Cloud pricing models directly impact business scalability and cost efficiency. Misaligned pricing structures lead to wasted resources and higher expenses. Here’s a quick summary of key findings:
- Idle Resources: 83% of container costs come from unused resources, with overprovisioning accounting for 54% of this waste.
- Data Transfer Costs: Cross-Availability Zone (AZ) traffic makes up 50% of transfer expenses, affecting 98% of organisations.
- GPU Costs: AI workloads have driven GPU expenses to 14% of compute costs.
- Commitment Discounts: Only 29% of organisations fully utilise commitment-based savings on eligible spend.
- Arm-Based Instances: These now account for 18% of compute budgets, offering 40% better price-performance.
To optimise costs, businesses should align workloads with the right pricing models. Pay-As-You-Go suits unpredictable needs, Reserved Instances cut costs for stable tasks, and Spot Instances save up to 90% on flexible workloads. Combining these strategies can reduce expenses by 50–90%.
UK businesses can further improve scalability by auditing cloud usage, right-sizing resources, and colocating workloads. Tools like autoscaling and AI-powered recommendations can help minimise waste and enhance performance.
The article explores these strategies and highlights real-world examples of cost-saving practices.
::: @figure 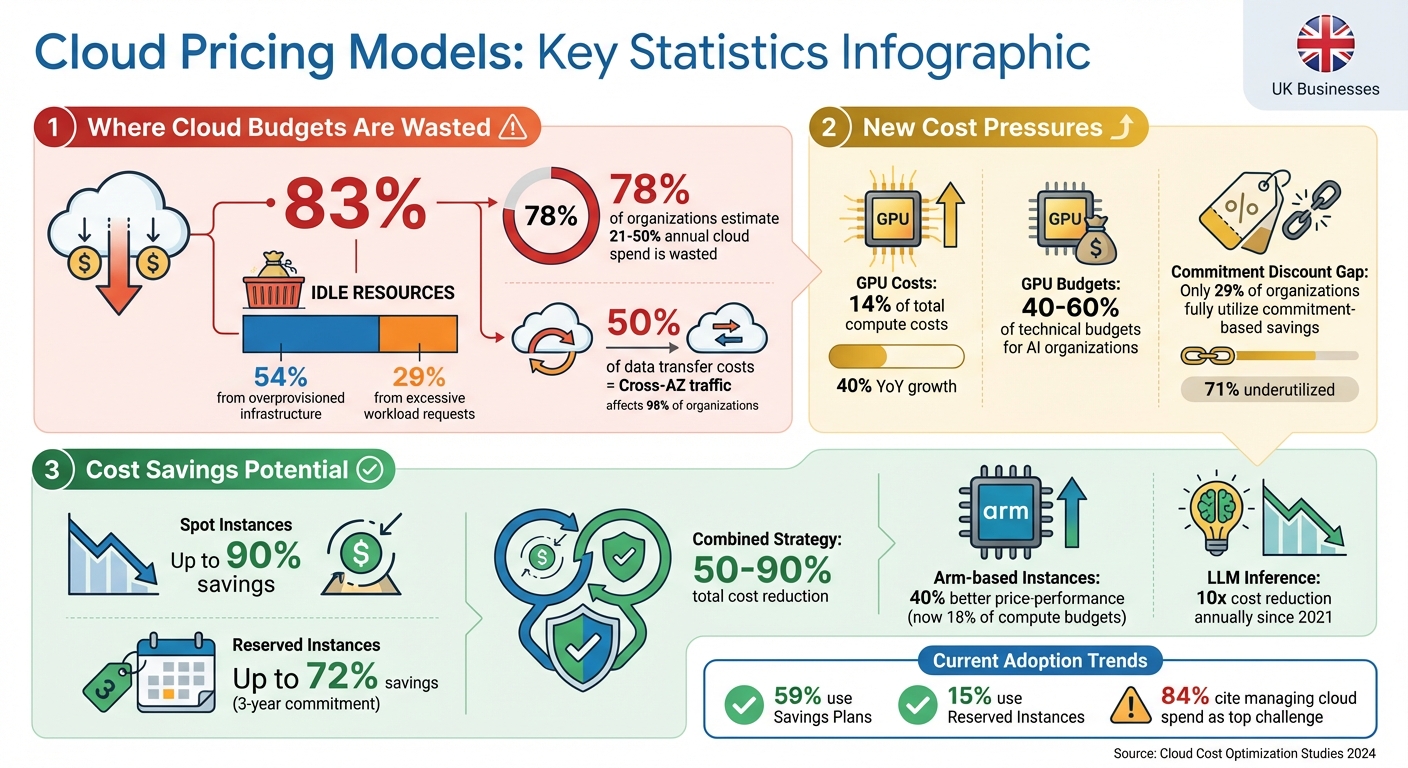 {Cloud Cost Waste Statistics and Optimization Opportunities 2024}
:::
{Cloud Cost Waste Statistics and Optimization Opportunities 2024}
:::
Main Cloud Pricing Models and How They Scale
Pay-As-You-Go: Flexibility for Changing Workloads
Pay-As-You-Go (PAYG) pricing transforms fixed infrastructure costs into variable expenses, meaning businesses only pay for the resources they actually use [5]. This approach works well for unpredictable workloads, short-term projects, or instances of sudden spikes in demand [3]. It's a default choice for highly elastic services like serverless functions and auto-scaling groups [3][6].
The cloud allows you to trade fixed expenses (such as data centres and physical servers) for variable expenses, and only pay for IT as you consume it.- AWS Whitepaper [5]
While PAYG offers flexibility, it comes with higher hourly rates compared to committed pricing. However, shutting down cloud instances when they're idle can slash costs by 70% or more compared to running them continuously [5]. Tools like AWS Cost Explorer can help UK businesses analyse hourly usage patterns and identify when PAYG or Spot deployments make sense [3]. For instance, serverless APIs like Azure Functions start at £0.16 per million executions (about $0.20 at the current exchange rate) [7]. That said, predictable workloads might benefit more from Reserved Instances for greater savings.
Reserved Instances: Lower Costs for Stable Workloads
Reserved Instances (RIs) are ideal for reducing costs on always-on
workloads. By committing to a longer-term plan, such as three years, UK businesses can save up to 72% on Windows and Linux virtual machines compared to PAYG pricing [8]. Pairing Azure Hybrid Benefit with a three-year RI commitment can push savings up to 80% [7].
However, RIs trade flexibility for these savings. Since reservations are region-specific, UK organisations need to carefully weigh their commitment against potential migration needs or drops in demand [8][10][3]. For example, ABN AMRO managed to cut its Azure costs by over €1 million per month by using Azure Reserved Virtual Machine Instances, as noted by Hans De Kruif, Platform Engineer and Azure Cost Manager [8].
For organisations mindful of cash flow, Azure offers monthly payment options for reservations without additional fees, though exchange rates (e.g., GBP/USD) can affect costs [8][9]. The best strategy is to reserve only the minimum predictable workload while using PAYG or Spot Instances for handling variable peaks [4][3]. For workloads that can handle interruptions, Spot Instances may provide even better flexibility and cost-efficiency.
Spot Instances: Using Spare Capacity
Spot Instances allow businesses to tap into unused cloud capacity at discounts of up to 90% compared to On-Demand pricing [11][12][13]. They are perfect for stateless, flexible, or interruptible workloads like big data, containerised applications, CI/CD pipelines, and high-performance computing [11]. On average, Spot Instances face interruptions less than 5% of the time [3].
The NFL, for instance, has saved over $20 million since 2014 by using Amazon EC2 Spot Instances to manage its complex regular-season scheduling, according to Mike North, NFL VP of Broadcasting Planning [11]. Similarly, Lyft cut monthly costs for specific workloads by 75% with just four lines of code to integrate Spot Instances [11]. Delivery Hero also reported a 70% cost reduction by running Kubernetes clusters on Spot capacity [11].
Providers can reclaim Spot capacity with little notice - AWS gives a 2-minute warning, while Google Cloud offers just 30 seconds [11][13]. To make the most of Spot Instances, applications must be designed for graceful shutdowns. UK firms operating in the London region (eu-west-2) can benefit from Spot pricing while meeting data sovereignty requirements. To improve capacity availability, it's wise to remain flexible with instance families and sizes and to distribute workloads across multiple Availability Zones [11].
What Recent Studies Show About Scalability Trends
Measuring Scalability: Performance vs. Cost
Balancing performance and cost has become central to scalability, as recent studies highlight. Metrics like latency, throughput, IOPS (input/output operations per second), and cost-efficiency are often used to measure scalability. However, the challenge is steep: 84% of organisations identify managing cloud spend as their biggest hurdle [14]. On top of that, 78% estimate that 21% to 50% of their annual cloud spend goes to waste [15].
Managing cloud spend remains the top challenge for 84% of organisations, with 59% now maintaining dedicated FinOps teams up from 51% in 2024.
– Saurabh Deochake, SentinelOne Inc. [14]
Pricing models for Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) and Container-as-a-Service (CaaS) are heavily influenced by CPU usage, which directly impacts cost-efficiency [2]. However, containerisation can also lead to inefficiencies, with resource misallocations becoming a noticeable problem [1]. To avoid unnecessary expenses - like overprovisioning, which can double costs - organisations are increasingly adopting right-sizing
practices. This involves aligning allocated resources closely with actual workload demands [14].
Combining Pricing Models for Better Results
Strategic use of pricing models has proven to save organisations between 50% and 90% on costs [14]. A layered approach - using Reserved Instances for predictable workloads and Spot Instances for more variable, burstable needs - has been especially effective.
Currently, 59% of organisations use Savings Plans, offering flexibility, compared to just 15% relying on traditional Reserved Instances [1]. For example, Legal and General reduced their total cost of ownership by 50% by migrating core workloads to Azure SQL Database while maintaining compliance with FCA security standards [17]. Similarly, Cipher International adopted Azure Virtual Desktop, using a pay-only-when-in-use
model. This approach not only cut costs but also enabled efficient global remote work [16].
Another area where expenses add up is Cross-Availability Zone traffic. This affects 98% of organisations, with such traffic accounting for up to 50% of total data transfer costs [1]. A practical solution is to colocate related resources within the same Availability Zone, provided high availability requirements allow it [1]. These strategies are laying the groundwork for organisations to integrate AI and automation, further improving scalability.
How AI and Automation Improve Scalability
AI tools are becoming increasingly essential for refining scalability, especially when paired with cost-saving strategies. For instance, the cost of Large Language Model (LLM) inference has dropped by about 10x annually since 2021, thanks to hardware advancements and techniques like model quantisation [14]. However, GPU compute remains a significant expense, making up 40–60% of technical budgets for AI-driven organisations. By 2024, GPU instances accounted for 14% of total compute costs [1].
Autoscaling is another game-changer, dynamically adjusting resources to meet demand. A standout example is Lloyds Banking Group, which enhanced performance by shifting 80 machine-learning models to Vertex AI, cutting mortgage income verification times from days to just seconds [17]. Additionally, ARM-based instances, such as AWS Graviton, offer up to 40% better price-performance than traditional x86-based options. Notably, spending on ARM-based instances doubled between 2023 and 2024 [1].
Despite these advancements, cluster idle time remains a persistent issue. Development teams often struggle to predict resource needs for new applications accurately [1]. AI-powered tools are stepping in to solve this by analysing historical usage data and recommending the optimal VM sizes, helping to minimise overprovisioning and unnecessary costs.
Cloud Pricing Models: Consumption, Serverless & Subscription
Need help optimizing your cloud costs?
Get expert advice on how to reduce your cloud expenses without sacrificing performance.
How UK Businesses Can Improve Scalability with Cloud Pricing
Recent studies highlight how UK businesses can better scale by aligning their cloud pricing strategies with specific workload demands.
Matching Pricing Models to Your Workload
The key to cost-effective scaling is understanding your workload patterns. For predictable and steady workloads, options like Reserved Instances or Savings Plans are ideal. For example, Azure Reservations can cut costs by up to 72%, while Azure Savings Plans offer up to 65% off for fixed hourly commitments [18]. On the other hand, workloads that fluctuate or require burst capacity are better suited to pay-as-you-go models or Spot Instances, which allow you to adjust resources dynamically without long-term contracts.
When scaling, choose between horizontal and vertical approaches based on your systems. Horizontal scaling works best for distributed microservices or web front-ends, with costs increasing more predictably. Vertical scaling, often used for legacy databases or monolithic applications, can lead to sharp cost increases as performance thresholds are reached. If your business relies on Windows Server or SQL Server, leveraging the Azure Hybrid Benefit could save up to 36% on Windows Server and 28% on SQL Server compared to standard pricing [18].
Tracking Costs and Scalability Metrics
Keeping a close eye on costs and scalability metrics is essential to avoid overspending. Regular monitoring ensures that resources match actual demand. A cross-functional Cloud Operations team can align technical decisions with financial goals. For instance, in 2021, the UK Home Office managed to cut its cloud expenses by 40% by fostering collaboration between architects and developers and implementing centralised oversight [19].
Event-based scaling offers more precision than traditional triggers like CPU or memory usage. For example, using metrics such as message queue length - enabled by tools like KEDA for Kubernetes - ensures scaling happens only when necessary. To prevent excessive scaling actions caused by temporary spikes (known as flapping
), setting cooldown periods is crucial [20]. Additionally, design strategies like queue-based load levelling and throttling can help manage sudden traffic surges, making them particularly useful for businesses facing seasonal demand or compliance-driven workloads.
Working with Hokstad Consulting for Cloud Cost Reduction

Hokstad Consulting offers expertise in cloud cost engineering and DevOps transformation. Their services include resource optimisation, automated CI/CD pipeline development, and cost-efficient migration strategies tailored to various hosting environments. They focus on reducing cloud expenses by 30–50% while improving deployment times and ensuring compliance with UK regulations, such as GDPR and data sovereignty.
Their No Savings, No Fee
model provides a low-risk solution for businesses aiming to optimise cloud spending. Whether you need help with infrastructure monitoring, performance tuning, or combining pricing models, Hokstad Consulting delivers personalised support to help UK organisations scale effectively without unnecessary costs.
Matching Cloud Pricing with Scalability Goals
Key Takeaways from the Studies
Cloud inefficiencies remain a pressing concern. A staggering 83% of container spending is wasted on idle resources - split between 54% from overprovisioned cluster infrastructure and 29% from excessive workload requests. On top of this, 50% of data transfer costs stem from cross-availability zone traffic [1].
Commitment-based discounts also see limited adoption. Only 29% of organisations purchase enough to cover more than half of their eligible spend [1]. However, there’s a noticeable shift towards flexibility, with 59% of companies opting for Savings Plans, compared to just 15% using traditional Reserved Instances [1].
When it comes to hardware choices, Arm-based instances emerge as a cost-effective option, delivering up to 40% better price-performance than x86-64 alternatives [1]. Meanwhile, GPU spending has soared by 40% year-on-year, now representing 14% of total compute costs [1]. These findings highlight the need for a focused and strategic approach to cloud management.
Practical Steps to Take
To tackle inefficiencies, start by auditing your current cloud usage. This will help you pinpoint areas of waste. Actions like right-sizing instances, enabling autoscaling for workloads and cluster infrastructure, and colocating resources within the same availability zone (where feasible) can make a big difference [1].
As the Microsoft Azure Well-Architected Framework aptly puts it: The goal of cost optimizing scaling is to scale up and out at the last responsible moment and to scale down and in as soon as it's practical
[20].
For UK organisations looking for expert help, Hokstad Consulting offers a No Savings, No Fee
model. Their tailored solutions focus on reducing cloud costs by 30–50% while enhancing deployment efficiency. With expertise in areas like container optimisation, event-based scaling, and pricing strategies, they ensure businesses can grow without overspending.
FAQs
What are the best ways to reduce cloud costs caused by idle resources?
To cut down cloud costs caused by idle resources, businesses can take some straightforward measures. Begin by spotting and turning off unused virtual machines, containers, or any other resources that are no longer in use. On top of that, using automation tools can be a game-changer. These tools monitor resource usage in real time and adjust capacity as needed, helping you steer clear of both over-provisioning and underusing resources.
By staying on top of your cloud setup, you can keep costs in check without compromising on performance or scalability.
What benefits do Arm-based instances offer compared to traditional x86-64 options?
Arm-based instances offer some standout benefits compared to traditional x86-64 options. For starters, they can provide up to 40% better price-to-performance ratios, making them an appealing option for businesses looking to optimise costs. On top of that, they boast greater energy efficiency, which can lead to substantial savings on cloud infrastructure costs - in some cases, cutting expenses by as much as 80%.
These instances shine in scenarios where scalability and performance optimisation are key, enabling businesses to do more while using fewer resources. This not only enhances operational efficiency but also helps reduce their environmental footprint.
How do AI and automation improve cloud scalability and reduce costs?
AI and automation have become essential for managing cloud resources more efficiently while keeping costs in check. With AI-powered tools, businesses can analyse usage trends and adjust resources automatically to match demand. This prevents both overprovisioning (paying for unused capacity) and underutilisation (not having enough resources), ensuring companies only spend on what they actually need.
Automation adds another layer of efficiency by integrating cost management directly into workflows. For example, policies can be set to optimise cloud spending without requiring manual intervention. These technologies also support smarter workload placement and cost-effective load balancing, which helps reduce operational costs without sacrificing performance. By leveraging AI and automation, organisations can scale their cloud infrastructure in a way that’s both efficient and economical.
