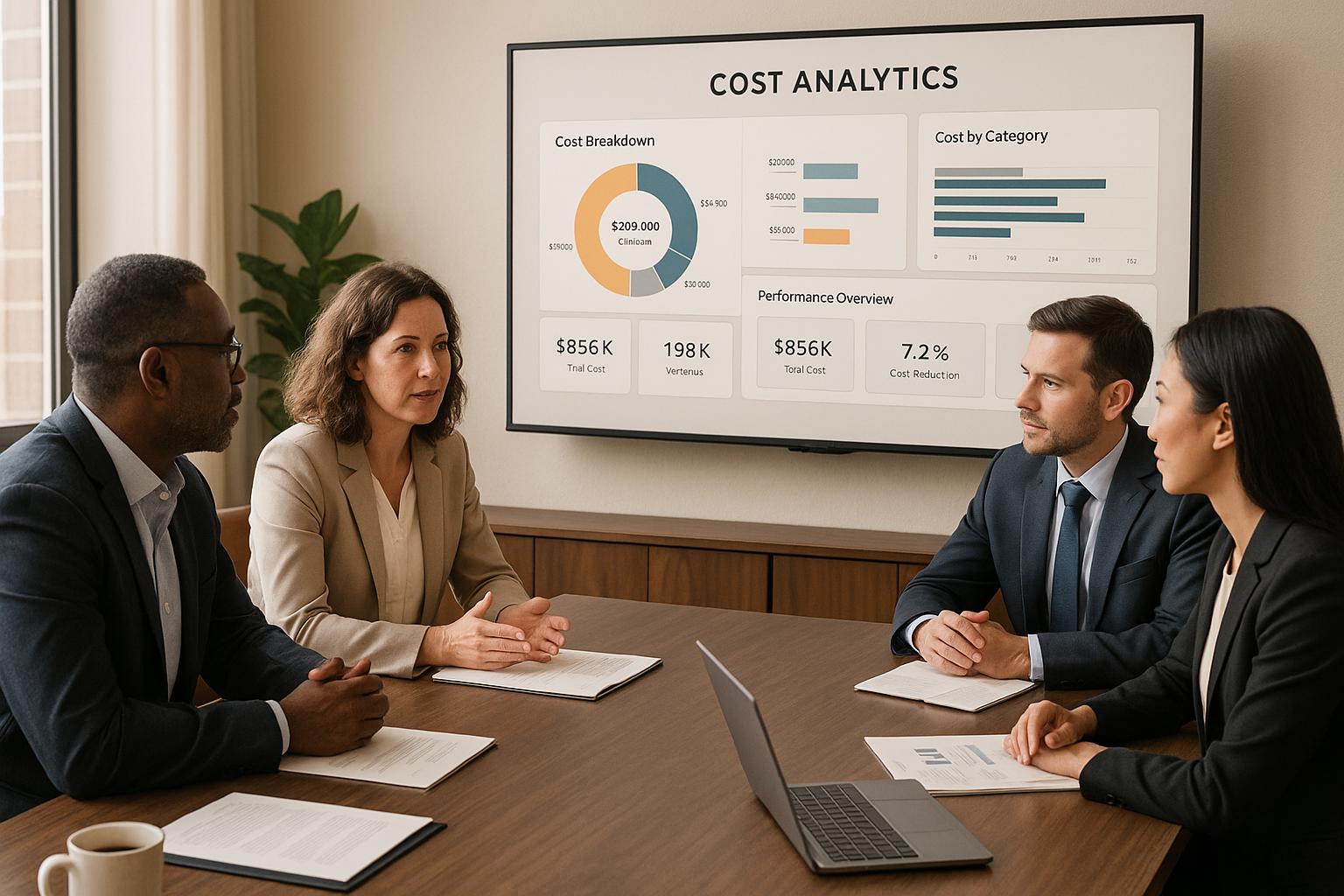
Cloud costs are rising, but you can control them. By implementing effective governance practices, businesses can cut cloud expenses by 30–50% while improving performance. Here's how:
- Real-Time Cost Visibility: Track expenses hourly, identify cost drivers, and reduce allocation disputes. Ensure data privacy with strict access controls and GDPR compliance.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Limit data access by job roles, protect sensitive financial information, and improve accountability with detailed audit trails.
- Resource Tagging Policies: Use standardised tags (e.g., owner, cost centre) for precise cost tracking and compliance with data protection laws.
- Automated Monitoring Tools: Detect cost anomalies, enforce policies, and maintain security with consistent oversight.
- Regular Audits: Validate cost allocation, ensure compliance, and identify inefficiencies through scheduled reviews.
- Cross-Team Collaboration: Align IT, finance, and compliance teams to improve reporting accuracy and streamline processes.
- AI and Advanced Analytics: Predict costs, detect irregularities, and automate data security measures.
These steps not only help save money but also strengthen compliance with UK regulations like GDPR. Hokstad Consulting offers tailored solutions to help businesses achieve these goals, cutting cloud costs by up to 60% while ensuring data security.
Building Cloud Cost Governance That Lasts | The Keys to AWS Optimization | S14 E10
1. Set Up Real-Time Cost Visibility and Transparency
Real-time cost visibility transforms how organisations monitor expenses by introducing systems that track resource usage, spending, and access patterns across all cloud environments - all while adhering to strict data governance standards. These tools provide detailed insights into spending trends and maintain comprehensive audit trails, showing who accessed resources and when. This level of oversight allows finance and IT teams to quickly identify unusual spending patterns, unauthorised resource use, or potential security threats. Such transparency lays the groundwork for accurate cost allocation and ensures compliance.
Improving Cost Reporting Accuracy
Real-time monitoring eliminates the delays often associated with monthly reporting, enabling organisations to track costs with hourly precision. This allows businesses to drill down into spending by individual resources, departments, or projects.
For companies operating across multiple cloud platforms, this precision is invaluable. Teams can pinpoint which specific workloads are driving costs and make better decisions about resource allocation. By linking cost data to performance metrics, organisations gain a clearer picture of the return on their cloud investments.
Another benefit is the reduction of cost allocation disputes between departments. When teams can directly see the resources they’re using and their associated costs, guesswork is eliminated, and resource usage becomes more accountable.
Balancing Data Privacy and Security
Introducing real-time cost visibility requires careful attention to data privacy. Monitoring systems must be designed to protect sensitive information while ensuring authorised personnel have the transparency they need.
- Implement strict access controls to limit who can view cost data, as this information can reveal insights about project budgets, resource usage, and strategic plans.
- Ensure the monitoring infrastructure is secure to prevent potential breaches that could expose critical spending data or cloud architecture details.
Aligning with UK Regulations (e.g., GDPR)
Real-time cost monitoring systems must comply with regulations like GDPR, particularly regarding transparency and accountability in data processing. Organisations need to ensure that monitoring practices do not unintentionally collect or process personal data without a valid legal basis.
Audit logs play a key role here, providing detailed records of data processing activities. These logs help organisations demonstrate compliance and respond effectively to data subject requests.
That said, businesses must also manage data retention carefully. Historical cost data and audit logs should only be kept for as long as they’re needed for operational purposes, in line with data protection rules.
Integration with Existing Systems and Processes
Modern cost monitoring solutions are built with API-driven architectures, making it easier to integrate them into existing enterprise systems. This centralises data, maintains audit trails, and embeds cost information into dashboards, reporting tools, and automated workflows.
For seamless integration, organisations can connect directly with cloud provider APIs to automate data collection and reporting. However, initial setup can be complex, especially in multi-cloud environments or when dealing with older systems. IT, finance, and compliance teams will need to collaborate closely to ensure all requirements are met while maintaining security and governance standards.
These integration efforts not only enhance cost reporting but also strengthen governance frameworks, which are essential for maintaining data privacy and security.
2. Use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) for Data Security
Building on cost visibility measures, Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) takes data security a step further by restricting access to information based on job roles.
RBAC ensures that sensitive financial data stays protected while allowing team members to access only the cost information relevant to their responsibilities. Instead of assigning permissions to individual user accounts, RBAC uses predefined roles, making it easier to manage access across large organisations while maintaining consistent security practices. By tailoring access to specific roles, RBAC not only safeguards data privacy but also complements real-time cost monitoring efforts.
The system works best when permission levels are carefully aligned with organisational roles. For instance, finance managers might have full access to departmental cost data, while project managers are limited to viewing costs tied to their initiatives. This targeted approach prevents unauthorised access and reduces the likelihood of data breaches.
Impact on Data Privacy and Security
RBAC enforces the principle of least privilege, meaning users can only access the data necessary for their tasks, reducing the exposure of sensitive financial details.
This approach offers more than just access restrictions. It adds a layer of protection against lateral movement within systems. If a user account is compromised, the attacker’s access is constrained to the permissions of that specific role, preventing widespread exposure of cost data across the organisation.
Modern RBAC systems take it further by dynamically adjusting permissions based on factors like time, location, or device. This feature is especially useful for protecting data when employees work remotely, adding an extra layer of security for sensitive financial information.
Compliance with UK Regulations (e.g., GDPR)
RBAC frameworks align seamlessly with GDPR requirements by promoting accountability and transparency in data processing. The detailed permission structures in RBAC provide clear evidence of how personal data in cost reports is accessed and managed, ensuring compliance with GDPR standards while maintaining cost efficiency.
Under GDPR’s data minimisation principle, RBAC ensures that employees only access the personal data necessary for their roles. For example, if cost reports include project details or employee information that could identify individuals, RBAC limits access to authorised personnel only.
The right to be forgotten is also easier to manage with RBAC. Organisations can quickly identify who has accessed specific data and ensure its complete removal when required.
Additionally, RBAC supports data protection impact assessments by documenting data flows, access patterns, and security measures. These records are invaluable for demonstrating compliance to regulators or conducting internal reviews.
Effectiveness in Improving Cost Reporting Accuracy
Controlled access through RBAC reduces errors by limiting data modifications to qualified personnel and creating audit trails that enhance accountability and version control. When only trained users can make changes, the chances of accidental data corruption or misconfiguration drop significantly.
RBAC also ensures data quality by restricting unauthorised modifications to key elements like resource tags, cost allocation rules, or reporting categories. By limiting these changes to designated administrators, organisations maintain consistency in their cost reporting processes.
Another key benefit is the improved segregation of duties. With RBAC, the same person cannot both input cost data and approve financial reports, reducing the risk of fraud and enhancing the integrity of financial processes.
Ease of Integration with Existing Systems and Processes
Most enterprise systems support RBAC integration through Single Sign-On solutions and identity providers, which automatically synchronise user roles. This ensures that when employees change roles or leave the organisation, their access to cost reporting systems is updated promptly.
However, successful implementation requires careful planning of role definitions. Starting with broad role categories and refining them based on actual usage patterns often works better than attempting to define every possible permission scenario from the outset. This approach keeps the system manageable while ensuring effective security.
3. Apply Standard Resource Tagging Policies
After setting up role-based access controls, the next step is implementing standard resource tagging policies. These policies help organise cloud resources by attaching metadata that categorises them by usage, ownership, and purpose. This approach is key to maintaining secure and accurate cost reporting.
A well-thought-out tagging system creates a uniform structure across all resources, making it easier to track costs by department, project, environment, or compliance needs. Without consistent tagging, cost allocation becomes chaotic, and sensitive data could be at risk.
To make tagging effective, clear naming conventions and mandatory tag categories should be set from the start. Common tag categories include:
- Owner: Identifies who is responsible for the resource.
- Environment: Specifies if the resource is for production, staging, or development.
- Cost centre: Links the resource to a specific budget or department.
- Project code: Associates the resource with a particular project.
- Data classification level: Indicates the sensitivity of the data (e.g., confidential, restricted).
These tags must be applied consistently across all platforms, whether in the cloud or on-premises, to ensure accurate reporting.
Impact on Data Privacy and Security
Resource tagging plays an important role in enhancing data privacy. By including sensitivity levels like confidential
, restricted
, or public
in tags, organisations can apply tailored security measures automatically. This ensures resources are protected according to their classification.
Tags are also crucial for meeting data residency requirements. For instance, tagging resources that contain personal data or need to stay within specific geographic boundaries helps organisations comply with regulations, especially in the UK. Post-Brexit, this is vital for businesses managing data under stricter data protection laws.
Moreover, tagging improves incident response. In the event of a security breach, teams can quickly identify which resources hold sensitive data and focus their efforts on securing those systems. This targeted response not only saves time but also minimises data exposure.
Compliance with UK Regulations (e.g., GDPR)
Standard tagging policies help organisations stay aligned with GDPR by simplifying data mapping and inventory management. Tags can identify data types, processing purposes, and retention periods, making it easier to meet the record-keeping requirements outlined in GDPR Article 30.
Tags also streamline the right to erasure process. By tagging resources with retention schedules and data subject information, automated systems can locate and delete personal data efficiently, ensuring compliance with deletion requests within the required timeframes.
Additionally, tagging supports data protection impact assessments by providing clear insights into data flows and processing activities. For example, tags that highlight data sources, processing purposes, or third-party integrations allow organisations to evaluate privacy risks and implement necessary safeguards more effectively.
Effectiveness in Improving Cost Reporting Accuracy
Consistent tagging significantly improves the accuracy of cost reporting. With standardised tags, cost allocation becomes automated, removing guesswork and ensuring precise billing for departments or projects.
This is especially beneficial in multi-cloud environments, where resources are spread across platforms like AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, or even on-premises systems. Standard tags ensure costs are allocated uniformly, no matter where the resources reside.
Tagging also aids in cost anomaly detection. By establishing clear baselines for resource categories, organisations can set up automated alerts for unexpected cost spikes. This allows teams to take action before expenses get out of hand.
Ease of Integration with Existing Systems and Processes
Most cloud platforms enforce tagging automatically, ensuring that resources without required labels cannot be deployed. This eliminates the need for manual checks by development teams and ensures compliance with tagging standards.
Features like tag inheritance simplify the process further. For example, if a tag is applied to a resource group or project, it automatically propagates to all associated resources, reducing administrative workloads while maintaining consistency.
When tags align with established organisational structures - like cost centres, business units, or project codes - they integrate easily with existing ITSM and financial systems. This seamless alignment allows cost data to flow into existing reporting and budgeting tools without requiring major system changes. It also lays the groundwork for future automation in cost management.
4. Use Automated Monitoring and Policy Tools
Implementing automated monitoring and policy tools is the logical next step after establishing standardised tagging policies. These tools play a key role in maintaining a strong framework for cost reporting governance. They continuously track resource usage, spending patterns, and any breaches of policy, ensuring a consistent and reliable oversight process.
Policy enforcement tools complement monitoring by taking immediate corrective action when violations occur. For instance, they can block non-compliant deployments or restrict access to incorrectly classified resources. Together, these tools create a powerful combination that strengthens security and ensures more accurate cost allocation.
Impact on Data Privacy and Security
Automated monitoring tools are essential for safeguarding data privacy. They keep a constant watch on data access patterns and resource configurations, identifying unusual behaviour such as unauthorised access attempts, unexpected data transfers, or risky configuration changes. When something suspicious is flagged, automated alerts enable quick responses.
Policy automation further bolsters security by ensuring data encryption standards are consistently met. These tools automatically encrypt storage resources containing sensitive information, both at rest and during transmission, based on resource tags or data classification levels. This eliminates the risk of human error in applying security protocols.
Another layer of protection comes from access control automation. These systems ensure that user permissions are always in line with current roles. When employees change roles or leave the organisation, their access to sensitive resources is revoked immediately, reducing the risk of data breaches. These measures also help organisations align with UK regulatory requirements.
Compliance with UK Regulations (e.g., GDPR)
Automated monitoring tools excel at maintaining audit trails, a key requirement of GDPR and other UK regulations. They automatically log data access, processing activities, and configuration changes, creating detailed records that demonstrate compliance during audits.
Data retention automation is another critical feature, helping organisations adhere to GDPR's storage limitation principle. By tracking data based on resource tags, these tools can automatically delete or archive personal data once its retention period expires.
Policy tools also address breach notification requirements under GDPR Article 33. If unauthorised access or data exposure is detected, automated systems can alert data protection officers immediately and initiate workflows to meet the 72-hour notification deadline.
Effectiveness in Improving Cost Reporting Accuracy
Automated monitoring tools significantly improve cost reporting by removing the errors associated with manual data collection. With real-time anomaly detection, they ensure accurate cost allocation and prevent mismanagement.
Policy automation adds another layer of precision. By automatically assigning the correct cost centre codes, project identifiers, and departmental tags to new resources, these tools eliminate the common problem of resources being deployed without proper financial attribution. This ensures accurate departmental billing and budget tracking.
Ease of Integration with Existing Systems and Processes
Automated monitoring tools are designed to integrate smoothly with existing ITSM platforms using standard APIs and webhooks. This allows cost alerts, policy violations, and compliance reports to flow directly into established ticketing systems, ensuring that issues are resolved within existing workflows rather than creating new, disruptive processes.
Integration with financial systems is equally seamless. Automated cost data can feed directly into enterprise resource planning systems and budgeting tools, removing the need for manual data transfers. This reduces errors and ensures financial reports are always up to date.
These tools are also designed to complement existing security infrastructure. Instead of replacing current systems, automated monitoring enhances them, providing a unified view of both cost and security metrics. Importantly, teams can implement these tools gradually, starting with basic alerts and expanding their use over time. This approach minimises disruption and builds trust in automated governance systems while improving overall visibility and control.
Need help optimizing your cloud costs?
Get expert advice on how to reduce your cloud expenses without sacrificing performance.
5. Run Regular Audits and Compliance Reviews
Conducting regular audits and compliance reviews plays a crucial role in maintaining strong governance over cost reporting. While real-time monitoring and Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) measures handle immediate oversight, audits dig deeper, uncovering systemic issues and long-term trends that might otherwise go unnoticed.
These audits typically involve scrutinising cost allocation methods, reviewing access controls, validating data accuracy, and ensuring compliance with both internal policies and external regulations. By doing so, they foster accountability across teams and identify weaknesses in the governance framework that need attention.
Impact on Data Privacy and Security
Periodic audits go beyond real-time controls by reinforcing and validating security measures. For example, auditors analyse user access patterns to detect vulnerabilities, such as employees retaining access to sensitive cost data after changing roles or external contractors having permissions beyond what’s necessary.
These reviews also assess encryption practices, examine exposure to vulnerabilities, and ensure that sensitive data remains well-protected. Security audits confirm that logging mechanisms are functioning correctly, capturing all necessary activities for forensic purposes in case of a breach.
The audit trail itself becomes a valuable resource, offering detailed records of who accessed what information and when. This not only acts as a deterrent against misuse but also enables quick responses to any suspicious activity identified during the reviews.
Compliance with UK Regulations (e.g., GDPR)
Compliance audits are essential to ensure cost reporting aligns with UK regulations, especially the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). These reviews verify the lawfulness of data processing, ensuring that any personal data included in cost reports has a valid legal basis and, where necessary, proper consent.
Audits also focus on data subject rights, confirming that processes are in place to handle access requests, data portability demands, and deletion requests within GDPR’s required timeframes. This includes verifying that cost data containing personal information can be located, extracted, and deleted when legally mandated.
For organisations operating internationally, audits assess the compliance of cross-border data transfers, ensuring that data moved to third countries meets adequacy standards or has the necessary safeguards in place. Additionally, they confirm that record-keeping for cost data handling meets regulatory requirements.
Effectiveness in Improving Cost Reporting Accuracy
Audits are instrumental in refining cost reporting accuracy. For instance, data reconciliation audits compare cost reports across multiple systems, identifying inconsistencies and ensuring financial records align with operational data.
Similarly, allocation methodology reviews evaluate whether current cost attribution methods remain relevant as business needs evolve. These reviews often uncover outdated rules that lead to inaccurate departmental or project charges, paving the way for more precise financial reporting.
Auditors also perform variance analysis, examining historical errors to spot recurring patterns. This helps recommend process changes that reduce future discrepancies, improving the reliability of cost reporting. In addition, audits validate the performance of automated monitoring systems, ensuring their outputs remain accurate and effective as business requirements shift.
Ease of Integration with Existing Systems and Processes
Modern audit frameworks are designed to integrate smoothly with existing governance structures. By adopting risk-based approaches, they align with enterprise risk management processes, ensuring that audits enhance rather than duplicate existing controls.
Many platforms now integrate directly with IT Service Management (ITSM) systems, streamlining the remediation process. For example, workflow integration allows audit findings to automatically generate tickets within ITSM platforms, ensuring that identified issues are addressed promptly within familiar systems.
Audit schedules can also be tailored to align with financial cycles, regulatory deadlines, and business planning timelines. This synchronisation ensures audits deliver maximum value while minimising disruptions. Quarterly audits, for instance, often strike the right balance, aligning with financial reporting needs and catching emerging issues early enough to address them effectively.
6. Build Collaboration Between IT, Finance, and Compliance Teams
Effective cost reporting and governance hinge on teamwork between IT, finance, and compliance teams. When these groups work in isolation, it often leads to fragmented data, inconsistent reporting, and potential security issues. Breaking down these barriers creates a unified approach, improving both cost accuracy and data security.
By aligning IT's focus on operational efficiency, finance's attention to precise budgeting, and compliance's regulatory expertise, organisations can establish a solid foundation for secure and accurate cost reporting.
Impact on Data Privacy and Security
Collaboration across departments plays a key role in improving data privacy and security through layered oversight. When IT, finance, and compliance teams work together, they can address technical vulnerabilities, protect financial data, and meet regulatory requirements in a cohesive manner.
For example, IT can identify technical weaknesses, finance can highlight sensitive data, and compliance can ensure all measures align with legal standards. This joint effort reduces the risk of security gaps that often arise when teams operate independently.
Compliance with UK Regulations (e.g., GDPR)
Working together also ensures compliance with regulations like GDPR. Finance teams can pinpoint personal data, IT can implement technical controls to secure it, and compliance teams can oversee adherence to legal standards.
Handling data subject requests becomes more streamlined with this approach. Finance can quickly locate relevant cost data, IT can retrieve or delete it from systems, and compliance can ensure responses meet legal deadlines and requirements.
Effectiveness in Improving Cost Reporting Accuracy
Collaboration enhances cost reporting accuracy by combining the unique strengths of each team. Finance brings expertise in cost allocation, IT ensures data quality and system integrity, and compliance guarantees that reporting methods meet regulatory standards.
Regular joint reviews provide an opportunity to catch errors that might go unnoticed by individual teams. These reviews not only improve accuracy but also refine reporting processes, ensuring compliance without sacrificing quality.
When all departments share responsibility for cost reporting, accountability improves. Setting clear accuracy metrics and standards together encourages teams to consistently deliver high-quality results. This shared ownership not only secures data but also optimises cost allocation, leading to better financial outcomes.
Ease of Integration with Existing Systems and Processes
Building collaboration doesn't have to disrupt existing workflows. Cross-functional steering committees can provide oversight without interfering with day-to-day operations, ensuring governance and efficiency coexist.
Using familiar tools like project management systems and communication platforms makes integration smoother. Teams can coordinate activities without the need for new technology, focusing instead on establishing collaborative processes.
A gradual approach works best. Starting with specific cost reporting projects allows teams to build trust and refine their working methods. These early successes can then serve as a foundation for broader collaboration, reducing resistance and fostering a culture of teamwork over time.
7. Use AI and Advanced Analytics for Cost Management
AI and advanced analytics are reshaping cost management by shifting it from a reactive process to a proactive strategy. These tools allow organisations to predict expenses, spot irregularities, and optimise how resources are allocated. By processing massive amounts of financial data in real time, they provide insights that traditional methods often overlook.
Modern AI systems can analyse historical spending patterns to forecast future costs with impressive precision. They can also flag unusual expenditures before they disrupt budgets. Machine learning algorithms continuously adapt, learning from spending behaviours to become more accurate and responsive to changing business needs. On top of that, these systems enhance data security by introducing smarter privacy measures.
Impact on Data Privacy and Security
AI-driven cost management systems strengthen data privacy by using intelligent data classification and automated security protocols. These tools can identify sensitive financial information, apply the right encryption levels, and monitor access patterns to pre-empt potential breaches.
Advanced analytics platforms also employ differential privacy techniques, which add controlled noise to datasets. This ensures organisations can extract meaningful insights without exposing sensitive details. Additionally, these systems maintain a detailed audit trail, continuously monitoring access and changes. This not only supports compliance but also flags suspicious activities that could indicate security threats.
Compliance with UK Regulations (e.g., GDPR)
AI systems play a key role in ensuring compliance with regulations like the GDPR. They can automatically identify and categorise personal data within cost reports, tracking its journey across systems to ensure proper handling.
When it comes to data subject requests, AI speeds up the process by aggregating relevant financial data quickly, compiling responses, and handling deletion requests - all while maintaining the integrity of data needed for legitimate purposes. These systems also adhere to privacy by design principles, applying data minimisation techniques to ensure only necessary personal data is included in reports. Where full identification isn't essential, they anonymise or pseudonymise the data automatically.
Effectiveness in Improving Cost Reporting Accuracy
AI enhances the accuracy of cost reporting through predictive anomaly detection, which identifies unusual spending patterns before they escalate. It also refines cost allocation models with adaptive learning, outperforming manual reviews in precision.
Using natural language processing, AI can extract cost data from unstructured sources like contracts and invoices. This automation reduces errors from manual data entry and ensures that all relevant information is consistently included in reports.
Machine learning algorithms further improve accuracy by continuously updating cost allocation models based on real-world spending and outcomes. This adaptability accounts for seasonal changes, shifts in business operations, and evolving expenditure trends, making cost reporting increasingly precise over time.
Ease of Integration with Existing Systems and Processes
Modern AI platforms are designed to integrate seamlessly with existing financial systems. Using API-first architectures, they easily connect to accounting software, ERP systems, and cloud platforms. These integrations are straightforward and can be rolled out gradually across different departments.
Pre-built connectors simplify the process, enabling organisations to implement AI-powered cost management within weeks. These connectors handle data synchronisation automatically, ensuring that reports always reflect up-to-date information from all linked systems.
Cloud-based AI solutions offer additional benefits for businesses aiming to enhance cost management without heavy infrastructure investments. For example, Hokstad Consulting uses these solutions in their DevOps and cloud cost engineering services, helping organisations implement smart cost management tools that align effortlessly with existing cloud setups and workflows.
Comparison Table
To summarise the discussion on data security and cost control, the tables below highlight key differences between various approaches to monitoring and access control. These comparisons provide a clearer understanding of how different methods impact financial governance and operational efficiency.
Monitoring Approaches
| Aspect | Manual Monitoring | Automated Monitoring | AI-Enhanced Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| Detection Speed | Slower, relying on periodic reviews | Faster, using rule-based alerts | Near real-time, leveraging predictive insights |
| Accuracy | Prone to human error and inconsistencies | More consistent with standardised rules | Highly accurate, using historical trend analysis |
| Resource Requirements | High reliance on manual oversight | Moderate, requiring setup and adjustments | Minimal after initial implementation |
| Cost Anomaly Detection | Reactive, addressing issues post-impact | Proactive, with predefined thresholds | Predictive, identifying patterns early |
| Compliance Reporting | Manual effort with error potential | Standardised automatic reports | Dynamic, reflecting regulatory changes |
| Data Privacy Controls | Basic access restrictions | Role-based permissions | Adaptive data classification methods |
| Scalability | Limited by human capacity | Scales with infrastructure improvements | Automatically adapts to business growth |
| Investment & ROI | Lower upfront cost, reduced efficiency over time | Moderate investment with better outcomes | Higher initial cost, strong long-term benefits |
This table highlights the progression from manual to AI-driven monitoring, showcasing how technology improves speed, accuracy, and scalability while reducing resource demands.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Similarly, RBAC systems have transitioned from manual processes to highly adaptive, technology-driven frameworks.
| Access Level | Manual RBAC | Automated RBAC | AI-Enhanced RBAC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Administrator | Full access with manual oversight | Policy-driven permissions | Dynamic access with continuous monitoring |
| Finance Manager | Manually managed departmental visibility | Structured access via automated rules | Contextual data tailored to role |
| Team Lead | Limited visibility, manually controlled | Rule-based spending limits | Proactive alerts and budgeting recommendations |
| General User | Restricted from cost details | Read-only summaries | Personalised cost insights |
| Security Risk | High, due to human error potential | Moderate, dependent on configuration | Low, with adaptive and continuous monitoring |
| Audit Trail | Relies on incomplete manual logging | Comprehensive, automatically generated logs | Intelligent auditing with real-time anomaly detection |
| Compliance | Inconsistent adherence | Systematic, more consistent controls | Highest adherence with adaptive updates |
These comparisons illustrate the evolution of RBAC systems, from manual oversight to advanced, AI-driven solutions. The shift enhances efficiency, reduces risks, and ensures stronger compliance, aligning with the broader trend of technology-enabled cost reporting governance.
Conclusion
Establishing clear governance practices for cost reporting has become a necessity for UK businesses navigating complex cloud environments and strict data protection laws. The seven practices discussed earlier provide a solid framework to enhance operational efficiency while meeting regulatory demands, particularly under GDPR and UK data protection legislation.
A key takeaway is how technology is reshaping governance. The move from manual processes to AI-powered systems is revolutionising financial management. These advanced tools offer real-time insights and automated analytics, ensuring sensitive data is protected while keeping costs under control.
A cornerstone of these practices is role-based access control, which safeguards cost reporting. When paired with standardised tagging policies and regular compliance checks, these measures create robust layers of protection that address both internal governance needs and external regulatory standards.
Beyond security, these practices open doors to strategic collaborations. For UK businesses aiming to adopt these governance strategies effectively, working with experts can streamline the process and minimise risks. Hokstad Consulting offers tailored cloud cost engineering solutions, helping organisations implement monitoring systems and cost-saving strategies across both cloud and on-premises platforms.
Your cloud bill is too high - we can fix that. At Hokstad Consulting Limited, we cut cloud costs by 30–60% while boosting performance. You only pay when we deliver. Stop overpaying for the cloud. Start saving today.- Michael Thompson, Consultant at Hokstad Consulting Ltd
Hokstad’s pay-for-performance model aligns seamlessly with the principle of accountability, ensuring businesses see tangible cost savings without upfront financial commitments. This approach removes the risk traditionally tied to adopting new governance frameworks, making it easier for organisations to embrace best practices.
FAQs
How does real-time cost visibility enhance financial accountability and compliance in cloud environments?
Real-time cost visibility plays a key role in boosting financial accountability and ensuring compliance. By offering ongoing insights into cloud spending, it enables organisations to stay on top of their budgets, spot discrepancies early, and align with financial and regulatory requirements.
Having precise and current data at their fingertips allows businesses to simplify cost reporting, be better prepared for audits, and prevent unnecessary expenses. This level of transparency not only aids smarter decision-making but also encourages responsible use of resources, reinforcing strong financial management.
How does Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) improve data privacy and security in cost reporting?
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) strengthens data privacy and security by restricting access to only the information users need to perform their specific roles. This approach minimises the chances of unauthorised access and helps prevent potential data breaches by adhering to the principle of least privilege.
RBAC also boosts accountability by allowing detailed tracking of user activities, simplifying the management of access to sensitive cost reporting data. By assigning permissions based on roles, organisations can maintain tighter control over their data while ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
How do AI and advanced analytics improve cost management and ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR?
AI and advanced analytics have become essential tools for managing costs and staying compliant with regulations like GDPR. These technologies enable real-time monitoring and automated enforcement of data governance rules, helping businesses spot and address risks swiftly. This reduces the chances of expensive compliance failures.
On top of that, AI bolsters clarity and responsibility by constantly reviewing transactions and data processing activities. This not only ensures organisations meet legal requirements but also cuts down on manual compliance tasks, ultimately saving money and streamlining operations.
