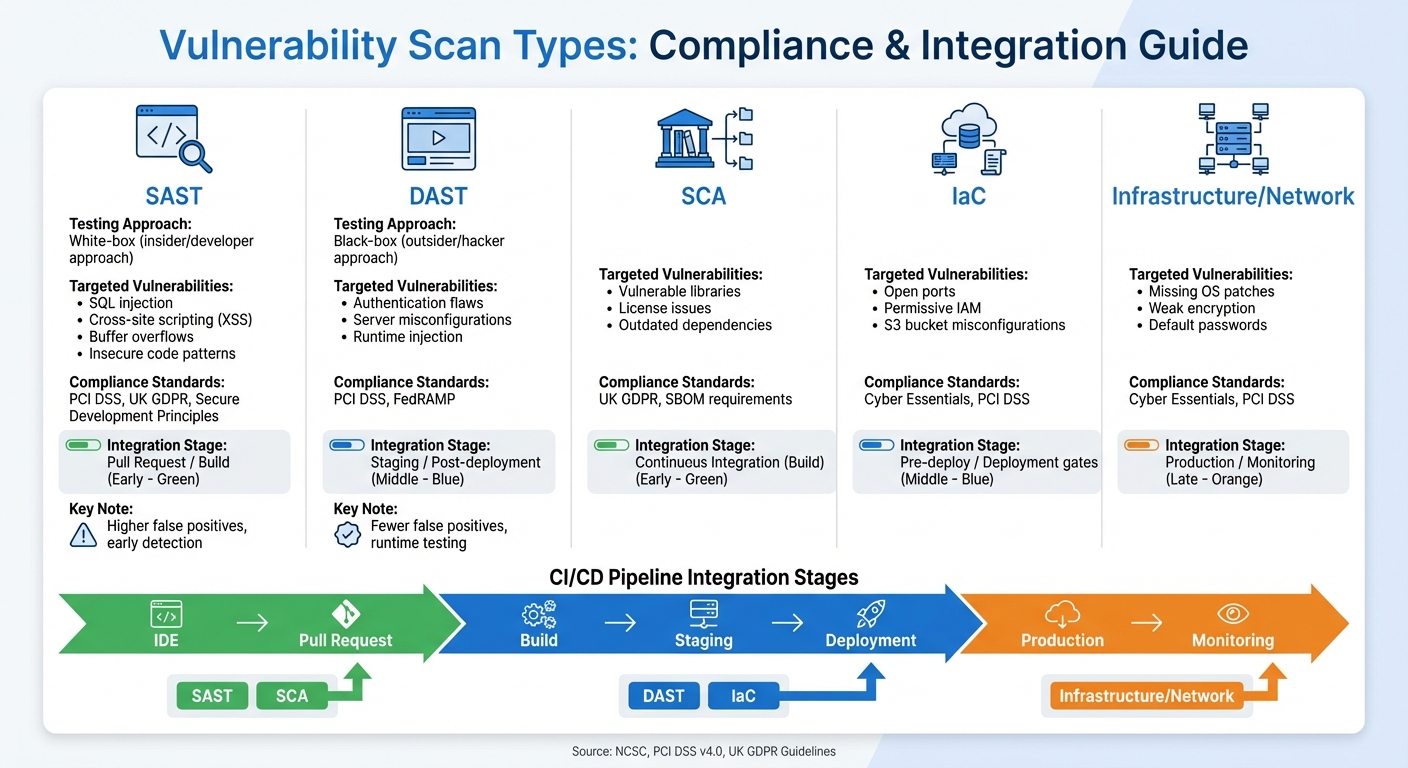 {Comparison of Vulnerability Scan Types for Compliance Standards}
:::
{Comparison of Vulnerability Scan Types for Compliance Standards}
:::
Static Analysis Security Testing (SAST)
SAST is a white-box
testing approach that analyses source code, bytecode, or binary code without actually running the application [10][11]. This method works early in the software development lifecycle - often integrated at stages like the IDE or pull-request phase - helping developers identify vulnerabilities before the code reaches production [9][10].
From a compliance perspective, SAST is excellent for detecting code-level issues such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), buffer overflows, and hardcoded secrets. These vulnerabilities often breach secure coding standards, making SAST a vital tool for meeting regulations like PCI DSS and UK GDPR, where secure handling of sensitive data is a must.
As OpenText highlights:
SAST reduces security risks in applications by providing immediate feedback to developers on issues introduced into code during development.
– OpenText [11]
However, SAST can generate more false positives because it lacks the runtime context of the application [10][11]. Despite this, its ability to pinpoint vulnerabilities directly in the code makes it a powerful tool for ensuring secure development practices and demonstrating proactive compliance during audits [11][12].
Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)
DAST, on the other hand, is a black-box
testing method that examines applications while they are running, simulating attacks from an external perspective [10]. Palo Alto Networks explains the difference well:
Think of SAST as the insider or developer's approach and DAST as the outsider or hacker's approach.
– Palo Alto Networks [10]
This type of testing is typically performed during later stages, such as in staging or production environments. DAST focuses on runtime issues, detecting vulnerabilities like server misconfigurations, authentication weaknesses, and problems with encryption that only appear in live environments [9][10]. Because DAST tests the application in its running state, it tends to produce fewer false positives compared to SAST [10].
For compliance, DAST ensures that deployed applications meet runtime integrity and hardening standards. It is especially useful for identifying vulnerabilities in third-party APIs or server-side configurations [1][11]. For example, UK Ministry of Justice guidelines require that internet-facing websites and digital services undergo weekly scans, making DAST a critical component of ongoing compliance efforts [2].
When combined, SAST and DAST create a layered approach to security, addressing vulnerabilities at multiple stages of the CI/CD pipeline.
Comparison of Scan Types and Compliance Standards
Understanding the role of each scan type helps organisations align their security efforts with compliance requirements and CI/CD processes. Different methods address vulnerabilities at various stages, offering comprehensive security coverage:
| Scan Type | Targeted Vulnerabilities | Compliance Standards | Integration Stage |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAST | SQL injection, XSS, buffer overflows, insecure code patterns | PCI DSS, UK GDPR, Secure Development Principles | Pull Request / Build |
| DAST | Authentication flaws, server misconfigurations, runtime injection | PCI DSS, FedRAMP | Staging / Post-deployment |
| SCA | Vulnerable libraries, licence issues, outdated dependencies | UK GDPR, SBOM requirements | Continuous Integration (Build) |
| IaC | Open ports, permissive IAM, S3 bucket misconfigurations | Cyber Essentials, PCI DSS | Pre-deploy / Deployment gates |
| Infrastructure/Network | Missing OS patches, weak encryption, default passwords | Cyber Essentials, PCI DSS | Production / Monitoring |
Need help optimizing your cloud costs?
Get expert advice on how to reduce your cloud expenses without sacrificing performance.
Research on Shift-Left Security for Compliance
Cost Efficiency and Faster Remediation
Shift-left security integrates vulnerability scanning into the earliest stages of development, making it a proactive approach to identifying and resolving issues. By catching vulnerabilities early, organisations can significantly cut costs while avoiding delays down the line [13][14]. Continuous scanning ensures that even minor vulnerabilities are detected and addressed quickly, enabling remediation to happen 45% faster and improving overall efficiency [13][15].
Studies reveal that automated policy gates can identify 89% of critical vulnerabilities before production, streamlining the remediation process by 45% [15]. This proactive approach also reduces compliance risks by ensuring vulnerabilities are resolved well before deployment.
The financial impact of such measures is impressive. For instance, Capital One implemented a robust Policy as Code framework across more than 3,000 applications in 2024, achieving a 99.2% compliance rate while also speeding up time-to-market [15]. Similarly, Goldman Sachs demonstrated the power of automation by slashing its security review times from two weeks to just two hours, achieving a 99% improvement in review velocity [15].
These examples highlight how integrating automated policy enforcement into CI/CD pipelines can lead to both cost and time savings, driving more efficient and secure development processes.
Policy Gates for Security and Compliance
Policy gates take compliance rules and translate them into code, enabling automatic enforcement of security standards within CI/CD pipelines. By blocking non-compliant code from progressing, these gates ensure only secure deployments make it through.
The adoption of Policy as Code has grown rapidly, with 71% of enterprises now using this method. Organisations that embrace this approach report a 73% reduction in production security incidents compared to traditional, reactive methods [15]. Many large enterprises rely on policy engines to automate compliance checks, ensuring quick and consistent evaluations [15].
These policy gates are particularly effective in meeting standards like Cyber Essentials, PCI-DSS, SOC 2, and HIPAA, demonstrating the broader shift toward automated compliance solutions.
As DevOpsTales aptly puts it:
Policy as Code is now essential for managing security at the scale and speed that modern business demands. – DevOpsTales [15]
Hokstad Consulting's Approach to Compliance-Driven Vulnerability Scanning

Custom CI/CD Pipeline Automation
Hokstad Consulting weaves automated vulnerability scanning directly into CI/CD pipelines, leveraging tools such as Snyk, Burp Suite, and Trivy. These scanners are deployed using Docker containers within pipeline agents on platforms like Azure DevOps and GitHub Actions. YAML-configured pipelines are set up to trigger SAST and DAST tools, with policy gates in place to halt builds if vulnerabilities surpass acceptable risk levels [5].
This method adheres to UK regulatory standards, including the NCSC's Web Check and Ministry of Justice requirements, which call for weekly scans of internet-facing services [2][1]. By embedding these checks early in the development lifecycle, critical vulnerabilities can be identified soon after they are publicly disclosed. This ensures compliance while maintaining the pace of deployments [1].
Continuous Security Audits and Optimisation
Beyond automated pipeline controls, Hokstad Consulting strengthens security through continuous audits. Their approach involves real-time compliance monitoring to track configuration changes and detect vulnerabilities as they emerge [17][4]. A structured CVSS v3 vulnerability register is maintained to align with UK government security guidelines.
A layered scanning strategy is employed, combining infrastructure scans to identify outdated software and weak encryption with web application scans targeting risks like SQL injection and cross-site scripting [1]. Logs and scan results are meticulously recorded, enabling security teams to conduct forensic investigations and support ongoing audit activities.
DevOps Transformation for Compliance
Hokstad Consulting complements scanning and audits with a DevOps transformation that embeds security practices throughout the development process. Their DevSecOps approach integrates security tools directly into developer environments, such as VS Code and PyCharm, providing instant feedback to developers. This reduces the manual workload for security teams and ensures faster response times [16]. As Liran Tal from Snyk explains:
Integrating security into every phase of the development lifecycle is crucial and it starts with optimal developer experience and proactive security remediation in the developer's IDE. [16]
The use of Terraform ensures consistent and auditable security configurations across all environments [18][19]. Automated workflows can initiate corrective actions or generate pull requests when critical vulnerabilities are identified. This approach addresses the challenges posed by the vast number of open-source dependencies - nearly 3 million on the npm registry alone [16]. By adopting these strategies, businesses can maintain rapid deployment cycles while meeting strict compliance requirements [19].
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
Vulnerability scanning transforms compliance from a reactive task into a proactive process by integrating automated scans directly into CI/CD pipelines [3][20]. Policy gates act as safeguards, preventing non-compliant code from entering production, while consistent logging ensures the creation of an audit trail that meets regulatory demands [3][4].
The financial benefits are equally compelling. Addressing vulnerabilities early in the development cycle - often referred to as shifting security left
- is far more cost-effective than resolving issues after deployment [1]. By automating these processes, organisations not only reduce manual workloads but also ensure compliance standards are consistently met. This approach aligns with earlier discussions on shift-left security, underscoring how early detection helps mitigate both costs and risks.
As the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) highlights:
Vulnerability scanning affords an organisation the ability to keep pace with individuals and groups intent on compromising systems, many of which use similar tools and techniques to discover security flaws [1].
This isn't just about ticking compliance boxes - it's about staying ahead in a landscape where threats evolve daily. These insights naturally set the stage for actionable steps to strengthen your compliance strategy.
Next Steps for UK Businesses
To build on these advantages, establish a comprehensive Vulnerability Management Programme that includes system discovery, asset classification, detection, triage, remediation, and disclosure [1][3]. Focus your efforts on internet-facing assets and systems handling sensitive data. Configure your CI/CD pipelines to include automated scanning and enforce policy gates that block deployments when critical vulnerabilities (CVSS scores of 7.0 or higher) are detected [2].
For tailored solutions, Hokstad Consulting offers expertise in embedding security controls within DevOps workflows. Their services include custom CI/CD pipeline automation, continuous security audits, and DevOps transformation designed to meet UK compliance frameworks. This approach ensures businesses can maintain fast deployment cycles while adhering to the rigorous standards set by the NCSC, Cyber Essentials, and other sector-specific regulations. Whether operating in public cloud environments, hybrid setups, or private hosting, incorporating vulnerability scanning into your development lifecycle is no longer optional - it’s a cornerstone of compliant and sustainable operations.
FAQs
How does vulnerability scanning support PCI DSS and ISO 27001 compliance?
Vulnerability scanning is an essential component in adhering to compliance standards like PCI DSS and ISO 27001.
Under PCI DSS, it fulfils the requirement for regular, authenticated internal scans of systems handling cardholder data, as specified in requirement 11.3.1.2. These scans allow businesses to pinpoint and resolve potential security gaps within their payment systems, ensuring the safety of sensitive information.
For ISO 27001, vulnerability scanning is a key part of a continuous vulnerability management programme. It helps organisations identify, evaluate, and address risks to critical information assets. This process not only strengthens security measures but also supports compliance with the framework's stringent requirements.
How does vulnerability scanning in CI/CD pipelines support compliance?
Integrating vulnerability scanning into CI/CD pipelines allows businesses to catch and fix security issues early in the development process. This forward-thinking strategy ensures software aligns with compliance standards by continuously checking for vulnerabilities and addressing them before deployment.
By embedding scanning tools directly into the development pipeline, teams can keep deployment cycles both secure and fast. This approach minimises security risks while ensuring compliance requirements are seamlessly met as a natural part of the workflow.
How does vulnerability scanning help reduce compliance costs?
Vulnerability scanning simplifies the task of spotting and fixing security flaws, helping organisations stay aligned with industry standards. By automating these processes, companies can sidestep expensive breaches and avoid regulatory penalties. Plus, it can cut cloud costs by as much as 30–50%.
This forward-thinking method doesn’t just bolster security - it also makes better use of resources, enabling businesses to save money while keeping their compliance efforts strong.
