Buffering kills streams. Did you know 78% of viewers abandon a video after just two buffering events? Or that a two-second start-up delay can increase drop-offs by 51%? These are just some of the challenges video platforms face as streaming now accounts for 70% of online traffic. The solution? Smarter CDN strategies powered by real-time analytics.
Here’s what matters most:
- Key metrics like start-up time, rebuffering ratio, and cache hit ratios directly affect viewer satisfaction and retention.
- Real-time monitoring helps spot and resolve issues before they impact users, especially during live events.
- Multi-CDN setups improve reliability and performance by distributing traffic across providers.
- AI tools predict demand, optimise caching, and ensure smooth playback even during surges.
- Cost control is achievable through refined caching, smarter routing, and efficient bitrate management.
CDNs aren’t just about speed - they’re about delivering a seamless experience while managing costs. Whether it’s live sports or on-demand series, optimising these networks with data-driven insights is vital to keeping viewers engaged. Let’s dive into how it’s done.
::: @figure 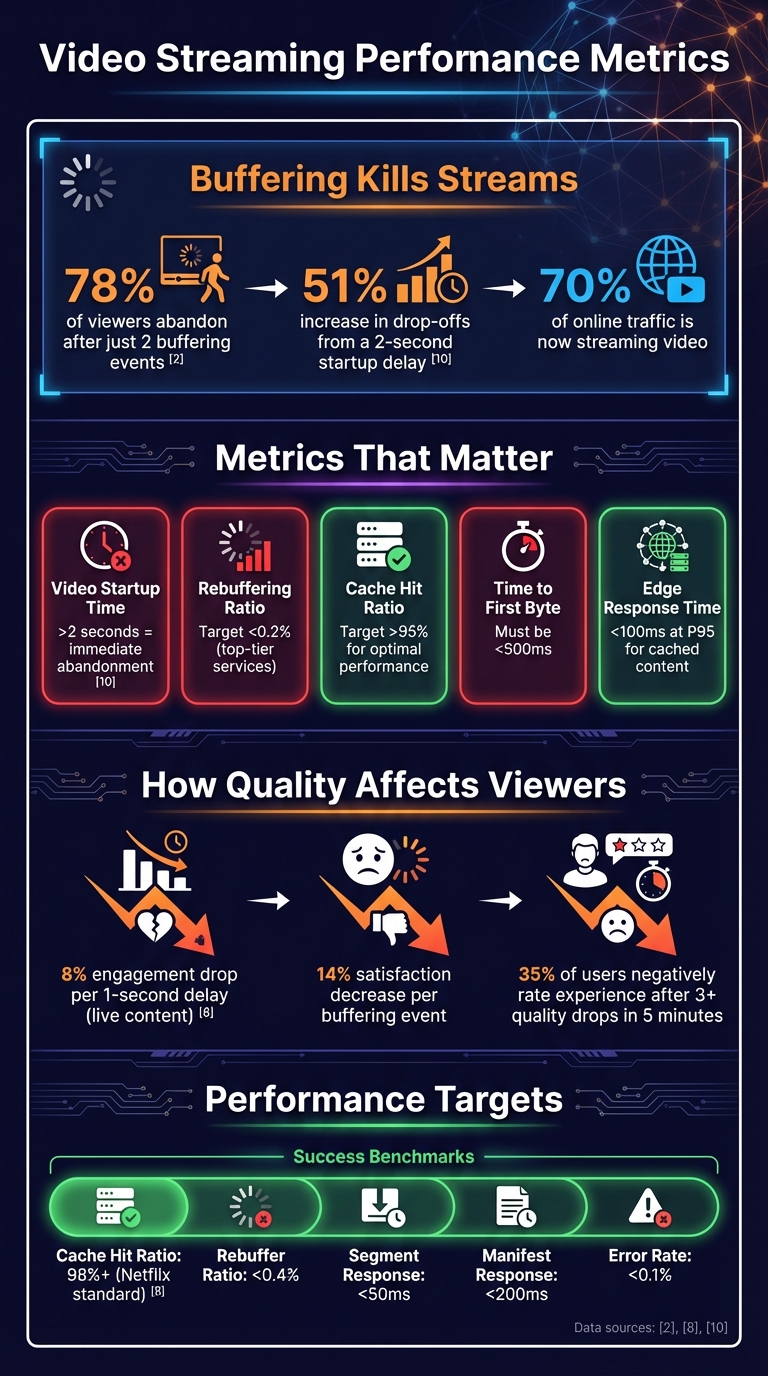 {Video Streaming Performance Metrics and Impact on Viewer Retention}
:::
{Video Streaming Performance Metrics and Impact on Viewer Retention}
:::
Key Metrics for Video Streaming Analytics
Core Metrics Explained
Metrics are the backbone of making informed decisions in video streaming. One key metric is Video Startup Time (or Join Time), which tracks the delay between hitting play and seeing the first frame. If this time exceeds two seconds, viewers often abandon the stream immediately [1]. For live content, like sports or breaking news, even a one-second delay can reduce engagement by up to 8% [8].
Another crucial factor is the Rebuffering Ratio, which measures the percentage of watch time lost to buffering. Just two buffering incidents can drive away 78% of viewers, and satisfaction drops by 14% with every buffering event [1]. Top-tier streaming services aim to keep buffering ratios below 0.2% [8].
Bitrate Switching Events track how often the Adaptive Bitrate (ABR) system adjusts video quality. While ABR prevents complete interruptions, frequent quality drops frustrate viewers. More than three quality reductions within five minutes lead 35% of users to negatively rate their experience [1]. Similarly, Cache Hit Ratio (CHR) reveals how efficiently content is delivered from edge servers. A CHR above 95% ensures lower origin server loads and faster response times [6].
Latency metrics, such as Time to First Byte (TTFB) and edge response time, directly influence startup speeds. TTFB exceeding 500ms harms user perception, while cached content should target response times under 100ms at the 95th percentile (P95) [6][8]. Lastly, Playback Failures measure errors that disrupt streaming, like failed starts or mid-stream crashes. Analysing these separately can help identify issues like DRM handshake errors, manifest corruption, or CDN routing problems [1][7].
A practical example comes from a Wimbledon OTT service, which reduced buffering during initial playback. This cut latency from six seconds to just 900ms, boosting repeat viewership by 18% [1].
Together, these metrics provide a solid foundation for both immediate troubleshooting and long-term performance reviews.
Real-Time vs Historical Analytics
Real-time analytics provide insights with a latency of under 20 seconds [7]. They monitor metrics like Current Concurrent Viewers (CCV), active buffering percentages, and immediate playback errors. This data allows for instant actions, such as load balancing, alerts for high error rates, or failover responses when cache hit ratios drop below 85% [6][8]. Real-time monitoring is especially critical for live events, where every second counts.
On the other hand, historical analytics compile data over longer periods, from minutes to days or more. These analyses help identify patterns, establish benchmarks, and investigate past issues. For example, one major subscription VOD platform used historical data to uncover an 8% session failure rate during a high-profile series launch. The root cause? Regional DRM handshake errors tied to specific device firmware. By adjusting CDN configurations based on geography, the failure rate dropped below 1%, saving the company millions in potential lost revenue [1].
Both real-time and historical analytics serve distinct yet complementary roles. Real-time monitoring addresses immediate problems, while historical data helps prevent future ones. Segmenting metrics by region can reveal ISP bottlenecks or under-resourced edge nodes [8]. Tracking P95 latency, rather than averages, highlights the experience of the slowest 5% of users - those most likely to churn [6][9]. Combining Quality of Service (QoS) stats with Quality of Experience (QoE) feedback offers a clearer picture of how technical performance affects viewer satisfaction [1].
These insights are critical for shaping strategies in areas like CDN caching, multi-CDN deployment, and AI-driven performance improvements.
Setting Up Real-Time Monitoring and Analytics Tools
Selecting Analytics Tools
To keep your video streaming services running smoothly, real-time monitoring is a must. It allows you to catch and address performance issues before they escalate. By using real-time log streaming, you can track key metrics like time-taken, sc-status, and x-edge-result-type almost instantly after each request. This quick feedback loop helps prevent problems that could lead to viewer frustration or abandonment [13][14].
A critical tool in this process is Common Media Client Data (CMCD). Developed by WAVE, CMCD enables media players to send client-side Quality of Experience (QoE) data - such as buffer starvation (bs), buffer length (bl), and session ID (sid) - directly to your CDN through HTTP headers or query strings. This provides a more complete picture by connecting backend infrastructure data with what users are actually experiencing [12].
For data handling, tools like Amazon Kinesis Data Streams are ideal for managing high-speed data ingestion. From there, you can use serverless functions like AWS Lambda to process logs, store metrics in time-series databases such as Amazon Timestream, and visualise insights with platforms like Grafana or Amazon CloudWatch Dashboards [12][13][14].
When choosing analytics tools, look for those that integrate seamlessly with your video players via APIs or SDKs. They should support real-time data ingestion and allow you to filter data by device type, location, and streaming format [8][12]. Combine this with client-side monitoring to capture real-user data (RUM), such as video decoding health and buffering events. One key metric to track is the Zero-Impact-Rate
- the percentage of sessions without buffering or errors. This is a valuable benchmark for customer satisfaction [3].
Once your tools are in place, be sure to configure alerts to detect and respond to anomalies quickly.
Configuring Real-Time Alerts
Setting up an effective alerting system requires a two-tiered approach: Warning
alerts for early signs of performance issues and Critical
alerts for major disruptions [6]. For instance, you might configure a critical alert if 5xx errors exceed 0.1% of requests in a five-minute window or if the cache hit ratio for segments falls below 85% [6][15]. Warning alerts could trigger when P95 response times go over 200ms or cache hit ratios drop below 90% [6].
Here’s a quick overview of suggested thresholds:
| Metric | Warning Threshold | Critical Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| Cache Hit Ratio (Segments) | < 90% [6] | < 85% [15] |
| Error Rate (5xx) | > 0.01% [6] | > 0.1% over 5 mins [6] |
| Response Latency (Manifests) | > 200ms [6] | > 500ms [15] |
| Response Latency (Segments) | > 50ms [6] | > 200ms [15] |
To avoid unnecessary alerts, establish baselines during normal operations. This helps you distinguish between genuine issues and random fluctuations. You can also use composite alarms, which only activate when multiple related conditions occur together, reducing alert fatigue [15][11]. Keep an eye on origin request volumes, as a sudden spike of 30% or more could indicate cache inefficiency or a surge in content popularity [15].
Whenever possible, automate your responses. For example, set up 30-second health checks on backup origins and trigger failovers after two consecutive failures [15]. Use CloudWatch Events to automate these failovers, freeing up your team to focus on critical tasks [11]. Additionally, track latency by Autonomous System Number (ASN) to pinpoint whether performance issues are linked to specific internet service providers [13].
Optimising CDN Caching and Edge Strategies
Cache Parameter Configuration
Fine-tuning your cache settings is essential to control costs and improve the viewer experience. With video expected to make up over 82% of global IP traffic by 2025, inefficient caching can cause origin server loads and bandwidth costs to skyrocket - by as much as 300% [2]. The trick lies in tailoring Time-to-Live (TTL) values to different content types.
For video segments (like TS or m4s files), set TTLs aggressively - 24 hours or more. These files are immutable, meaning they don’t change after creation, so caching them for extended periods poses no risk [18]. On the other hand, HLS or DASH manifests need much shorter TTLs. For live streams, aim for TTLs of 5 seconds or less, ideally no longer than half your segment duration, to keep playlists up-to-date [3][18]. If you’re delivering personalised ad-inserted manifests, set the TTL to 0 seconds to avoid showing one viewer’s ads to another [18].
Equally important is refining your cache keys. Strip out session tokens, user-specific cookies, and irrelevant query parameters to reduce cache fragmentation and maximise reuse [2][17]. Enabling automatic query string sorting ensures requests like ?id=1&user=a and ?user=a&id=1 are treated as identical [17]. These simple adjustments can significantly boost your Cache Hit Ratio (CHR), with top performers aiming for 98% or more [2].
Consider deploying an Origin Shield, a caching layer that consolidates multiple edge requests into a single origin request. This reduces the load on your origin server and improves analytics accuracy by centralising egress data [16][18]. For error responses, set short negative caching TTLs (5–120 seconds) to prevent prolonged exposure to stale error states during failures [3][17].
Once your caching strategy is in place, focus on refining your edge architecture to further minimise latency.
Edge Server Efficiency
The layout of your edge servers can make or break the viewer experience. A two-second delay in video start-up can increase abandonment rates by 51% [4], making strategic deployment of edge servers a top priority. Instead of relying solely on general geographic coverage, choose edge node locations based on your audience’s specific demographics [18].
Adopt a hierarchical caching structure, with edge tiers located closest to users, mid-tier regional caches for deeper storage, and an Origin Shield to protect your origin servers [2][3][18]. Enable partial cache sharing to cut down latency for viewers watching the same content simultaneously [5].
Leverage edge functions for tasks like ad stitching, tokenisation, and subtitle selection, while maintaining high cache hit ratios for core video assets [2]. Align keyframes across different bitrates to avoid buffering issues during Adaptive Bitrate (ABR) switching [4].
Continuously monitor edge performance using metrics such as Time-to-First-Frame (TTFF), rebuffer ratios (aiming for below 0.4%), and cache hit ratios - target 95%+ for video segments and 90%+ for ad segments [4][6]. For cached content, ensure response latency stays under 100 ms at the 95th percentile, with segment requests specifically under 50 ms [6].
Using Multi-CDN Architectures for Better Performance
Benefits of Multi-CDN Setups
A multi-CDN architecture helps mitigate the risks associated with relying on a single provider. It distributes traffic more effectively, enhancing streaming performance and reducing the likelihood of outages [23, 24, 26]. Another advantage is improved regional performance. Since different CDNs perform better in certain regions, routing users based on local peering and latency ensures an optimised experience for viewers [25, 26]. This approach becomes particularly valuable during massive live events, where a single CDN might struggle to handle traffic spikes. By combining the bandwidth of multiple CDNs, these setups can manage petabyte-scale demands [24, 25].
Multi-CDN is an approach for video delivery at high scale, driven by the need of more aggregated capacity, increased resiliency or better performance.
– Achraf Souk, Solutions Architect, AWS [20]
Dynamic traffic steering is another benefit. It uses real-time metrics like start-up times, buffering rates, and average bitrates to allocate viewers across CDNs effectively [24, 26]. To maintain smooth playback and avoid rebuffering, session stickiness is critical. This technique ensures that a viewer remains connected to the same CDN that successfully delivered their first segment [23, 26]. For instance, CloudFront’s 60-second DNS TTL allows for quick rerouting of traffic when needed [21].
A practical example of this strategy is Amazon Prime Video’s use of a multi-CDN architecture in 2018. They managed their global video-on-demand service by analysing sessions without rebuffering, fatal error rates, and time-to-first-frame. Their findings showed that 12% of titles accounted for 90% of playbacks. This insight allowed them to optimise caching strategies for both high-demand and less popular content [22].
Once performance is stabilised, it’s essential to integrate consistent analytics across all CDNs to fine-tune delivery further.
Analytics Integration Across Multiple CDNs
To maximise the benefits of a multi-CDN setup, monitoring practices across providers must be unified. One way to achieve this is by configuring each CDN to include a custom X-CDN header in responses. This allows player-side SDKs to automatically identify and report which CDN delivered each segment [10]. With this setup, performance data can be segmented by CDN, ISP, region, and device type, making it easier to identify and resolve bottlenecks [22].
A monitoring harness can be used to consolidate logs and APIs from different CDNs into a single, standardised framework. This simplifies troubleshooting and ensures consistent metrics across providers [23]. Combining client-side SDKs with synthetic probes is also key. While Real User Monitoring (RUM) reflects actual user conditions, synthetic probes are valuable for testing cold cache behaviour and verifying playlist accuracy before users are affected [7, 23, 25].
Consistency across CDNs is equally important. Aligning settings like token validation, TTL configurations, and purge policies helps prevent playback errors during CDN switches [19]. It’s also crucial to maintain steady traffic on each CDN to keep caches warm and ensure they can scale quickly when needed. Lastly, routing tables should be updated frequently - sometimes as often as every few seconds - to respond swiftly to any changes in CDN performance [22].
Need help optimizing your cloud costs?
Get expert advice on how to reduce your cloud expenses without sacrificing performance.
AI-Driven Optimisation and Adaptive Transcoding
AI for Predictive Optimisation
Artificial intelligence is reshaping how video content is delivered through CDNs by predicting demand before it even occurs. By analysing historical viewership trends and real-time data, machine learning models can forecast which content will gain popularity. This enables CDNs to distribute assets to strategic edge servers ahead of time, ensuring smoother delivery [24]. For instance, Netflix uses dynamic cache eviction strategies to maintain edge cache hit rates above 98% during peak times [27]. Similarly, Twitch employs advanced chunk prefetching for major live events, ensuring the first 5–10 segments of a stream are readily available at the edge. This allows the platform to manage over 6 million concurrent viewers during events [2].
AI also plays a key role in detecting anomalies, such as unexpected latency or quality drops, flagging these issues automatically [1]. Additionally, algorithms evaluate and optimise delivery paths by considering factors like user location, device type, and real-time network performance. This allows for automated rerouting when problems arise [24]. For live sports, DAZN has adopted pre-chunking and pre-fetching techniques, which have reduced video start-up times by 38% during high-demand UEFA matches [27].
While predictive optimisation enhances delivery efficiency, adaptive transcoding ensures consistent video quality throughout the streaming experience.
Adaptive Transcoding for Quality Control
To complement predictive strategies, adaptive transcoding ensures viewers enjoy high-quality video even when network conditions fluctuate. This involves creating multiple renditions of a video at different quality levels. CDNs then generate master manifest files, such as .m3u8 for HLS or .mpd for DASH, which include metadata for all available streams [25]. This is particularly crucial, as studies show that 78% of viewers will abandon a video after encountering just two buffering interruptions [1].
Technologies like QVBR (Quality-Defined Variable Bitrate) encoding dynamically adjust bitrates based on the complexity of the content. High-motion scenes receive more data, while simpler scenes use less, optimising bandwidth usage. Tools such as VMAF, PSNR, and SSIM are commonly used to benchmark compression efficiency and fine-tune encoding settings [26]. Aligning keyframes across all bitrate tiers is also essential, as misaligned keyframes can lead to buffering issues in adaptive bitrate streaming [4].
A growing trend is edge AI transcoding, which moves the transcoding process closer to the user by leveraging edge nodes. This allows for real-time adjustments based on Quality of Experience (QoE) scores. Configuring your CDN to support Accept-Ranges: bytes for seeking and partial content fetching, along with setting appropriate Cache-Control headers for manifests, can further reduce reload churn and enhance the viewing experience [4].
Working with Hokstad Consulting for Custom CDN Solutions

Custom CDN Strategies
Hokstad Consulting specialises in crafting tailored CDN strategies by conducting thorough, data-driven audits. These audits dive deep into performance metrics and cost structures, examining elements such as bitrate tier configurations and geographic traffic patterns. This analysis pinpoints inefficiencies in video delivery, paving the way for customised solutions. By aligning these strategies with real-time analytics, Hokstad ensures each optimisation is rooted in measurable performance improvements.
In the UK, they consider the diverse network environments found in urban and rural areas when deploying edge caching nodes. Adaptive caching strategies are used to position content closer to viewers, guided by regional traffic data. This approach is particularly effective in addressing differences across ISPs and local network conditions, ensuring consistent performance.
For clients transitioning from single-CDN to multi-CDN setups, Hokstad adopts a phased migration approach. This begins with an in-depth audit, followed by the step-by-step integration of additional providers, with constant performance monitoring. Their routing systems dynamically direct traffic to the best-performing CDN in real time, improving both speed and reliability. By upgrading protocols to HTTP/2, QUIC, and implementing CMAF, they achieve streaming latency of under three seconds. These optimisations not only enhance performance but also contribute to lowering operational costs, a topic explored further in the next section.
Cost Reduction with Performance Improvements
Hokstad Consulting places equal emphasis on cost efficiency alongside performance gains. Their team identifies ways to cut bandwidth usage without sacrificing visual quality by analysing encoding ladders and bitrate configurations. For high-volume streamers, even minor adjustments can translate into significant savings, especially with CDN rates as low as £0.003 per GB (around £3 per TB).
They bring additional value by leveraging regional delivery insights during CDN contract negotiations, helping clients secure more favourable pricing terms. Automated alerts are used to monitor provider performance, ensuring traffic can be rerouted instantly if standards drop. Furthermore, they develop AI-powered machine learning algorithms that analyse real-time network conditions and user behaviour. These tools optimise bitrate selection and buffer management, ensuring resources are used efficiently across the delivery network. This combination of cost-conscious strategies and advanced technology ensures clients benefit from both savings and superior service quality.
Tomas Bacik - CDN Challenges of HTTP-based Low Latency Live Streaming Delivery
Conclusion
Getting CDNs right for video streaming analytics is a big deal for platforms where even small performance hiccups can drive viewers away. Keeping key metrics in check - like high cache hit ratios, minimal buffering, and quick start-up times - makes all the difference in keeping audiences engaged [8][2].
Real-time monitoring takes things a step further by shifting the focus from fixing problems after they happen to preventing them in the first place. When you combine Quality of Service metrics with Quality of Experience data, you get a fuller picture - not just of technical performance, but also how viewers actually feel about their experience. Automated alerts for things like cache misses or latency spikes mean you can jump on issues before they snowball into bigger problems.
These quick fixes pave the way for more advanced optimisation. For example, AI-powered predictive tools and adaptive transcoding can fine-tune performance. Machine learning can forecast content surges and adjust caching strategies on the fly, while edge-based transcoding ensures viewers get the best possible quality for their connection. Multi-CDN setups add another layer of reliability, offering better routing options and protection against failures.
And let’s not forget the financial angle. Poorly optimised CDNs can drive up origin server loads and bandwidth costs. On the flip side, smarter caching not only cuts expenses but also boosts overall performance.
Whether you're scaling up a streaming platform or bracing for a surge in traffic, the formula stays consistent: focus on the right metrics, keep improving, and rely on trusted tools and strategies to balance performance with costs. By nailing CDN optimisation through accurate metrics, proactive monitoring, and cutting-edge techniques, you’ll keep your viewers happy and engaged.
FAQs
How does real-time monitoring enhance video streaming performance?
Real-time monitoring plays a key role in improving video streaming by spotting and fixing potential problems before they affect the viewer's experience. By keeping an eye on crucial metrics like latency, cache hit ratios, and ad response times, it helps ensure smoother playback with fewer interruptions or buffering.
This forward-thinking method not only keeps the quality of service consistent but also boosts viewer satisfaction and makes network operations more efficient. It’s a vital part of delivering a hassle-free streaming experience for audiences.
What are the advantages of using a multi-CDN setup for video streaming?
A multi-CDN setup brings several advantages to video streaming. By spreading traffic across multiple CDNs, it helps minimise latency and ensures smoother playback, even during peak usage times. Reliability gets a boost thanks to redundancy - if one CDN faces a problem, others can step in without disrupting the service.
On top of that, a multi-CDN system leverages real-time data to smartly direct traffic to the most efficient network. This improves performance and delivers viewers a consistently high-quality streaming experience.
How can artificial intelligence improve video streaming and help reduce costs?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming video streaming by boosting performance and cutting costs. One way it achieves this is through real-time analytics. AI continuously monitors streaming activity, spotting issues like bottlenecks and making quick adjustments to ensure playback stays smooth. This means viewers enjoy a seamless experience, and resources are used more efficiently.
AI also plays a key role in refining video encoding. By analysing the complexity of the video content and the devices viewers are using, AI can adjust compression dynamically. This keeps visuals sharp while reducing the amount of data needed. On top of that, AI-powered caching predicts what content viewers are likely to watch and pre-loads it closer to their location. This reduces bandwidth costs and cuts down on delays.
These advancements not only improve the viewing experience but also help businesses save money - especially those running large-scale, global streaming platforms.
