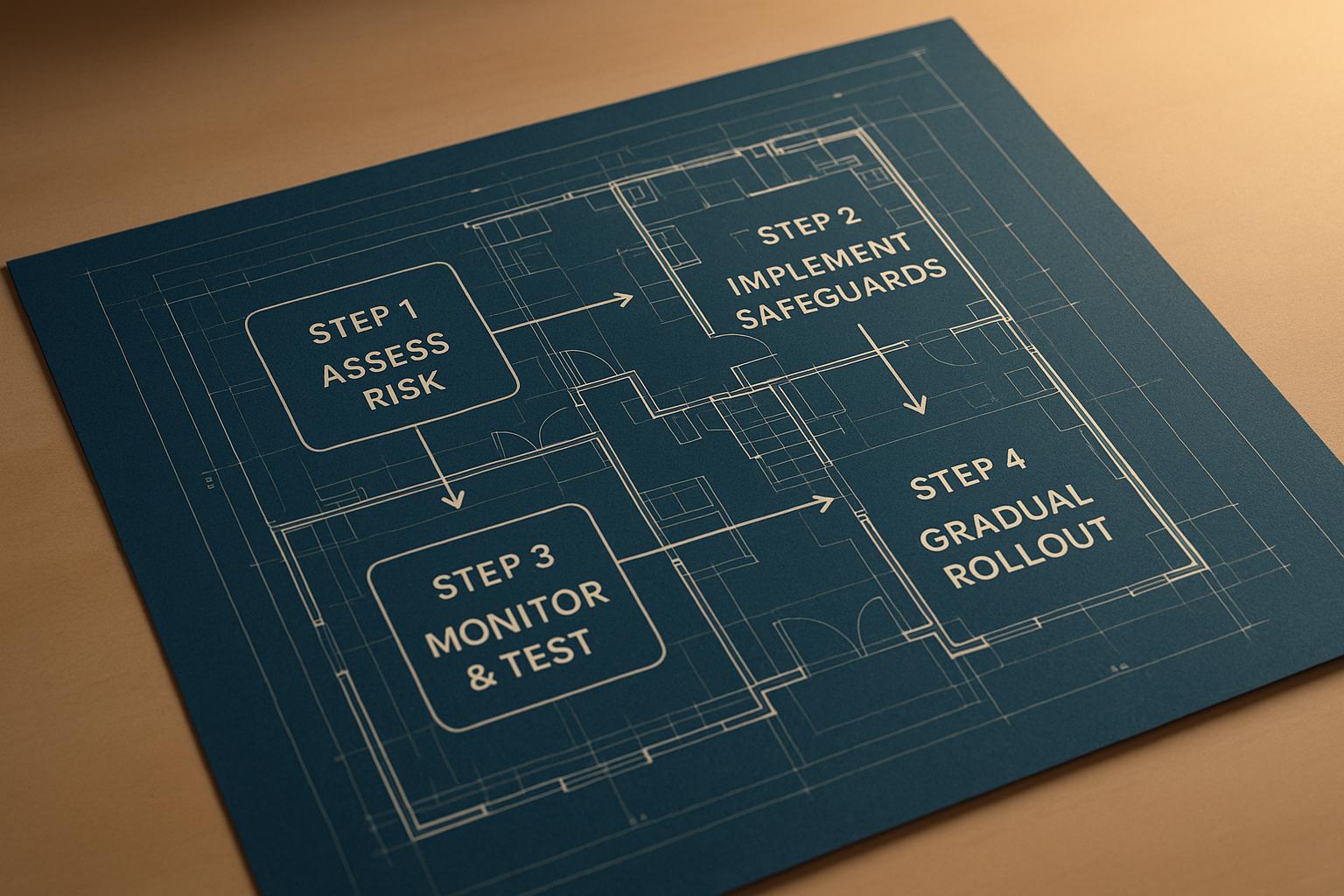
Progressive delivery pipelines allow you to release features gradually, reducing deployment risks. However, they come with their own challenges, including deployment failures, security vulnerabilities, and compliance issues. Here's how to manage these risks effectively:
- Identify Risks Early: Use failure mode analysis to map pipeline vulnerabilities and anticipate issues like configuration drift or dependency failures.
- Monitor Progressive Techniques:
- Feature Flags: Regularly audit configurations and use telemetry to detect issues across user groups.
- Canary Releases: Monitor real-time data for traffic adjustments or rollbacks.
- Blue-Green Deployments: Ensure environment consistency with quality checks during switchovers.
- Shift-Left Security: Integrate automated security checks into the pipeline to catch vulnerabilities early. Use key management services to protect secrets and enforce strong access controls.
- Best Practices: Automate rollouts, use quality gates, and deploy updates during working hours for faster responses to issues.
Tools like LaunchDarkly, Azure DevOps, and Prometheus can help streamline these processes while improving monitoring and control. For businesses in the UK, addressing these risks is critical to avoid downtime, ensure compliance (e.g., GDPR), and maintain customer trust.
Pro Tip: Gradual rollouts, combined with automated rollback mechanisms and robust monitoring, can reduce errors by up to 90% and downtime by 95%.
Reduce risk and increase developer confidence with Argo Rollouts for progressive delivery
How to Identify Risks in Progressive Delivery
Spotting risks before they escalate into major problems is key to mastering progressive delivery. Instead of waiting for issues to pop up in production, teams need to proactively identify potential trouble spots throughout their deployment pipelines. Building on the common risks outlined earlier, this section dives into effective ways to pinpoint them early.
Using Failure Mode Analysis for CI/CD Pipelines
Failure Mode Analysis (FMA) offers a structured way to examine your CI/CD pipeline and identify weak points that could disrupt rollback or roll-forward operations. This method involves a detailed review of every stage in the pipeline - from code compilation to deployment - to understand how failures could occur and what impact they might have on the delivery process [3].
Start by mapping out your entire pipeline, including build steps, testing phases, deployment processes, and rollback mechanisms. Then, evaluate what could go wrong at each stage. Pay close attention to configuration drift - when development, staging, and production environments fall out of sync - as this is a common cause of production failures. Also, scrutinise dependency management, as external services, databases, and third-party APIs can introduce risks during progressive rollouts [4].
By anticipating where failures might occur, teams can prepare automated rollback triggers, establish escalation protocols, and ensure everyone knows how to respond when issues arise. Once you've identified pipeline vulnerabilities, it's time to focus on risks tied to specific progressive delivery techniques.
Finding Risks in Feature Flags, Canary Releases, and Blue-Green Deployments
Each progressive delivery strategy comes with its own set of risks, requiring tailored detection methods. By understanding these risks, teams can implement the right monitoring tools and controls before deployment.
Feature flags can be tricky when it comes to managing multiple configurations across different user groups. The main challenge is keeping track of these variations and ensuring they don't cause issues. To catch problems early, use telemetry to link user feedback with deployment phases. This helps you quickly pinpoint which rollout group might be experiencing issues [3].
Canary releases bring another set of challenges, especially around deciding when to increase traffic or roll back changes. These decisions often rely on real-time data, making it essential to have tools that can scan logs and metrics on the fly. Without this, teams risk delays in responding to issues, which can lead to bigger problems in production [4].
Blue-green deployments pose risks related to maintaining consistency between environments during a switchover. Mismanaged keys, secrets, database states, and configuration settings can all lead to service interruptions. Beyond technical risks, there’s also an operational challenge: coordinating the switchover without losing data or causing downtime.
| Technique | Primary Risk | Detection Method |
|---|---|---|
| Feature Flags | Configuration drift across user segments | Telemetry correlation and regular flag audits |
| Canary Releases | Delayed decision-making on traffic increment | Real-time metrics scanning and automated alerts |
| Blue-Green Deployments | Environment consistency during switchover | Robust smoke testing and quality gates |
These tailored detection strategies create a foundation for integrating security measures early in the process.
Adding Shift-Left Security Practices
Shift-left security is all about addressing risks early by embedding security checks throughout the deployment pipeline. This approach ensures that software undergoes thorough verification at every stage before moving forward [4].
Automated security checks are the backbone of shift-left practices. By integrating these checks into the CI/CD pipeline, teams can catch issues early through unit tests, security scans, smoke tests, and configuration validations [4].
One critical area to manage is secrets - like passwords and API tokens - that grant access to services and applications. To avoid exposing these credentials during deployment, use a key management service. These services encrypt and store secrets securely, only injecting them at runtime when needed [5]. It’s also important to inventory all pipeline connections and treat them as potential vulnerabilities [5].
Access controls are another vital component. Regularly audit permissions to ensure only authorised users have access, and perform threat modelling to identify and address potential risks. Regularly scan and patch connections to maintain pipeline integrity [5].
Finally, use automated scanning tools to detect vulnerabilities early. These tools can flag hardcoded secrets in repositories, configuration files, and container images, giving developers immediate feedback on potential security risks. Early detection like this helps prevent issues from reaching production environments, saving time and effort in the long run.
Best Practices for Reducing Risks in Progressive Delivery
To address potential risks effectively, adopting best practices is key. Controlled, automated, and observable deployment processes help detect issues early and allow for swift action.
Controlled Rollouts with Progressive Techniques
Gradual rollouts are a smart way to limit the impact of potential failures. By introducing changes to a small group of users first, teams can validate updates before a full-scale release. For example, canary deployments direct a small portion of traffic to the new version, providing a real-world test environment. When downtime is a major concern, blue-green deployments offer a solution by maintaining two parallel environments - one live and one ready for immediate switch-over if issues arise. For even finer control, feature flags allow teams to enable or disable specific features directly within the application code, making real-time adjustments possible. Often, teams use a combination of these techniques as they gain confidence in their deployment process [6].
Automation and Quality Gates
Manual processes can be error-prone, but automation ensures consistent and repeatable deployments. In fact, automated CI/CD pipelines have been shown to reduce deployment errors by up to 90% [1]. A strong automation strategy includes quality gates, such as automated tests, security scans, and configuration checks, to catch issues early [4]. Real-time analysis of logs and metrics is also crucial for informed decision-making. Additionally, automated rollback mechanisms and Infrastructure as Code (IaC) help reduce manual errors and enable quick recovery when needed. Together, these practices create a solid foundation for reliable deployments and rapid responses.
Monitoring, Observability, and Quick Response
Effective risk management depends on robust monitoring and observability. This includes a mix of workload monitoring, alert systems, application performance tracking, and detailed logging to quickly identify anomalies [3]. Telemetry plays a vital role in linking user-reported issues to specific deployment stages, especially in environments with multiple configurations running simultaneously. Problems might surface through failed smoke tests, user feedback, or alerts from monitoring tools. When issues arise, a structured five-step response process ensures swift recovery and ongoing improvements [3]. Deploying updates during working hours, when full support teams are available, can also streamline escalation and resolution. Companies that implement these strategies as part of their DevOps approach have reported up to a 95% reduction in downtime caused by infrastructure issues [1]. This approach replaces the old deploy and hope for the best
mindset with a methodical, data-driven strategy for reliable and confident releases.
Need help optimizing your cloud costs?
Get expert advice on how to reduce your cloud expenses without sacrificing performance.
Tools and Frameworks for Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Modern progressive delivery depends on specialised platforms that can identify risks, manage rollouts, and respond quickly when issues arise.
Feature Management and Control Tools
Feature flags are one of the most effective techniques for managing risks in software delivery. Platforms like LaunchDarkly allow teams to control how and when features are exposed without requiring new code deployments. This means features can be activated gradually while their performance is continuously monitored [2].
When integrated into CI/CD pipelines, feature flags provide a reliable safety mechanism for making data-driven decisions. For instance, a fintech company might initially release a new payment feature to a small group of users, track transaction success rates, and then expand access step by step based on the results [2].
CI/CD Pipeline Tools
Platforms like Azure DevOps and GitLab automate deployments while incorporating safeguards to minimise risks. These tools support features like automated rollbacks, staged deployments, and quality gates to prevent flawed code from reaching live environments [3].
GitLab’s canary deployment approach, for example, allows teams to direct a small portion of traffic to new code versions while monitoring performance metrics. Azure DevOps offers similar features, with added integration options tailored for Microsoft ecosystems. Both platforms also include Infrastructure as Code (IaC) capabilities, which reduce human error and ensure consistent deployments [3].
To complement these deployment tools, robust monitoring solutions play a critical role in identifying and addressing risks.
Monitoring and Security Solutions
Prometheus and Datadog go beyond basic uptime monitoring, offering insights into application performance, user experience, and the impact of deployments [5].
Datadog is particularly effective at linking deployment events to system performance changes, alerting teams to any anomalies. Meanwhile, tools like Snyk integrate security checks directly into the CI/CD pipeline, automating vulnerability assessments. This shift-left
approach to security can reduce remediation costs by as much as 30% [5].
Prometheus also enables custom metric tracking, allowing teams to monitor both technical indicators (like server response times) and business-specific metrics (like conversion rates) during progressive rollouts.
Hokstad Consulting's Approach

The effective integration of these tools often requires expert guidance, and this is where Hokstad Consulting excels. They specialise in creating risk mitigation strategies tailored for UK businesses, delivering measurable results. Their clients have reported up to 75% faster deployments and a 90% reduction in errors thanks to optimised toolchains [1].
For example, Hokstad Consulting helped a UK tech startup cut deployment times from 6 hours to just 20 minutes by automating workflows that connect feature management, CI/CD, and monitoring tools. Their expertise in cloud cost engineering also ensures these tools run efficiently, often reducing cloud costs by up to 50% while improving deployment reliability [1].
Additionally, Hokstad Consulting leverages AI to predict potential deployment issues and automate responses, leading to a 95% reduction in infrastructure-related downtime. Their deep understanding of UK regulations and business practices ensures their strategies align with compliance requirements while supporting ambitious growth goals. Through a retainer model, they provide ongoing optimisation, continuously adapting tool configurations as businesses evolve [1].
Comparison Table: Progressive Delivery Risk Mitigation Techniques
Pros and Cons of Key Techniques
When choosing the right technique for managing deployment risks, UK businesses should consider their specific needs, infrastructure capabilities, and risk appetite. Each method has its own strengths and challenges. Here's a breakdown of the main approaches:
| Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Canary Releases | Limits the impact of failures; allows real-time performance tracking; enables user feedback collection before full deployment | Adds complexity to pipelines; requires strong monitoring systems; may cause delays if problems arise | Ideal for UK fintech firms aiming to test with small user groups to minimise financial risks |
| Blue-Green Deployments | Ensures minimal downtime; simplifies rollback by redirecting traffic between identical environments | Requires double the resources; less suited for detailed feature testing | Best for UK e-commerce businesses where even short service interruptions could lead to major revenue losses |
| Feature Flags | Offers granular control; supports A/B testing; allows quick feature rollbacks | Can introduce technical debt if poorly maintained; increases codebase management complexity | Useful for UK retailers experimenting with new checkout processes for a limited user group |
| Automated Rollbacks | Quickly reverts to a stable version; minimises recovery time; reduces customer impact | Needs reliable failure detection; risks reverting changes that could affect data or user experience | Critical for UK healthcare providers requiring swift action during deployment issues |
These methods provide UK businesses with tools to balance risk and operational efficiency. For instance, blue-green deployments, while resource-intensive, are indispensable for services where even minor downtime is unacceptable. On the other hand, feature flags require strict controls to prevent unauthorised access, a key concern for companies adhering to GDPR.
A practical example: A UK online banking service implemented canary releases with just 5% of its users, closely monitored transaction data, and swiftly applied automated rollbacks when issues were detected. This approach not only minimised risks but also ensured compliance with UK regulations.
By layering these techniques, businesses can create a robust risk mitigation strategy. Experts often suggest starting with canary deployments for gradual rollouts, incorporating blue-green deployments for uninterrupted service, and using feature flags for precise feature control. Automated rollbacks act as a safety net, ensuring rapid recovery from failures.
While these methods may require upfront investment, they often prove worthwhile by reducing downtime and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
Key Steps to Reduce Risks
Reducing risks in progressive delivery hinges on a mix of controlled rollouts, automation, and robust monitoring. Automation minimises manual errors by ensuring that only validated code advances through quality gates. Meanwhile, effective monitoring and observability allow teams to spot anomalies early and respond quickly. To measure the safety and efficiency of your pipeline, focus on key metrics like deployment frequency, Mean Time to Detect (MTTD), Mean Time to Recover (MTTR), change failure rate, and the success of automated rollbacks.
Adopting shift-left security practices is another essential step. Addressing vulnerabilities early - before they reach production - is not only more efficient but also significantly more cost-effective. Industry estimates suggest that resolving security issues in the early stages can be up to 30 times cheaper than fixing them post-deployment [7]. Combining proactive security measures with automated quality gates and thorough testing creates multiple layers of protection throughout the delivery process. Beyond the technical aspects, fostering a culture of deployment safety through shared ownership, regular retrospectives, and continuous learning strengthens these efforts further. Together, these practices lay a solid foundation for enhancing delivery pipelines, which can then be refined with expert consultancy.
The Role of Expert Consultancy
While technical best practices are vital, expert consultancy can accelerate the process and ensure your pipeline reaches its full potential. For many UK organisations, implementing progressive delivery pipelines demands specialised skills that may not be readily available in-house. This is where Hokstad Consulting comes in, offering extensive experience in DevOps transformation. Their proven methods have helped organisations achieve up to 75% faster deployment times and 90% fewer errors [1].
Hokstad Consulting integrates automation, CI/CD pipelines, Infrastructure as Code, and advanced monitoring solutions into every stage of deployment. Their approach not only reduces risks but also optimises operational efficiency. For instance, their strategies in cloud cost engineering and migration have enabled clients to cut infrastructure-related downtime by 95% while reducing cloud expenses by 30–50% [1]. This demonstrates that effective risk management doesn’t have to come at the expense of cost efficiency.
For UK businesses looking to adopt progressive delivery safely and efficiently, partnering with experienced consultants like Hokstad Consulting provides access to proven frameworks, state-of-the-art tools, and ongoing support. Their no savings, no fee
model ensures that investments in risk mitigation deliver tangible results.
Given the intricate nature of modern deployment environments, attempting to implement comprehensive risk mitigation strategies without expert guidance can lead to missed opportunities or inefficiencies. Partnering with professional consultants not only speeds up transformation but also ensures long-lasting improvements that continue to add value over time.
FAQs
How does failure mode analysis help identify risks in progressive delivery pipelines?
Failure mode analysis is a structured way to pinpoint where things might go wrong in a progressive delivery pipeline before they actually do. By carefully reviewing every stage of the pipeline, teams can predict potential trouble spots, like deployment glitches, integration hiccups, or performance slowdowns.
This approach helps teams rank risks by how likely they are to happen and how much damage they could cause. With this insight, they can take steps to prevent problems. For instance, they might use automated testing, set up monitoring tools, or have rollback systems ready to tackle any weak points. These measures help ensure deployments run more smoothly and reliably.
What are the benefits of adopting shift-left security in CI/CD pipelines?
Adopting shift-left security in CI/CD pipelines allows organisations to spot and tackle vulnerabilities early in the development cycle. This approach not only helps reduce the risk of costly problems down the line but also creates a more secure and dependable software delivery process. By embedding security checks during the coding and testing phases, teams can address potential issues before they escalate.
Here’s why it matters:
- Cost savings: Fixing security flaws early in development is far cheaper than dealing with them after deployment.
- Stronger teamwork: Developers, testers, and security experts collaborate from the outset, encouraging a shared focus on security.
- Quicker releases: Identifying problems early avoids last-minute delays, making the release process smoother and faster.
This forward-thinking strategy makes security a core part of development, rather than something added at the end.
How can tools like LaunchDarkly and Prometheus help manage risks in progressive delivery pipelines?
Tools like LaunchDarkly and Prometheus are essential for managing risks in progressive delivery pipelines, offering teams better control and visibility during deployments.
LaunchDarkly enables teams to use feature flags, allowing for incremental feature rollouts. This approach means new features can be tested with specific user groups before a full-scale deployment, significantly lowering the chance of widespread issues. Additionally, if a feature causes problems, it can be quickly disabled without needing a complete rollback - saving time and reducing disruption.
Prometheus, meanwhile, serves as a robust monitoring tool that delivers real-time insights into system performance and health. By gathering and analysing metrics, it helps teams spot potential problems early, such as performance slowdowns or unexpected behaviour. This proactive approach allows for timely responses, minimising any negative impact on users.
Together, these tools help teams ensure stability, improve user experience, and manage the risks of deploying changes in complex systems effectively.