Drift in Infrastructure as Code (IaC) occurs when your live cloud infrastructure no longer matches your code. This happens due to manual changes, automated processes, or updates from cloud providers. Ignoring drift can lead to security risks, compliance failures, and higher costs.
To manage drift effectively, you need a combination of detection methods and tools:
- Manual checks: Commands like
terraform planorpulumi previewcompare your code with live infrastructure but require frequent execution. - Automation: CI/CD pipelines, event-driven detection (e.g., AWS CloudTrail), and GitOps tools like Flux or ArgoCD ensure continuous monitoring.
- Specialised tools: Platforms like Spacelift and env0 offer features like scheduled scans and automated remediation.
Prevention strategies include strict access controls, policy-as-code frameworks, and automation to minimise manual changes. For UK businesses, addressing drift is crucial to meet regulations like GDPR and avoid operational inefficiencies.
Key takeaway: Drift detection isn't just about finding issues - it's about maintaining alignment between your infrastructure and code to ensure security, compliance, and cost control.
Manage Infrastructure with Drift Detection for Terraform
Techniques for Detecting IaC Drift
Choosing the right drift detection method depends on your environment's complexity, the importance of your resources, and how quickly you need to identify changes.
Manual detection is still a useful option in certain situations. By running commands like terraform plan or pulumi preview --refresh, you can compare your code with the live environment. This method is particularly effective during development or when addressing specific issues. For AWS users, the CloudFormation drift detection command offers a similar capability, allowing you to control when detection occurs. As Christie Koehler, Developer Advocate at HashiCorp, explains:
Within the context of your configuration, it happens when adding or removing resources or changing resource definitions. External to your configuration, drift occurs when resources have been terminated or have failed, and when changes have been made manually or via other automation tools.[4]
The downside? Manual checks only work when you run them, so drift could go unnoticed for days or even weeks. To address this limitation, automated methods provide a more consistent solution.
Automated detection through CI/CD pipelines turns drift detection into a continuous process. By setting up scheduled workflows with cron syntax - like 0 2 * * * to run daily at 02:00 - you can ensure discrepancies are flagged within a day [10][6]. The real advantage lies in using exit codes: for example, terraform plan -detailed-exitcode returns an exit code of 2 if drift is detected, allowing you to trigger alerts or fail builds automatically [10][6]. For nearly instant updates, event-driven detection uses cloud provider event streams like AWS CloudTrail to identify changes. These events can then trigger policy checks via Amazon EventBridge as soon as a resource is modified [11][6]. This approach is especially important for organisations in the UK that need to balance compliance with operational efficiency.
Building on automated pipelines, the GitOps approach leverages Git as the single source of truth for detecting drift. Tools like Flux or ArgoCD continuously monitor your live infrastructure and compare it to the desired state stored in your Git repository [12][13]. If discrepancies are detected, the GitOps controller can either reconcile the environment automatically or notify your team. Trevor Rae, Cloud Platform Engineer at 1Password, shared:
With Spacelift, one of the first things we did was a big drift detection. We overhauled our drift detection, drift remediation, how to handle and solve it, and how to prevent it from happening.[7]
This constant reconciliation ensures environments remain synchronised while providing a detailed audit trail for every change.
In the UK, organisations often take a layered approach. They might combine scheduled CI/CD workflows for core resources, stateless scans to uncover unmanaged assets, and event-driven detection for high-security infrastructure [6]. This strategy ensures thorough coverage without overwhelming teams with excessive alerts.
Key Tools for IaC Drift Detection
::: @figure 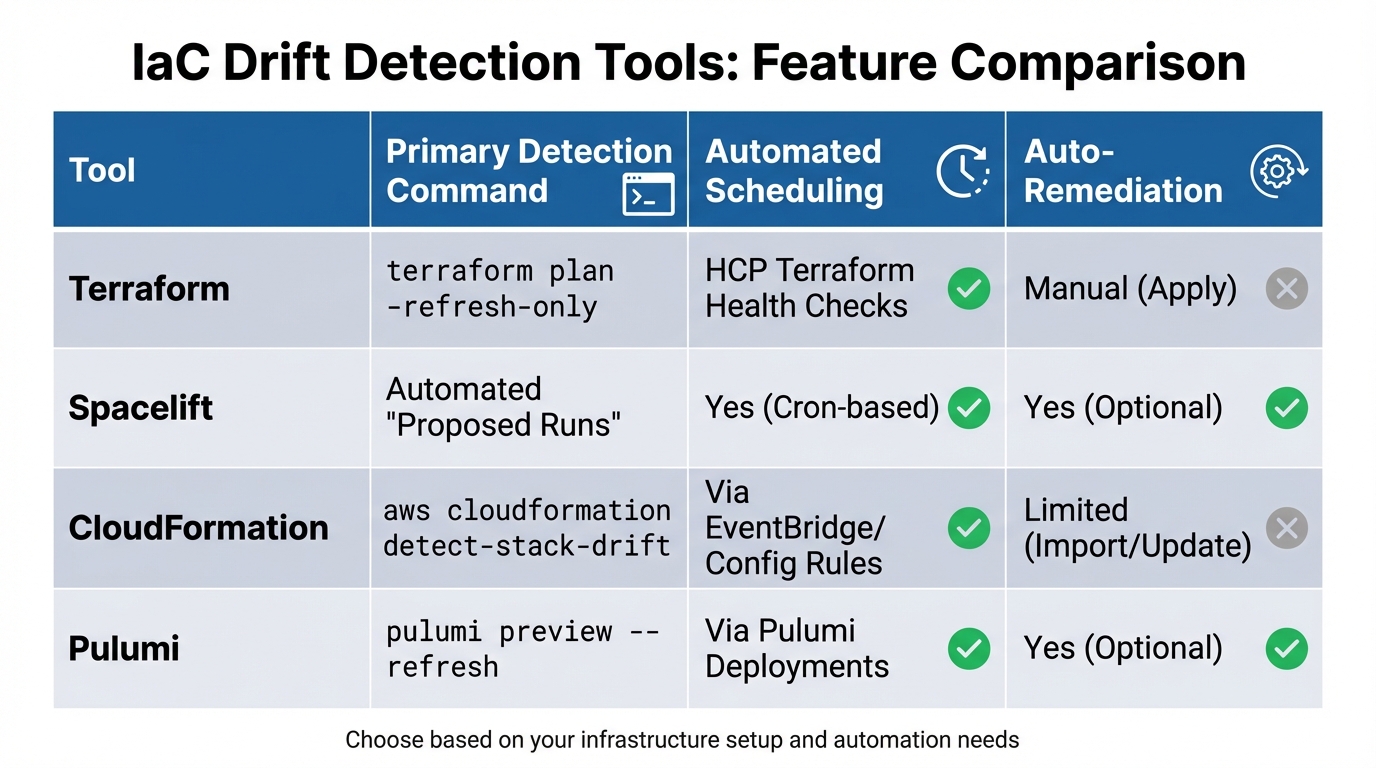 {IaC Drift Detection Tools Comparison: Features and Capabilities}
:::
{IaC Drift Detection Tools Comparison: Features and Capabilities}
:::
Once you've explored the methods for detecting Infrastructure as Code (IaC) drift, the next step is choosing the right tool to keep things under control. The choice depends on your infrastructure setup and automation needs. While native tools offer simplicity, specialised platforms bring advanced scheduling and remediation features.
Terraform and Native Tools
Terraform comes equipped with commands to identify drift. Running terraform plan refreshes the state and highlights any discrepancies, while terraform plan -refresh-only focuses solely on identifying pending changes without making modifications [14]. This command replaces the now-deprecated terraform refresh, helping you avoid unintentional updates.
For those using HCP Terraform, the platform adds an extra layer of functionality. It performs automatic health assessments every 24 hours, verifying your infrastructure against the state file [1]. Available in the Standard Edition, these assessments ensure resources align with configuration-defined health checks [1][8]. However, a notable limitation is that both Terraform and CloudFormation only monitor properties explicitly defined in your configuration. Any properties relying on provider defaults won't be tracked for drift [1][3].
Spacelift and env0
Spacelift simplifies drift detection with automated proposed runs
that use cron-based scheduling to flag discrepancies visually [14][15]. When drift is detected, Spacelift can trigger a tracked run
(essentially a terraform apply) to restore the desired state [14]. Organisations can also integrate policies via Rego, allowing them to either automate reversion or require manual approval, depending on internal guidelines [15].
Spacelift has enabled Checkout to scale from a handful of deployments per day to averaging over 500 per day- Joe Hutchinson, Director of Engineering - Developer Platform, Checkout [15]
For UK teams working in multi-tool environments - combining Terraform, Pulumi, and OpenTofu - Spacelift offers unified drift management across all providers [7][15].
Similarly, env0 uses scheduled scans to compare live infrastructure with IaC definitions [17]. Its Smart Remediation
feature offers two options: Code-to-Cloud
(deploying changes to match the code) or Cloud-to-Code
(creating a pull request to update the code to reflect the current state). This flexibility is particularly useful when drift results from intentional changes that need to be codified rather than reverted [17].
CloudFormation and Pulumi
Both CloudFormation and Pulumi include built-in drift detection features.
AWS CloudFormation provides drift detection via the aws cloudformation detect-stack-drift CLI command [3]. It assigns statuses like DRIFTED, IN_SYNC, or NOT_CHECKED to stacks and individual resources, with details showing whether properties have been MODIFIED or DELETED [3]. Drift-aware change sets allow you to compare templates against the actual state before deployment [7]. However, drift detection must be triggered manually or automated using custom AWS Lambda or EventBridge configurations [17]. Additionally, certain properties, such as KMSKeyId, cannot be monitored for drift due to their ability to reference multiple aliases [3].
Pulumi, on the other hand, uses the pulumi preview --refresh command to list proposed changes by comparing code with live infrastructure [7]. The pulumi refresh command updates its state file, and scheduled deployments can automatically resolve discrepancies [9][16]. Pulumi also features an ignoreChanges option, which helps prevent unnecessary alerts for expected property variations [16][18]. These automated capabilities are available in Pulumi's Enterprise and Business Critical editions [9].
| Tool | Primary Detection Command | Automated Scheduling | Auto-Remediation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Terraform | terraform plan -refresh-only |
HCP Terraform Health Checks | Manual (Apply) |
| Spacelift | Automated Proposed Runs |
Yes (Cron-based) | Yes (Optional) |
| CloudFormation | aws cloudformation detect-stack-drift |
Via EventBridge/Config Rules | Limited (Import/Update) |
| Pulumi | pulumi preview --refresh |
Via Pulumi Deployments | Yes (Optional) |
These tools provide a range of options, allowing teams to choose a solution that best fits their workflows and infrastructure requirements. Each one contributes to a proactive approach to managing and preventing IaC drift.
Need help optimizing your cloud costs?
Get expert advice on how to reduce your cloud expenses without sacrificing performance.
Preventative Strategies for IaC Drift
Preventing drift is all about staying ahead of the curve. By using strict access controls, automation, and constant validation, you can keep your infrastructure aligned with your code, saving time and reducing risks.
Policy as Code and RBAC
Policy as Code (PaC) acts like a security checkpoint for your infrastructure. Tools such as HashiCorp Sentinel and Open Policy Agent (OPA) allow you to set up rules that ensure every deployment meets your organisation's standards before it goes live [19]. For instance, you could create a rule to block security groups with overly open ingress permissions (e.g., 0.0.0.0/0), a common source of security vulnerabilities [19][4]. PaC can also help with workflow governance, like enforcing policies that prevent deployments late on a Friday to minimise the chance of weekend incidents [19].
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) tackles drift at its root by limiting who can make changes. A read-only-by-default
approach ensures most team members can view but not alter cloud resources [6]. Only senior engineers should have write access, and even then, emergency manual changes should follow a formal break-glass procedure. Any changes made in such scenarios must be quickly updated in the IaC code to avoid untracked modifications causing drift.
For organisations using HCP Terraform, the Free Edition supports one policy set with up to five policies. The Standard Edition, on the other hand, offers advanced features like health assessments and integration with version control systems for policy management [19][1].
When combined with governance controls, automation ensures that no changes can bypass your approved processes.
Immutable Infrastructure and Automation
Adopting a GitOps approach ensures that all changes pass through your IaC pipeline. This method establishes a single source of truth, making it much harder for unauthorised modifications to slip through.
Scheduled automation is another key tool. For example, running automated refresh-only plans every night - triggered by workflows like GitHub Actions at 02:00 - helps detect and address drift early, before it snowballs into a bigger issue [6][18]. For critical resources, protection mechanisms such as Terraform's prevent_destroy lifecycle hook or Pulumi's protect: true option can prevent accidental deletions during automated updates [18].
David Flanagan from Pulumi highlights the importance of addressing drift promptly:
The longer drift is left unattended, the harder it becomes for automation to reconcile in a manner that can be considered safe for your organisation, SLAs, and customers happiness[18].
For near-continuous alignment, tools like the Pulumi Kubernetes Operator can be configured with a resyncFrequencySeconds as low as 60 seconds, ensuring that code and reality remain in sync [18].
Emerging technologies, including AI and machine learning, are taking drift prevention to the next level, as we’ll explore in the next section.
AI and ML for Drift Prevention
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are changing the game in drift management. These systems analyse historical data and real-time telemetry to distinguish between expected and problematic drift [1][7]. For example, an automated scaling event that changes instance counts might be flagged as expected, while an unauthorised security group modification would trigger an immediate alert.
While still evolving, these technologies are shifting the focus from merely detecting drift to actively preventing it. By establishing infrastructure baselines and monitoring for deviations in real time, AI-driven systems can alert teams to suspicious changes before they escalate into production issues. Combined with tools like PaC and RBAC, this multi-layered approach offers a strong defence against drift in UK cloud environments.
Best Practices for Drift Remediation
After putting proactive prevention measures in place, addressing drift promptly is crucial for maintaining the integrity of your infrastructure. Once drift is detected, taking swift and calculated action helps minimise disruption and ensures systems remain aligned. The right approach depends on the type of change, the resource affected, and the level of operational risk involved.
Revert, Update, or Reconcile
When dealing with drift, there are three main strategies to consider.
- Reverting involves using an IaC
applycommand to overwrite manual changes and restore your infrastructure to its defined state. This is ideal for unauthorised changes, such as opening an SSH port to 0.0.0.0/0, which could introduce security vulnerabilities [1][7]. - Updating your IaC code to reflect intentional manual changes can make sense in scenarios like emergency fixes during an incident or permanent scaling adjustments that signify a
new normal
[20][7]. - Reconciling uses a
plan-refresh-onlyapproach to update the state file without applying new code changes. This is especially useful when the infrastructure itself is correct, but the state file is out of sync, or when there are pending code changes that aren’t ready to go live [2].
| Resource Type | Remediation Mode | Approval Level | Compliance Relevance (UK) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security Groups | Automatic | None | ISO 27001 / GDPR |
| Production Databases | Approval-gated | Senior Engineer | Data Protection Impact |
| Network Routing | Manual | Infrastructure Team | Regulatory Change Tracking |
| Resource Tags | Automatic | None | Cost Allocation / Audit |
The appropriate remediation method depends on the nature of the drift and whether continuous or on-demand remediation is the better fit.
Continuous vs On-Demand Remediation
Continuous remediation automates fixes in real time or at set intervals (e.g., every 15–60 minutes), cutting down manual effort and speeding up recovery in large-scale environments. This approach works well for low-risk resources, such as security groups and tags, and is supported by policy-as-code guardrails to avoid unintended changes [20]. It also provides detailed audit logs, which are helpful for meeting ISO 27001 compliance standards.
On the other hand, on-demand remediation is manually triggered or initiated in response to specific incidents. While slower and more susceptible to human error, this method offers greater oversight, making it ideal for high-risk resources like production databases or complex networking setups [20]. Many UK organisations adopt a hybrid approach, using continuous remediation for development environments and reserving on-demand fixes for production systems during scheduled change windows.
Tailored Solutions with Hokstad Consulting

For businesses facing persistent drift issues, expert guidance can make all the difference. UK organisations can turn to Hokstad Consulting for help with DevOps transformation and custom automation solutions. Their services include building automated CI/CD pipelines, establishing policy-as-code frameworks, and developing monitoring systems tailored to UK compliance requirements, such as ISO 27001 and GDPR.
Conclusion
Infrastructure drift poses a serious challenge to security, compliance, and operational stability. Talha Tariq, CISO at HashiCorp, highlights the issue perfectly:
Drift can dramatically undercut the reliability and security benefits of IaC[5].
When manual changes bypass your infrastructure-as-code (IaC) workflows, systems deviate from their documented state. This misalignment creates blind spots, increasing the risk of data breaches, failed audits, and unplanned downtime.
The solution lies in combining the right tools, automation, and disciplined processes. Whether you're using Terraform's built-in drift detection, adopting GitOps workflows, or implementing policy-as-code frameworks like OPA and Sentinel, the goal is clear: make drift detection a continuous, automated process. Daily health checks, strict role-based access control (RBAC), and well-documented remediation procedures can turn drift from an unpredictable issue into a manageable aspect of your infrastructure lifecycle.
Key Takeaways
- IaC Repository as a Single Source of Truth: Ensure all changes go through strict GitOps and CI/CD pipelines to maintain consistency.
- Automation is Essential: Manual drift checks aren’t enough to keep up with the pace of modern cloud environments.
- Policy-as-Code Integration: Prevent non-compliant resources from being created and catch unauthorised changes before they escalate into bigger issues.
For UK businesses, maintaining audit trails and adhering to standards like ISO 27001 and GDPR is critical. A solid drift detection strategy not only ensures regulatory compliance but also helps manage cloud costs by identifying unused or over-provisioned resources. These insights can guide immediate and effective action.
Next Steps for UK Businesses
To secure infrastructure and improve operations, UK businesses should start by evaluating their current drift detection capabilities. Ask yourself:
- Are automated checks running daily?
- Do RBAC policies limit manual console access effectively?
- Is your remediation process well-documented and consistently applied?
If any of these are lacking, they should be your priority.
Take a phased approach to implementation. Begin with automated drift detection in non-production environments. Set up policy-as-code safeguards for critical resources, and gradually extend continuous remediation to lower-risk components. For production systems, approval-gated workflows can ensure a balance between agility and oversight.
For expert advice on optimising cloud costs and improving deployment reliability, visit Hokstad Consulting.
FAQs
What steps can I take to prevent drift in my Infrastructure as Code (IaC) setup?
To keep IaC drift in check within your cloud infrastructure, the first step is to store your desired state in version-controlled IaC templates. This acts as your baseline for consistency. Then, integrate automated drift detection tools, like Terraform or AWS Config, into your CI/CD pipelines. These tools help spot any mismatches between the defined state and the actual infrastructure.
During deployments, enforce strict policies and pre-conditions to maintain uniformity. For any drift that arises, automated remediation scripts can step in to fix the issues swiftly. Lastly, make it a habit to regularly review and update your IaC templates to ensure they accurately reflect changes in your infrastructure, keeping your desired state aligned with real-world operations.
What are the most effective tools for detecting IaC drift?
Detecting Infrastructure as Code (IaC) drift is essential to keep your infrastructure aligned with its intended configurations. Several tools can help automate this process effectively. Terraform, for instance, allows you to use the plan command or leverage HCP health assessments for drift detection. Similarly, AWS Config rules and Pulumi Deployments offer strong capabilities in this area.
You can also turn to policy-as-code engines like Open Policy Agent or Sentinel, which help enforce compliance while identifying drift. Platforms such as Spacelift and Harness IaCM add another layer of automation and monitoring to ensure consistency.
If you're interested in open-source options, driftctl is a standout tool built specifically for detecting and resolving IaC drift. Incorporating these solutions into your workflow ensures you can monitor and address configuration discrepancies proactively, maintaining a stable and predictable infrastructure.
Why is drift detection crucial for meeting GDPR requirements?
Drift detection is crucial for ensuring compliance with GDPR, as it keeps your infrastructure aligned with its intended configuration. It acts as a safeguard against unauthorised changes that might introduce security weaknesses, mishandle personal data, or compromise adherence to data protection standards.
By actively monitoring and addressing configuration drift, organisations can minimise the risk of breaches, maintain accurate documentation, and uphold accountability - key aspects of GDPR's strict requirements. This approach not only protects the integrity of your infrastructure but also helps secure your compliance status.
