Cross-platform patch management ensures all your devices - Windows, macOS, Linux, and third-party apps - stay updated from one central system. This approach boosts security, saves time, and simplifies compliance. Without it, inconsistent updates can leave your systems vulnerable to cyberattacks, as seen in breaches like WannaCry and Equifax.
Key takeaways:
- Security: Apply updates consistently to close vulnerabilities across platforms.
- Efficiency: Automate patching to save time and reduce errors.
- Compliance: Meet regulations like GDPR and PCI DSS with automated audit trails.
- Prioritisation: Focus on high-risk vulnerabilities using CVSS scores.
- Testing: Always test patches before full deployment to avoid disruptions.
Benefits of Cross-Platform Patch Management
Consistent Security Across All Platforms
Using a unified patching strategy ensures that security updates are applied consistently across all systems - whether it's Windows, Linux, macOS, cloud workloads, or mobile devices [5]. This uniformity helps plug potential security gaps that attackers could exploit to navigate through networks. When patches are deployed unevenly, an unpatched system on one platform can become a gateway for cybercriminals to access others.
Take the 2017 Equifax breach as an example. Delays in applying patches left millions of sensitive records exposed [4]. With a centralised patch management system, these risks can be mitigated by ensuring that all devices receive critical updates within set timeframes.
Adding risk-based prioritisation to the mix makes this approach even stronger. Tools that use scoring systems like CVSS allow organisations to focus on the most severe vulnerabilities, particularly in internet-facing systems, instead of trying to patch every minor issue at once [6]. By addressing the most dangerous threats first, businesses can significantly shrink their attack surface. This method also complements efforts to reduce manual work and simplify patch deployment processes.
Reduced Time and Resource Requirements
Automating patch scanning and deployment not only reduces manual workload but also minimises the chance of errors. This frees up IT teams to focus on more strategic projects [7]. With centralised visibility through a single interface, there's no need to juggle multiple tools, cutting down on unnecessary complexity and administrative burdens.
Prioritisation based on CVSS scores also helps avoid overwhelming teams with an endless list of vulnerabilities. Instead, resources can be directed towards the most critical threats. For instance, organisations can set tiered schedules - addressing high-risk internet-facing vulnerabilities within 24–72 hours while allowing up to 30 days for less critical updates. The UK Ministry of Justice, for example, requires critical patches to be applied within 3–7 days for infrastructure and up to 14 days for end-user devices [5].
Easier Compliance Reporting
Centralised patch management tools simplify compliance by automatically generating audit trails that align with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS [8]. These tools maintain a single, verifiable record of patching activities, creating an immutable audit trail [8].
By treating patch management as both a security safeguard and an operational discipline, IT teams can reduce risk, prevent downtime and maintain consistent system performance.– Datto [7]
Meeting compliance deadlines becomes much more manageable when systems can track remediation windows across platforms. For example, PCI DSS mandates that critical patches be applied within 30 days of release [4], while ISO 27001 Annex A.8.8 emphasises technical vulnerability management as a key control [8]. Automated reporting not only ensures compliance but also provides auditors with clear evidence that robust patching processes are in place, extending beyond just ticking regulatory boxes.
Smarter Patch Management: Mastering Ring Deployments, Preferred Servers & Real-Time Feedback
Best Practices for Cross-Platform Patch Management
::: @figure 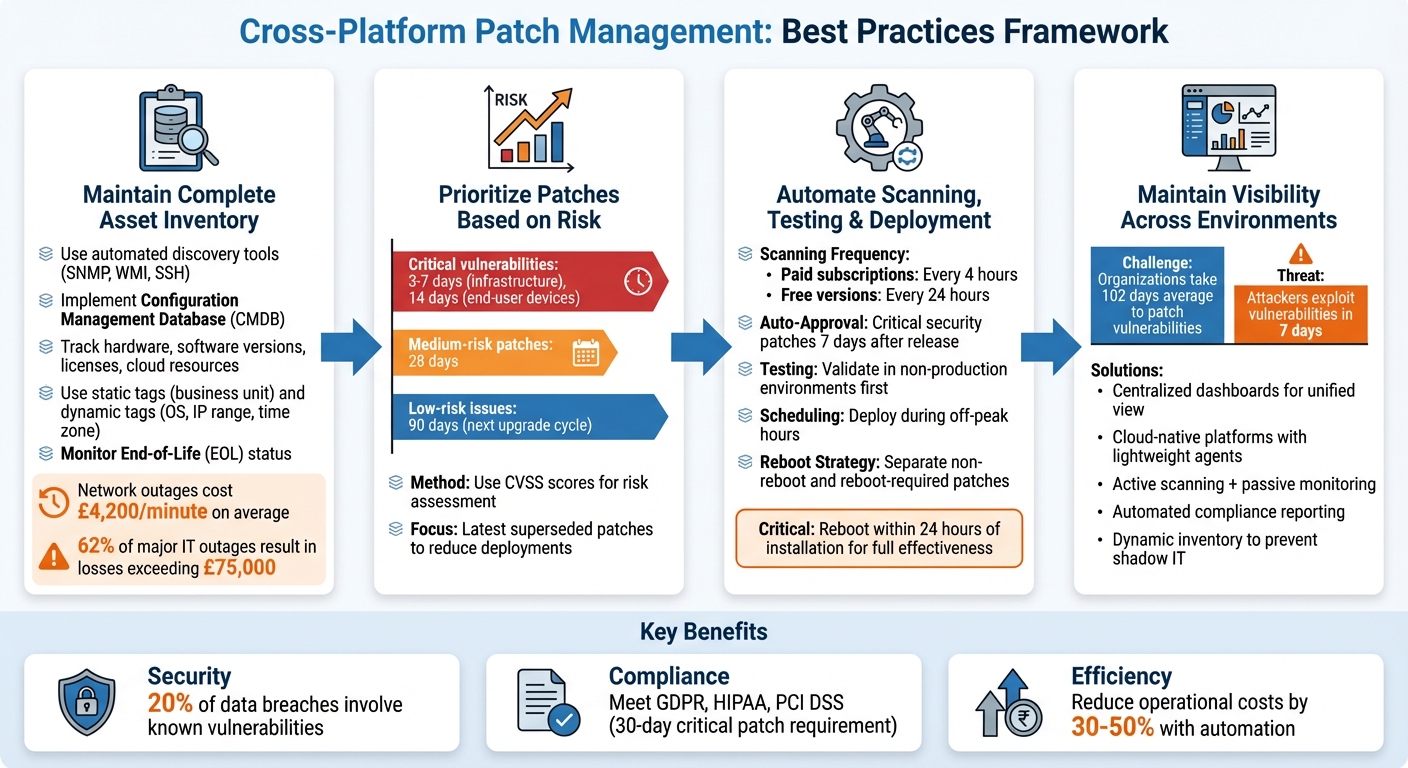 {Cross-Platform Patch Management Best Practices: 4-Step Framework}
:::
{Cross-Platform Patch Management Best Practices: 4-Step Framework}
:::
Keep a Complete Asset Inventory
Having a detailed asset inventory is the cornerstone of effective patch management. Automated discovery tools, capable of working across multiple protocols like SNMP for network devices, WMI for Windows systems, and SSH for Linux machines, can help identify all IP-enabled devices within your infrastructure.
Maintaining a Configuration Management Database (CMDB) as your centralised source of information is invaluable. It allows you to track hardware, software versions, licences, and cloud resources in one place. This is especially important for hybrid environments that span physical servers, virtual machines, cloud instances, and containers. Use static tags to categorise assets by business unit and dynamic tags to group systems by factors like operating system, IP range, or time zone [2].
The stakes are high - network outages can cost an average of £4,200 per minute, and a 2021 survey revealed that 62% of major IT outages resulted in losses exceeding £75,000, with 15% surpassing £750,000 [9]. Keeping tabs on the End-of-Life (EOL) status of your assets through your inventory helps you prioritise upgrades before vendors stop providing security patches. This ensures your systems don’t become unmanageable vulnerabilities.
Prioritise Patches Based on Risk
Not every patch demands the same level of urgency. A tiered approach works best: aim to patch critical vulnerabilities within 3–7 days for infrastructure and within 14 days for end-user devices. Medium-risk patches can be addressed within 28 days, while low-risk issues can wait for the next scheduled upgrade cycle, as long as it’s within 90 days [5].
This strategy hinges on risk advisory teams assessing both the likelihood of exploitation and the potential impact on your business. Focusing on the latest superseded patches also reduces the number of individual deployments needed [2]. Once priorities are set, automation can streamline the process even further.
Automate Scanning, Testing, and Deployment
With a solid asset inventory and risk-based prioritisation in place, automation can take your patching efforts to the next level. Automated scans, running as frequently as every 4 hours for paid subscriptions or every 24 hours for free versions, help identify missing updates and vulnerabilities across your systems [2]. Centralised management tools can cover everything from on-premises servers to edge devices and virtual machines in multiple cloud environments, ensuring consistent patching throughout [11].
Auto-approval rules can simplify deployments. For instance, you might automatically approve critical security patches seven days after they’re released [3][11]. However, testing remains a must. Always validate patches in non-production environments using patch groups before rolling them out to production systems [3][10]. Schedule maintenance windows during off-peak hours, and automate tasks like shutting down applications before patching and validating systems afterward [11].
To minimise downtime, separate patch jobs based on whether they require a reboot. Deploy non-reboot patches first, then handle those that do require restarts. Keep in mind that a patch isn’t fully effective until the asset is rebooted - ideally within 24 hours of installation [2]. For environments using immutable infrastructure, automate the creation and testing of new machine images instead of patching existing systems directly [10].
Need help optimizing your cloud costs?
Get expert advice on how to reduce your cloud expenses without sacrificing performance.
Common Challenges in Cross-Platform Patch Management
Handling Compatibility Issues
Managing compatibility issues in cross-platform patching can be tricky and demands thorough planning. These problems often show up as installer crashes, corrupted files, or failed connections to update servers [2]. Sometimes, patching one system can unintentionally disrupt other components or third-party libraries that are integrated into enterprise applications [5].
Another common hurdle is that generic patches may not work on language-specific applications unless they meet local requirements [2]. Older, unsupported legacy systems add to the challenge since they can’t accept standard patches and need alternative approaches to mitigate risks [5].
A practical way to tackle this is through phased testing. Start by testing patches on a small, representative group of devices before rolling them out across the board [2]. Additionally, set up patch jobs with rollback functionality so you can quickly restore operations if conflicts arise [2]. If a vendor patch causes instability or is unavailable, consider using virtual patches or temporarily disabling the vulnerable feature as a short-term fix [5]. As the Ministry of Justice advises: The default is for patches to be applied as soon as possible. You should not normally delay patching because of concerns about possible issues with the patches themselves
[5].
Reducing Downtime
Downtime during patching can be expensive, both financially and operationally. Minimising these interruptions is critical for maintaining system resilience. One way to achieve this is by separating non-reboot and reboot-required patches, which helps reduce system downtime [2].
Scheduling maintenance windows is equally important. Define specific Patch Windows
- for instance, a six-hour window during non-critical hours - so updates don’t interfere with essential operations [2][3]. Dynamic tagging can also help by categorising assets according to time zone, operating system, or business function (e.g., web servers versus databases), ensuring patches are applied in the right environment at the right time [2][3]. For cloud systems using immutable infrastructure, it’s often better to update the machine image and redeploy it rather than patching the existing systems, which can lead to configuration drift [3].
Maintaining Visibility Across Hybrid Environments
Monitoring patch status across on-premises servers, cloud platforms, and remote devices presents its own set of challenges. On average, organisations take 102 days to patch a vulnerability, while cyber attackers can exploit new vulnerabilities in as little as seven days [12].
Centralised dashboards can provide a clear, unified view of patch compliance across all environments. Cloud-native platforms with lightweight agents that communicate via HTTPS eliminate the need for VPNs or complex on-premises setups, making it easier to monitor off-network devices [12]. Pair active scanning with passive monitoring to identify unmanaged hosts or appliances that could otherwise go unnoticed [16]. Additionally, maintain a dynamic, automated inventory of hardware and software assets to ensure no shadow IT
or unmanaged cloud instances escape patching [14][15]. Automating compliance reports can also help track patch status for auditors, giving you a clear view of which systems are falling behind [13]. This kind of visibility is essential for effective patch management across diverse platforms.
Tools and Services for Cross-Platform Patch Management
Choosing Patch Management Tools
When it comes to executing a seamless patch management strategy, having the right tools makes all the difference. The ideal patch management tool should support multiple operating systems - Windows, macOS, and Linux - through a single console. Why? Because juggling separate tools for each platform often leads to inefficiencies and unnecessary complexity. Beyond OS coverage, a good tool should also handle third-party application updates. This means automatically detecting and deploying patches for widely used software like Adobe, Chrome, and Slack across all platforms. For example, modern solutions like Automox manage updates for over 580 third-party applications and oversee more than 1,250,077 endpoints for customers worldwide [1].
To simplify intricate tasks, look for features like advanced scripting (using PowerShell or Bash) and automated prioritisation based on CVSS scores. These capabilities are particularly important given that known vulnerabilities account for 20% of all data breaches [7]. Centralised visibility is another must-have, allowing you to monitor patch statuses across on-premises, cloud, and remote environments from a single dashboard. Cloud-native, agent-based tools are especially efficient - they eliminate the need for on-premises hardware and can often be set up and operational in under 30 minutes [1]. Features like time-zone-aware scheduling, reboot management, and custom maintenance windows add even more flexibility, ensuring patches are deployed with minimal disruption.
For organisations needing more than just tools, consulting services can provide the strategic direction required to align patching with larger infrastructure goals.
Consulting Services by Hokstad Consulting

Effective patch management isn’t just about the tools - it’s about integrating updates into your organisation’s broader infrastructure and DevOps strategies. This becomes especially important in hybrid environments, where consistency across on-premises and cloud systems is crucial. Hokstad Consulting offers expertise in DevOps transformation and automation, helping organisations streamline patch management across complex setups like hybrid and multi-cloud environments. Their approach often leads to significant cost reductions, with operational expenses cut by 30–50%, all while improving deployment efficiency.
For businesses managing hybrid environments - combining on-premises servers with platforms like AWS or Azure - Hokstad Consulting provides tailored solutions to unify operations. They specialise in integrating patch management into existing CI/CD pipelines, ensuring that golden images
are patched upstream before being deployed to production. Whether you need ongoing DevOps support or assistance with a smooth, zero-downtime cloud migration, their services are designed to adapt to your specific needs. Plus, their No Savings, No Fee
model guarantees you’ll only pay when measurable results are delivered.
Conclusion
Managing patches across multiple platforms is essential for keeping IT systems secure, compliant, and running smoothly. With one in five breaches linked to the exploitation of known vulnerabilities [7], it's clear that delaying updates can have serious consequences. High-profile incidents from the past serve as stark reminders of the risks involved.
To address these challenges, implementing key best practices is crucial. Start with a thorough asset inventory to ensure no device is overlooked. Use CVSS scores to prioritise patches based on risk, and automate tasks like scanning, testing, and deployment. Automation not only reduces the chance of human error but also ensures consistency, freeing IT teams to focus on more strategic initiatives. Additionally, having centralised visibility across hybrid and cloud environments is vital to avoid leaving any endpoint unprotected.
For organisations dealing with complex hybrid systems or integrating patching into DevOps workflows, expert advice can make a big difference. Hokstad Consulting offers specialised services in DevOps transformation and automation. They help businesses embed patch management into CI/CD pipelines, cut operational costs by 30–50%, and achieve zero-downtime migrations - all while maintaining consistent patching across diverse infrastructures. This approach supports a seamless and efficient patching strategy tailored to modern IT environments.
Effective patch management is about finding the right balance between security and operational demands. By leveraging automation, focusing on risk-based priorities, and seeking expert guidance when needed, organisations can close security loopholes, comply with regulations like GDPR and PCI-DSS, and ensure the stability that today’s businesses rely on.
FAQs
What are the security benefits of cross-platform patch management?
Cross-platform patch management plays a key role in strengthening security by ensuring operating systems and third-party applications across various devices are updated promptly. This approach helps to tackle vulnerabilities before they can be exploited, lowering the likelihood of cyberattacks.
With a unified view of patch compliance, identifying and addressing security gaps becomes far more straightforward. Automated patching guarantees that no device is overlooked, eliminating potential weak spots that could jeopardise the entire network. This is critical for creating and maintaining a secure and resilient IT infrastructure.
What are the advantages of automating patch management?
Automating patch management brings a host of benefits to the table. For starters, it speeds up the deployment of updates and ensures they’re rolled out consistently across all systems. This reduces the chance of vulnerabilities caused by delays or human mistakes. Plus, by cutting down on the need for manual work, it lowers the risk of errors and allows IT teams to focus their energy on more strategic, high-value tasks.
On top of that, automation plays a critical role in bolstering an organisation’s security. By ensuring essential patches are applied without delay, it helps guard against cyber threats. It’s not just about security either - this streamlined approach improves operational efficiency and helps organisations stay aligned with security standards and best practices.
What’s the best way to prioritise which patches to apply first?
To manage patches effectively, organisations should focus on a risk-based strategy. This means evaluating vulnerabilities based on their severity, how likely they are to be exploited, and the importance of the systems they affect. Start by using a recognised scoring system, like CVSS, to gauge the risk level. Then add context, such as whether the vulnerability is currently being exploited, if the system is exposed to the internet, or if it supports essential services.
Patches addressing high-risk issues - like actively exploited vulnerabilities on critical systems - should be prioritised and applied immediately. Lower-risk updates can be handled during routine patch cycles. Automated tools can simplify this process by assessing risks, tagging affected systems, and creating prioritised patch lists.
Hokstad Consulting provides support in building and implementing these frameworks, ensuring they align with your existing DevOps workflows and cloud strategies. This approach enables smooth patching across diverse environments, including Windows, Linux, and containerised systems.
