Want to cut cloud costs by up to 90%? Spot instances offer discounted access to spare cloud capacity, making them a cost-saving option for workloads that can handle interruptions. However, their reliability depends on smart scaling strategies.
Key Takeaways:
- Spot Instances: Unused cloud capacity sold at lower prices, but interruptible with a 2-minute notice.
- Best Workloads: Fault-tolerant tasks like big data, machine learning, and CI/CD pipelines.
- Scaling Tips:
- Use Auto Scaling Groups with diverse instance types and Availability Zones.
- Enable Capacity Rebalancing to pre-launch replacements for at-risk instances.
- Monitor interruptions using AWS tools like EventBridge and CloudWatch.
- Diversification: Spread workloads across at least 10 instance types and multiple zones to reduce risks.
- Automation: Combine scaling policies with AWS-managed services to handle interruptions efficiently.
Spot instances are ideal for cost-conscious businesses when paired with robust scaling and resilience strategies. Learn how to prepare your workloads and automate scaling for maximum savings.
Leveraging Amazon EC2 Spot Best Practices Using the New Capacity Optimized Allocation Strategy
Preparing Workloads for Spot Interruptions
The trick to making the most of spot instances isn’t trying to avoid interruptions altogether - it’s about designing your workloads to handle them smoothly. The focus should be on building resilience so your applications can adapt to occasional disruptions [3].
Designing Fault-Tolerant Applications
For a robust setup, design your applications to be stateless. This means storing critical data externally, using services like Amazon S3, DynamoDB, or EBS. By doing so, you safeguard your data even if an instance is interrupted.
For tasks that take a long time - like machine learning training or batch processing - regular checkpointing is key. Save progress to persistent storage at intervals, such as saving model weights after each epoch for machine learning workloads [8]. This way, if an interruption happens, you can pick up where you left off instead of starting over.
AWS suggests spot instances are best suited for stateless, fault-tolerant, and flexible applications. They’re not ideal for workloads that are tightly coupled, inflexible, stateful, or unable to tolerate faults [7]. To further enhance resilience, configure your Auto Scaling groups to use at least 10 different instance types across multiple Availability Zones [7].
Using Interruption Notices for Graceful Shutdowns
AWS provides a two-minute interruption notice before reclaiming capacity. However, you can get an earlier warning through the rebalance recommendation, which alerts you to an increased risk of interruption before the final countdown begins [6].
There are two ways to monitor for interruptions. Inside the instance, you can poll the instance metadata URL every five seconds. If it returns a 404, there’s no interruption scheduled; if it returns a 200, termination is imminent [3]. Alternatively, you can use Amazon EventBridge to capture EC2 Spot Instance Interruption Warning
events and trigger AWS Lambda functions. These functions can handle tasks like detaching instances from load balancers [10].
For container workloads, the process is even more streamlined. If you’re using Amazon ECS, set ECS_ENABLE_SPOT_INSTANCE_DRAINING=true in the container agent configuration to stop new tasks from being scheduled on nodes at risk [3]. For Amazon EKS, deploy the AWS Node Termination Handler to automatically cordon and drain nodes when an interruption notice is received [3]. Also, adjust your load balancer deregistration delays to around 90 seconds - just under the two-minute window - so in-flight requests can finish before the instance goes offline [10].
These steps naturally tie into dynamic Auto Scaling setups for better overall resilience.
Integrating with Auto Scaling
Dynamic Auto Scaling adds another layer of strength to your spot instance strategy when combined with resilient application design and proactive shutdown measures.
EC2 Auto Scaling groups are essential for building a reliable spot strategy. Enable Capacity Rebalancing so that when a rebalance recommendation is triggered, the Auto Scaling group launches a replacement instance before the at-risk one is terminated [6]. AWS even allows a temporary increase of up to 10% above your group’s maximum size to ensure the new instance is healthy before the old one is removed [6].
Instead of focusing solely on the lowest price, consider using the price-capacity-optimised allocation strategy. This method selects instance pools with the best combination of availability and lower interruption risks. Additionally, configure termination lifecycle hooks to extend the life of an instance briefly for cleanup tasks [9].
Finally, test your setup to ensure everything works as planned. Use AWS Fault Injection Service (FIS) to simulate spot interruptions and confirm that your shutdown scripts and checkpointing mechanisms function correctly [8].
Diversifying Spot Instance Strategies
To minimise interruptions, it’s crucial to tap into multiple capacity pools. At the heart of a strong spot strategy lies diversification - relying on a variety of independent capacity pools rather than depending on just one. When paired with resilient workload preparation and auto scaling, diversification adds an extra layer of security to your infrastructure.
Flexibility in Instance Types and Sizes
A spot capacity pool consists of unused EC2 instances of the same type within a specific Availability Zone, such as m5.large. The more pools you can access, the better your chances of maintaining capacity during high-demand periods elsewhere [7][2].
AWS suggests following the Rule of 10
, encouraging flexibility across at least 10 different instance types for each workload [7]. This doesn’t mean randomly picking 10 options. Instead, define your workload requirements - such as vCPU, memory, and storage - and allow the system to choose from a wide range of instance families and generations. By matching your minimum vCPU and memory needs to multiple families, you can include older instance families, which often have more available capacity [5]. This approach not only reduces the risk of interruptions but also helps cut costs.
Automation can simplify this process with attribute-based instance type selection (ABS). ABS allows you to specify criteria like minimum vCPU or memory, eliminating the need to hardcode specific instance names [7][1]. This ensures your pool automatically includes newer or less popular instance types, keeping your strategy up to date.
The National Football League (NFL) provides a great example of this strategy in action. In 2023, the NFL ran about 4,000 EC2 Spot Instances across more than 20 instance types to perform the complex simulations needed to create its season schedule. This diversification allowed the NFL to save £2 million per season while maintaining high reliability for its large-scale workloads [5].
The fundamental best practice when using Spot Instances is to be flexible.- Pranaya Anshu and Sid Ambatipudi, EC2 Specialists [5]
Using Multiple Availability Zones
Diversifying across multiple Availability Zones (AZs) is just as important as diversifying instance types. Each AZ represents an independent capacity pool, so leveraging all available zones in your region significantly increases your options [7][5].
Set up Auto Scaling groups to span all AZs within your VPC. This configuration helps mitigate the impact of localised capacity shortages [7][3]. For larger or long-running fleets, distributing instances evenly across pools ensures that interruptions in one pool only affect a small portion of your fleet [12].
When you combine AZ diversity with instance type flexibility, you create a robust safety net. For instance, if you’re flexible across 10 instance types and three AZs, you’re effectively drawing from 30 separate capacity pools. This dramatically reduces the chances of simultaneous interruptions.
Once you’ve diversified instance types and AZs, you can fine-tune your strategy further by evaluating capacity availability using placement scores.
Spot Placement Scores and Region Selection
The Spot Placement Score tool helps identify regions and AZs with the best capacity availability. Scores range from 1 to 10, with 10 indicating the highest likelihood of securing capacity [13][11].
To get a detailed view, you can generate placement scores for specific AZs by enabling the SingleAvailabilityZone parameter. This provides a ranked list of AZs with the most capacity for your needs [11]. For workloads like data analytics or high-performance computing, comparing scores across multiple regions can help you make the most of off-peak capacity.
Pairing placement scores with a price-capacity-optimised strategy allows you to choose instances that balance availability and cost [7][3]. This combination minimises the risk of interruptions while keeping expenses under control. With this approach, your infrastructure is well-prepared for advanced scaling and automation.
Advanced Spot Scaling with Automation
Once you've diversified your spot strategy, the next step is to automate the scaling process. Automation takes the manual effort out of scaling, allowing your infrastructure to adjust effortlessly as needed. By using Auto Scaling Groups alongside AWS-managed services and CloudWatch monitoring, you can create a self-managing spot fleet that balances cost efficiency with reliability. Here's how you can configure Auto Scaling Groups to make the most of these strategies.
Auto Scaling Groups with Mixed Instance Policies
Mixed Instance Policies let you combine On-Demand and Spot instances in a single Auto Scaling Group, giving you better control over costs while maintaining reliability. You can set a base number of On-Demand instances for stability and fill the remaining capacity with Spot instances to cut costs significantly [14][4].
For instance, you might allocate five On-Demand instances for critical workloads and configure 80% of your additional capacity to use Spot instances. This approach secures your essential operations while benefiting from savings of up to 90% on the rest of your fleet [7]. The price-capacity-optimised allocation strategy ensures you choose instances with the best combination of availability and pricing [6][7].
To maintain smooth operations, Capacity Rebalancing can pre-launch replacement instances when an existing instance is at risk, temporarily exceeding your desired capacity by up to 10% [6][14].
Attribute-based instance selection (ABS) simplifies scaling by letting you define requirements like minimum vCPU and memory, instead of specifying exact instance types. This way, your Auto Scaling Group automatically includes new instance types that meet your criteria, saving you the hassle of manual updates [14][7]. It’s also a good idea to avoid setting a maximum Spot price; leaving it at the default On-Demand price ensures your instances keep running as long as the Spot price stays within limits, reducing unnecessary disruptions [14][4].
Using AWS Services for Spot Scaling
AWS services can handle interruptions for containerised and batch workloads seamlessly [7][16]. Tools like Amazon ECS, EKS, and AWS Batch come with built-in logic to reschedule tasks automatically during interruptions, making them ideal for workloads that can tolerate brief delays.
For containerised applications, ECS and EKS can spread tasks across mixed capacity types and automatically drain containers from instances flagged for interruption. AWS Batch, on the other hand, manages job queues and compute environments, retrying failed jobs on replacement instances. When combined with Auto Scaling Groups configured for spot diversity, these services ensure your workloads keep running even during capacity shifts.
Lifecycle hooks add extra flexibility by giving you additional time - within the two-minute interruption window - to wrap up critical tasks like completing SQS worker jobs or uploading logs to S3 [6]. This integration of AWS services with spot automation builds a strong, interruption-resistant system that operates without manual intervention.
Monitoring and Optimisation with CloudWatch
Once you’ve automated scaling, CloudWatch provides the tools to monitor and fine-tune your strategy in real time. Enabling 1-minute detailed monitoring allows faster Auto Scaling responses [15]. This level of detail helps prevent scaling decisions based on outdated data and ensures performance is maintained during sudden demand spikes.
Track the gap between your target and fulfilled capacity using 1-minute monitoring. If you notice a consistent shortfall, it may indicate the need to diversify instance types or expand to additional Availability Zones [7][15]. Metrics like CPUUtilization can also be used to trigger step scaling or target tracking policies, ensuring the scaling process aligns with your actual workload demands [17].
Need help optimizing your cloud costs?
Get expert advice on how to reduce your cloud expenses without sacrificing performance.
Spot Instances vs On-Demand: A Practical Comparison
::: @figure 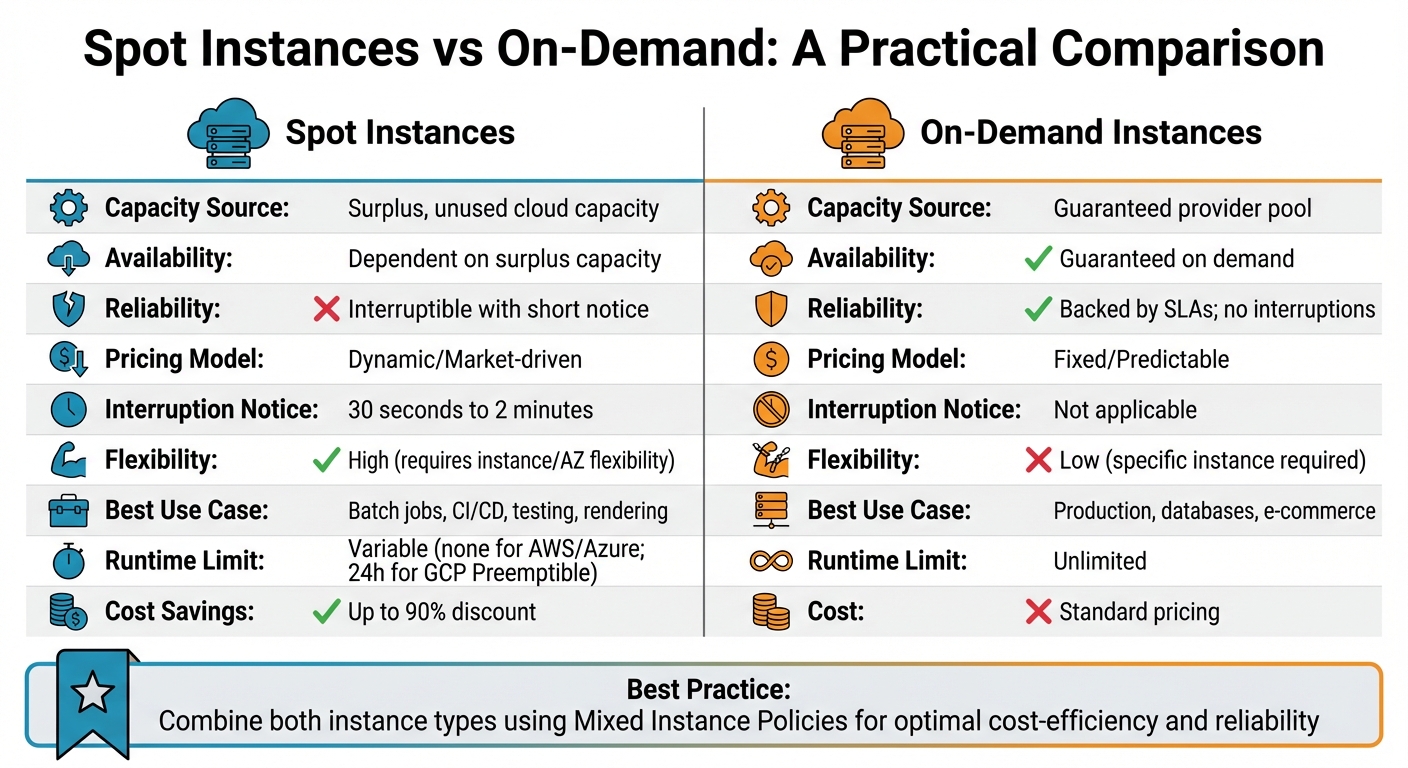 {Spot Instances vs On-Demand Instances Comparison Chart}
:::
{Spot Instances vs On-Demand Instances Comparison Chart}
:::
Spot instances operate by using surplus cloud capacity at dynamic, fluctuating prices, while On-Demand instances provide guaranteed access to resources at fixed rates. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each can help optimise your cloud budget and scaling strategy.
Spot instances come with a trade-off: they can be interrupted with as little as 30 seconds to 2 minutes' notice. This makes them unsuitable for critical systems that require continuous availability. On the other hand, On-Demand instances offer uninterrupted service, making them ideal for essential workloads like databases or payment systems.
The pricing models differ significantly. Spot instances are priced dynamically, based on supply and demand, which can lead to considerable savings for workloads that can tolerate interruptions. Conversely, On-Demand instances have fixed pricing, providing cost predictability for high-priority applications. Spot instances work well for tasks such as batch processing, CI/CD pipelines, and containerised microservices, where interruptions can be managed easily. Meanwhile, On-Demand instances are better suited for production environments where reliability is non-negotiable.
One way to mitigate the risk of interruptions with Spot instances is by diversifying across instance types and availability zones. This strategy helps maintain cost efficiency while reducing the likelihood of disruptions.
Comparison Table: Spot vs On-Demand
Here’s a quick breakdown of the key differences:
| Feature | Spot Instances | On-Demand Instances |
|---|---|---|
| Capacity Source | Surplus, unused cloud capacity | Guaranteed provider pool |
| Availability | Dependent on surplus capacity | Guaranteed on demand |
| Reliability | Interruptible with short notice | Backed by SLAs; no interruptions |
| Pricing Model | Dynamic/Market-driven | Fixed/Predictable |
| Interruption Notice | 30 seconds to 2 minutes | Not applicable |
| Flexibility | High (requires instance/AZ flexibility) | Low (specific instance required) |
| Best Use Case | Batch jobs, CI/CD, testing, rendering | Production, databases, e-commerce |
| Runtime Limit | Variable (none for AWS/Azure; 24h for GCP Preemptible) | Unlimited |
This comparison highlights the complementary nature of Spot and On-Demand instances, allowing you to align your choice with the specific needs of your workloads.
Optimising Spot Scaling with Hokstad Consulting

Spot scaling can be a game-changer for managing cloud costs, but it requires careful setup, continuous oversight, and smart workload distribution. Hokstad Consulting brings expertise in cloud cost engineering and DevOps automation to the table, helping businesses save 30-50% by crafting spot instance strategies that align perfectly with their unique infrastructure. This hands-on approach is at the heart of Hokstad Consulting's tailored solutions.
Custom Spot Scaling Solutions
Hokstad Consulting creates tailored auto-scaling configurations that prioritise cost-efficiency and reliability. By using price-capacity-optimised strategies, they ensure instances are launched from pools with the lowest risk of interruption [6][3]. These strategies incorporate proven techniques - like auto scaling and capacity rebalancing - into a seamless service that adapts to each client's specific needs.
What sets them apart is their advanced interruption handling. Instead of relying only on basic graceful shutdowns, they integrate capacity rebalancing directly into auto-scaling groups. This means instances are proactively replaced before interruptions even happen. As Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling Documentation explains:
With proactive replacement in Capacity Rebalancing, you benefit from graceful continuity[6].
The result? A reliable scaling setup that safeguards performance while slashing costs.
Cloud Cost Audits and Optimisation
Hokstad Consulting also conducts in-depth cloud cost audits to identify inefficiencies and expand the use of spot instances for tasks like batch processing, CI/CD pipelines, and development environments. They dive into your instance types, availability zone usage, and scaling policies to uncover hidden savings opportunities.
These insights feed directly into their No Savings, No Fee
pricing model, ensuring their success is tied to yours. Fees are capped at a percentage of the savings achieved, so it’s a low-risk way to optimise your cloud spending.
Their services go beyond audits, offering automated monitoring tools, custom deployment pipeline development, and strategic cloud migration planning. All these efforts are designed to cut costs while improving reliability and performance, making your cloud infrastructure leaner and more efficient.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
By applying the strategies discussed, scaling with spot instances becomes a dependable and cost-effective solution. Approaches like diversifying across at least 10 instance types and multiple Availability Zones, implementing capacity rebalancing, and using price-capacity-optimised allocation help build a resilient and efficient infrastructure.
Take the NFL as an example: their ability to manage thousands of EC2 Spot Instances across a variety of instance types demonstrates that even the most complex workloads can run smoothly on spot capacity when designed thoughtfully.
Here’s a quick recap of the most important lessons from the discussion.
Key Takeaways
Diversification ensures stability. Distributing workloads across various instance types, families, and Availability Zones taps into the largest capacity pools available. AWS data shows that fewer than 5% of spot instances are interrupted by AWS before users terminate them [3]. By diversifying, you can further enhance overall reliability and minimise disruptions.
Automation simplifies management. Auto Scaling Groups with capacity rebalancing take care of replacing at-risk instances automatically, ensuring smooth operations. By monitoring service-level indicators like load balancer error rates, you can prioritise application availability without getting bogged down by interruption metrics [3].
If you're ready to start saving, consider reaching out to Hokstad Consulting. They offer a free 30-minute consultation to help identify cost-saving opportunities in your infrastructure. With their expertise in cloud cost engineering, they typically cut expenses by 30–50%, and their No Savings, No Fee
model ensures zero risk. Visit hokstadconsulting.com to learn more.
FAQs
How can I manage interruptions effectively when using Spot Instances?
To manage interruptions effectively when working with Spot Instances, it's essential to design your workloads with resilience in mind. Start by using persistent storage solutions like Amazon S3, EBS, or DynamoDB for critical data, rather than relying on local instance storage. Structure your tasks into smaller, idempotent units that can be retried or resumed without losing progress. Adopting a stateless or containerised architecture can also make your workloads more adaptable. Additionally, keeping your instance type selection broad increases reliability by giving you more options in the event of interruptions.
Incorporate Spot Instances into an Auto Scaling group or an EC2 Fleet to ensure that interrupted instances are automatically replaced. Take advantage of Capacity Rebalancing to proactively replace instances that are at risk of termination. When creating Spot requests, select an interruption behaviour - such as stop or hibernate - that allows instances to resume quickly once capacity becomes available.
Stay vigilant by monitoring the two-minute interruption notices provided by AWS. Automate recovery steps, such as saving in-progress data or alerting your CI/CD pipeline, to minimise disruption. It's also a good idea to regularly test your setup by simulating interruptions. This ensures that your scaling policies and recovery mechanisms are functioning as intended.
For expert guidance, Hokstad Consulting can assist in implementing these strategies, helping you cut costs while maintaining robust service performance.
What are the best practices for scaling with Spot Instances?
To save more and keep things running smoothly when scaling with Spot Instances, it's smart to mix up your strategy. Start by spreading your requests across different instance types and Availability Zones. This helps reduce the chances of losing all your resources if there's a capacity shortage. Using attribute-based instance selection can also be a game-changer. This lets the system automatically pick any compatible instance type that matches your needs, like specific CPU or memory requirements.
You should also make use of Spot placement scores to pinpoint regions with plenty of capacity. Pair this with the price-capacity-optimised allocation strategy, which focuses on pools with the best availability to cut down on interruptions. If you're running containerised workloads, enabling Cluster Autoscaler with Spot diversification can ensure your resources are rebalanced automatically across different pools whenever interruptions happen.
To tie it all together, integrate these tactics into automated scaling groups or Spot Fleet configurations, and regularly test how well your system handles interruptions. If you need help, Hokstad Consulting offers expertise in building a resilient Spot Instance setup tailored to your business needs, letting you save big without sacrificing reliability.
How does automation improve the reliability of scaling with spot instances?
When using spot instances, automation plays a key role in maintaining reliability by swiftly addressing interruptions. If a spot instance is terminated, tools like AWS Auto Scaling Groups or Kubernetes autoscalers step in to detect the issue and quickly allocate replacement capacity. This ensures your workloads experience minimal disruption.
By eliminating the need for manual intervention, automation helps keep applications running seamlessly, even when unexpected changes occur. This not only saves valuable time but also lowers the chances of downtime, making it a crucial tactic for businesses relying on spot instances.
