Pre-trained AI models are transforming DevOps by automating repetitive tasks like log analysis, YAML generation, and compliance checks. These tools help reduce errors, speed up deployments, and lower costs. Key benefits include:
- Faster CI/CD: AI can generate pipeline configurations and troubleshoot failures.
- Anomaly Detection: Spot irregularities in logs and metrics with greater accuracy.
- Automated Testing: Generate test cases, detect bugs, and optimise performance.
- Cloud Provider Tools: AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure offer specialised AI solutions for DevOps.
These models are ideal for UK businesses aiming to improve efficiency while maintaining compliance. Providers like Hokstad Consulting integrate these tools into workflows, offering cost-saving solutions tailored to specific needs.
Which AI Model is Best for DevOps? I Tested 10 (Shocking Results)
How Pre-Trained AI Models Work in DevOps
Pre-trained AI models have become powerful tools in the DevOps lifecycle, going beyond static scripts to dynamically interpret context, make decisions, and adapt throughout development. These models are reshaping how pipelines are managed, anomalies are detected, and testing is automated. Let’s explore how they’re making an impact.
CI/CD Pipeline Improvements
AI agents like Claude 4.0 Sonnet and GPT-4o are transforming how Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines are managed. They can generate complete pipeline configurations from simple conversational prompts, removing the need for manual YAML coding. Additionally, they analyse pipeline failures by comparing recent changes with historical data, offering actionable fixes [1][3].
The concept of Shift Everywhere
testing is also gaining traction. Here, AI agents create tailored test cases based on application code and user requirements - sometimes even before the code is written [3]. This proactive approach enhances quality assurance at every stage of development. A report by IBM's Institute for Business Value highlights this trend, with 86% of executives predicting that by 2027, AI agents will significantly improve process automation and workflow redesign [3]. These advancements in pipeline management set the stage for more efficient anomaly detection.
Detecting Anomalies in Logs and Metrics
Pre-trained models are particularly adept at spotting irregularities that traditional, rule-based systems might miss. For example, tools like Amazon DevOps Guru leverage years of operational expertise to detect patterns in application behaviour that signal potential issues [5]. These models learn what normal
looks like in time-series data, accounting for trends and seasonality, and can quickly flag deviations [6][7].
Anomaly detection often relies on multiple specialised detectors, each tuned for specific metrics. For instance, the patterns behind latency spikes differ from those causing error rate increases, so dedicated models are used for each scenario [5]. When an anomaly is detected, these systems correlate related logs and metrics to pinpoint root causes, grouping them into insights
to reduce alert fatigue and speed up detection times [5][6][7]. Large Language Model (LLM)-based approaches have shown measurable improvements over traditional methods in metrics like F1-score, precision, and recall [4]. This robust anomaly detection capability enhances automated testing workflows.
Automated Testing and Bug Detection
AI is taking on increasingly complex testing tasks. Models like Claude can generate unit tests on demand and even review pull requests, suggesting code improvements and enforcing best practices [9]. When pipeline failures occur, tools like Harness Error Analyzer (powered by GPT-4o) diagnose issues by analysing dependencies and matching them to historical failure patterns, offering targeted solutions [1].
Generative AI also identifies performance bottlenecks by highlighting code hotspots
- such as inefficient SQL queries or heavy Redis payloads - that slow down systems [8]. These tools provide clear, actionable reports to guide developers. As Claude AI pointed out, AI won't replace DevOps engineers - but DevOps engineers who use AI will replace those who don't
[9].
Additionally, machine learning models excel at detecting rare bugs in distributed systems. By recognising deviations from established baselines in performance metrics, they identify issues that might otherwise go unnoticed during manual reviews of extensive telemetry data [6]. This anomaly-driven approach ensures that even subtle bugs are caught and addressed efficiently.
Pre-Trained AI Models from Major Cloud Providers
::: @figure 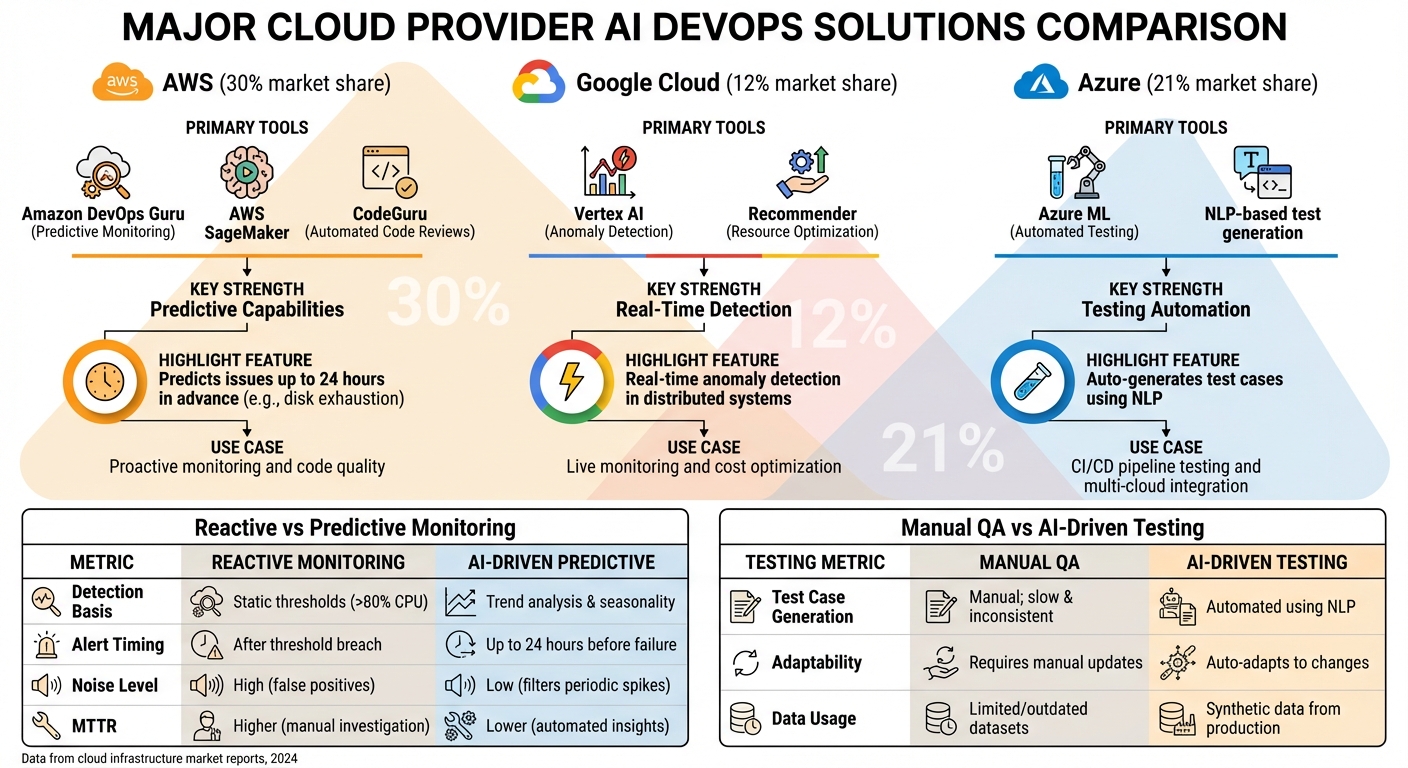 {AWS vs Google Cloud vs Azure AI DevOps Tools Comparison}
:::
{AWS vs Google Cloud vs Azure AI DevOps Tools Comparison}
:::
When it comes to AI solutions for DevOps, AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure each bring something different to the table. Knowing how these platforms compare can help you choose the right tools to tackle your specific operational challenges.
AWS SageMaker and DevOps Guru for Predictive Monitoring
AWS offers powerful tools for predictive monitoring. Take Amazon DevOps Guru, for example - it uses pre-trained models to spot potential problems before they happen [5]. By analysing metrics like latency, error rates, and resource usage, these models can predict issues such as disk exhaustion up to 24 hours in advance. One standout feature is its ability to filter out periodic spikes and group related anomalies into actionable insights. This not only cuts down on unnecessary alerts but also helps teams resolve issues faster.
| Metric Type | Reactive Monitoring | Predictive Monitoring (AI-Driven) |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Basis | Static thresholds (e.g., >80% CPU) | Trend analysis and seasonality tracking |
| Alert Timing | After a threshold breach | Up to 24 hours before failure (e.g., disk exhaustion) |
| Noise Level | High (false positives from batch jobs) | Low (filters out periodic spikes) |
| MTTR | Higher, due to manual investigation | Lower, thanks to automated insights |
Source: [5]
AWS also provides CodeGuru, a machine learning tool for automated code reviews. It flags resource leaks and security issues before your code even hits production. Integrated directly into CI/CD pipelines, it ensures continuous quality checks [10].
While AWS focuses on predictive capabilities, Google Cloud takes a different approach with real-time anomaly detection.
Google Cloud Vertex AI for Anomaly Detection
Google Cloud Vertex AI is tailored for real-time anomaly detection, making it a great fit for DevOps teams managing distributed systems. It’s designed to handle both regression and classification tasks, identifying irregularities in data streams as they occur. This is especially useful in environments where anomalies might pop up across multiple services.
Another useful tool from Google Cloud is Recommender, which monitors resource usage and automatically adjusts compute resources to optimise costs [12]. This combination of operational monitoring and cost management makes it a strong choice for organisations running large-scale deployments.
While Google Cloud shines with its real-time capabilities, Azure ML takes the lead in automating the testing lifecycle.
Azure ML for Automated Testing
Azure ML is all about streamlining the testing process. Its models analyse testing patterns and offer pipeline fix recommendations based on past failures [12]. Using natural language processing (NLP), Azure ML automatically generates test cases from requirements and dynamically adapts to application changes. This ensures that high-risk areas are prioritised, saving time and effort in manual quality assurance.
| Testing Metric | Manual QA Effort | AI-Driven Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Test Case Generation | Manual creation; slow and inconsistent | Automated generation using NLP |
| Adaptability | Requires manual updates for changes | Automatically adapts and prioritises high-risk areas |
| Data Usage | Limited or outdated datasets | Generates synthetic test data based on production scenarios |
Source: [34, 35]
Azure also integrates seamlessly with other cloud platforms, enabling multi-cloud workflows. For instance, you could use Azure for CI/CD pipelines and AWS for model training and hosting [11]. This flexibility is particularly useful for teams working across multiple cloud environments.
As of late 2024, AWS holds the largest share of the global cloud infrastructure market at 30%, with Microsoft Azure at 21% and Google Cloud at 12% [12]. Each provider offers unique strengths, making them well-suited to different DevOps challenges and workflow needs.
Need help optimizing your cloud costs?
Get expert advice on how to reduce your cloud expenses without sacrificing performance.
Best Practices for Using Pre-Trained AI Models in DevOps
Making the most of pre-trained AI models in DevOps requires thoughtful selection, customisation, and ongoing management. By carefully choosing, fine-tuning, and monitoring these models, you can address challenges like reducing Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR), automating repetitive tasks, and boosting pipeline reliability.
Choosing the Right Pre-Trained Models
When selecting pre-trained models, consider five critical factors: output quality, latency and throughput, development time, usage costs, and regulatory compliance [13][2]. The maturity of your organisation's MLOps practices also plays a role. For instance, teams at Level 0 rely on manual solutions, while those at Level 2 can leverage automated CI/CD workflows [14].
Many organisations are now leaning towards foundation models that use prompt engineering. This choice often involves balancing the simplicity of managed models with the flexibility of open models [13].
Take, for example, the Harness AI DevOps Agent, which employs Claude 4.0 Sonnet for DevOps tasks and OpenAI GPT-4o for support and error analysis [1]. Once you've identified a model that aligns with your needs, the next step is tailoring it to your operational data.
Fine-Tuning Models for Your DevOps Data
Pre-trained models perform better when customised to your specific environment. Start by collecting and cleaning domain-specific data - like logs, code, and documentation. Format this data in JSONL to ensure compatibility with fine-tuning platforms [15][16].
You'll then need to decide between full fine-tuning, which updates all model parameters, or Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) methods such as LoRA or QLoRA. PEFT is particularly advantageous if you're working with limited infrastructure, as it updates only a small subset of parameters, saving both compute resources and memory [16][17].
Here’s a quick comparison between fine-tuning and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG):
| Feature | Fine-Tuning | Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) |
|---|---|---|
| Main Difference | Updates the model's internal parameters [16] | Enhances prompts with external knowledge [16] |
| Advantages | Higher accuracy, reduced latency, handles niche jargon [16] | Dynamic knowledge integration, lower training costs [16] |
| Challenges | Risk of overfitting or performance degradation [16] | Limited by data availability; prone to hallucinations [16] |
Before fine-tuning, establish a baseline using evals
to measure the model's performance [15]. Implement ping
pipelines to ensure fine-tuned models stay active, as some providers (like Azure OpenAI) may delete inactive models after 15 days [18]. Post fine-tuning, continuous monitoring is key to adapting to new data and maintaining reliability.
Monitoring and Adjusting Model Performance
Did you know that poor MLOps practices are responsible for most machine learning failures and the fact that 87% of projects never make it to production? [19][20]. Monitoring can help you avoid these pitfalls.
Your monitoring strategy should cover several areas: infrastructure metrics (CPU, memory usage), model performance (accuracy, latency), data quality (drift, schema skews), and business KPIs (user engagement, revenue impact). Embedding LLM-as-a-judge
methods within CI/CD pipelines allows you to score outputs for relevance and fail builds if scores fall below defined thresholds.
Testing new models safely is essential. Use shadow deployments, A/B testing, and canary releases to minimise risks. Netflix, for instance, manages recommendations for over 230 million users with sub-200ms latency by running over 1,000 concurrent A/B tests [20].
The difference between a data scientist and an ML engineer is production deployment. MLOps skills are what turn experimental models into systems that create millions of dollars in business value.
- The AI Internship [20]
Finally, treat prompts as versioned assets in source control, and set up automated retraining triggers for when performance drops or data distribution shifts significantly. Keep an eye on vendor deprecation dates for pre-trained models to avoid unexpected service disruptions when support ends.
How Hokstad Consulting Supports AI-Driven DevOps Automation

Hokstad Consulting brings the power of pre-trained AI models into the world of DevOps, crafting tailored strategies specifically for UK businesses. By designing AI-driven systems, they aim to cut cloud costs, speed up deployments, and bolster security. These solutions align seamlessly with the AI strategies previously discussed, offering a well-rounded approach to DevOps automation.
Tailored AI Solutions for DevOps
Hokstad Consulting embeds pre-trained AI models directly into CI/CD pipelines to deliver tangible improvements. For instance, they use predictive modelling to establish cost benchmarks and identify anomalies within just 24 hours. This real-time detection helps businesses tackle inefficient resource usage before it impacts their budgets. They also implement dynamic resource scaling, adjusting to each organisation's unique demands for better resource efficiency.
On the security side, Hokstad Consulting employs advanced AI tools like Transformer models (BERT and RoBERTa) for live code analysis. These models can spot vulnerabilities as soon as developers commit changes. Additionally, they use Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) to evaluate Infrastructure as Code (IaC) configurations, highlighting risks before they make it to production.
End-to-End Implementation Support
Hokstad Consulting doesn’t stop at designing solutions - they ensure smooth integration into existing workflows. Their team incorporates AI-driven insights into day-to-day operations and continuously monitors performance to prevent issues like model drift. This ongoing supervision ensures the AI models stay accurate and effective, even as infrastructure evolves or data patterns shift.
Proven Impact for UK Businesses
The benefits of Hokstad Consulting’s customised AI solutions are clear. UK organisations have reported 30–50% reductions in cloud costs thanks to AI-powered optimisation. Their DevOps transformation services focus on automating repetitive tasks, increasing deployment frequency, and cutting Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR). Whether you're moving to the cloud, managing a hybrid setup, or integrating AI agents into your operations, Hokstad Consulting offers flexible engagement options. One standout feature is their no savings, no fee
model, where fees are capped based on the actual cost savings achieved.
Conclusion
Pre-trained AI models are reshaping DevOps practices across the UK. By enabling engineers to query logs and metrics in natural language, these tools speed up incident response, uncover root causes like memory leaks, and even suggest fixes during critical moments. They also streamline routine configuration tasks, cutting down on manual errors and making it easier for new team members to get up to speed.
When it comes to cost management, AI-driven predictive scaling and workload tiering can slash GPU expenses by 30%–50% [21]. Automated, cost-aware autoscaling ensures organisations can handle fluctuating demands without blowing their budgets. This blend of efficiency and savings is a game-changer for operational management.
Pre-trained models are also moving monitoring from reactive problem-solving to proactive issue prevention. With behavioural anomaly detection, teams can spot performance issues before they escalate into outages, allowing for a more structured and effective response. These advancements not only enhance day-to-day operations but are also earning recognition across the industry. As Prerit Munjal, CTO of KubeCloud & InfraOne, puts it:
The entire Cloud-DevOps landscape will change drastically in 2025... A big rise towards monetising the tools and services with AI integrated at every level, may it be a cloud cost optimiser or a pipeline builder
Hokstad Consulting, based in London, plays a pivotal role in this transformation for UK organisations. Their vendor-neutral approach, combined with expertise in GDPR compliance and hybrid cloud architectures, ensures that businesses can adopt AI-driven DevOps solutions tailored to their specific needs. Whether through hourly consulting, project-based work, or their no savings, no fee
model, they bring both strategic insight and technical know-how to help organisations turn AI automation into a practical, impactful solution.
FAQs
How can pre-trained AI models improve the management of CI/CD pipelines in DevOps?
Pre-trained AI models play a key role in making CI/CD pipeline management more efficient and reliable. They take over repetitive tasks, speed up vulnerability detection and resolution, and simplify testing procedures. Tasks like code analysis and policy compliance can also be automated, saving time and reducing errors.
With less need for manual intervention and consistent, round-the-clock monitoring, these models help ensure faster and more dependable deployments. This frees up DevOps teams to concentrate on higher-level strategic work, leading to more streamlined workflows and improved results for organisations.
How do AI models improve anomaly detection in DevOps workflows?
AI models play a crucial role in spotting anomalies within DevOps workflows by analysing operational data like metrics, logs, and performance indicators. This helps teams take early action on potential problems, such as system outages, security vulnerabilities, or performance slowdowns, before they become major issues.
Using pre-trained AI models, organisations can automate the detection process, cutting down on manual effort and speeding up response times. These models continuously learn and adjust to new patterns, which helps reduce false alarms and delivers more precise insights. With AI-powered anomaly detection, DevOps teams can build systems that are not only more reliable but also more efficient, enabling smoother operations and quicker problem-solving.
How can businesses keep their pre-trained AI models effective over time?
To keep pre-trained AI models running effectively, businesses need to prioritise ongoing monitoring, frequent updates, and retraining. These models, particularly those used in DevOps automation, are highly sensitive to shifts in data and operational conditions. Staying current is crucial. Take, for example, models that optimise CI/CD pipelines - they must be closely monitored to quickly spot vulnerabilities and adjust to new threats as they arise.
Incorporating MLOps practices plays a crucial role in maintaining long-term performance. This approach involves managing every stage of the AI model lifecycle, from retraining with updated data to addressing biases and maintaining version control. Viewing AI models as living systems
allows businesses to adapt them to changing requirements, keeping them accurate and effective. Fine-tuning models for specific tasks and securely integrating updates into existing workflows are also essential steps for ensuring consistent results.
By implementing these methods, businesses can ensure their AI models remain aligned with their goals and continue to provide meaningful results over time.
