Zero downtime is critical for businesses handling high traffic and global users. Multi-cluster Kubernetes solves this by distributing workloads across independent clusters, ensuring uninterrupted service even during failures or updates.
Key takeaways from this case study:
- Problem: Single-cluster setups face scaling limits, risk downtime during updates, and struggle with performance under heavy traffic.
- Solution: Multi-cluster architecture isolates workloads, improves redundancy, and allows safe testing without affecting production. Tools like ArgoCD, Terraform, and Cloudflare streamline deployments and traffic management.
- Results: Companies reduced downtime from hours to minutes, improved scalability, and cut costs by optimising resources.
This approach ensures reliable operations, faster updates, and better performance for global users.
The Problem: Scaling and Reliability Challenges
Infrastructure Bottlenecks
The single-cluster setup hit its scalability ceiling. Even the largest AWS-managed Kubernetes control plane instances maxed out, limiting scalability to around 1,500 nodes and handling up to 700,000 requests per minute before performance started to degrade [3]. Ram Vennam from Solo.io summed it up perfectly:
Once a cluster grows, every hidden networking edge case emerges... Performance stalls, security boundaries blur, and the failure domain covers your entire company[6]
Applications with high resource demands competed for limited CPU and memory, leading to noisy neighbour
problems that hurt the performance of other workloads [7][5]. Adding to the strain, European users faced slow response times because the cluster was hosted in a US region [5]. These constraints made the system more vulnerable to downtime during heavy deployment periods.
High Risk of Downtime
Each deployment felt like a roll of the dice. Routine rolling updates caused 502 NGINX errors because pods were terminated before load balancers updated, leaving requests routed to shutting-down processes [8]. Upgrading critical components, such as the Container Network Interface, required in-place changes that were fraught with risk and hard to execute without disrupting production [3]. A single misstep - like a configuration error by one team - could cascade into a platform-wide outage, affecting all tenants and multiplying the impact [6].
Deployment and Resource Management Inefficiencies
Running a monolithic cluster meant that any infrastructure change affected the entire customer base [3]. In-place upgrades required extensive planning and testing but still carried risks that were hard to justify [6]. The business found itself stuck in a cycle where each new customer pushed the infrastructure closer to its breaking point, leaving no room for further growth [6].
The Solution: Implementing Multi-Cluster Kubernetes
Designing the Multi-Cluster Architecture
To tackle their scaling challenges, the engineering team at monday.com, led by Alon Shirion, restructured their infrastructure by breaking a single monolithic cluster into multiple identical clusters. Each of these clusters hosted the same microservices, which helped isolate the impact of infrastructure changes and resolved the performance bottlenecks they faced at 700,000 requests per minute [3]. For simplicity and organisation, every cluster was assigned a unique code name, making it easier to manage and monitor the entire setup [3].
This new design also allowed for infrastructure A/B testing. For example, one cluster could experiment with new configurations - such as different instance types or CNI versions - without risking the stability of the entire system [3]. If a test cluster encountered issues, production traffic remained unaffected. To facilitate this, the team used Cloudflare for traffic management and ArgoCD for GitOps-based delivery. Deployments were handled via ApplicationSets, ensuring microservices stayed synchronised across all clusters [3].
Automating Deployments and Updates
With the shift to a multi-cluster approach, automation became a necessity to handle the complexity of distributed systems. The team relied on Terraform for infrastructure provisioning and Cloudflare load balancer rules to streamline updates. Standardised Helm charts were used for deployments, reducing the chances of conflicts [3][10]. Through ArgoCD's ApplicationSets, they managed deployments across all clusters from a single repository, using the App of Apps
pattern to handle dependencies efficiently [3].
Alon Shirion highlighted the benefits of this approach:
ArgoCD enables us to manage deployments across multiple clusters... reducing cluster initialisation time to under 1 hour[3].
To ensure quick recovery from issues, they set DNS Time-to-Live (TTL) to just 60 seconds, enabling near-instant rollbacks during traffic shifts [9]. Before fully transitioning to a new cluster, the team mirrored 100% of live traffic to the new setup using service mesh capabilities. This allowed thorough testing without impacting users [9].
Setting Up Monitoring and Alerting Systems
To complement these automated processes, the team established robust monitoring systems to maintain visibility and quickly resolve any issues. They used Datadog to implement cross-cluster alerts, which helped detect version drift - a frequent indicator of failed deployments [3]. The system worked by comparing expected pod counts in each namespace against the actual counts for each version. If discrepancies persisted for more than two hours, an alert was triggered to flag the issue [3].
Consistent naming conventions and tagging across resources made it easy for engineers to drill down from a regional overview to specific cluster details [3]. Additionally, the team ran external health checks as CronJobs. These checks regularly pinged health endpoints across all clusters and triggered webhooks if any became unreachable, providing an early warning system for potential problems before users experienced disruptions [11].
Multi-cluster, multi-apps, multi-value deployments using Argo CD Application Sets - Kostis Kapelonis
Need help optimizing your cloud costs?
Get expert advice on how to reduce your cloud expenses without sacrificing performance.
Results: Zero Downtime and Improved Scalability
::: @figure 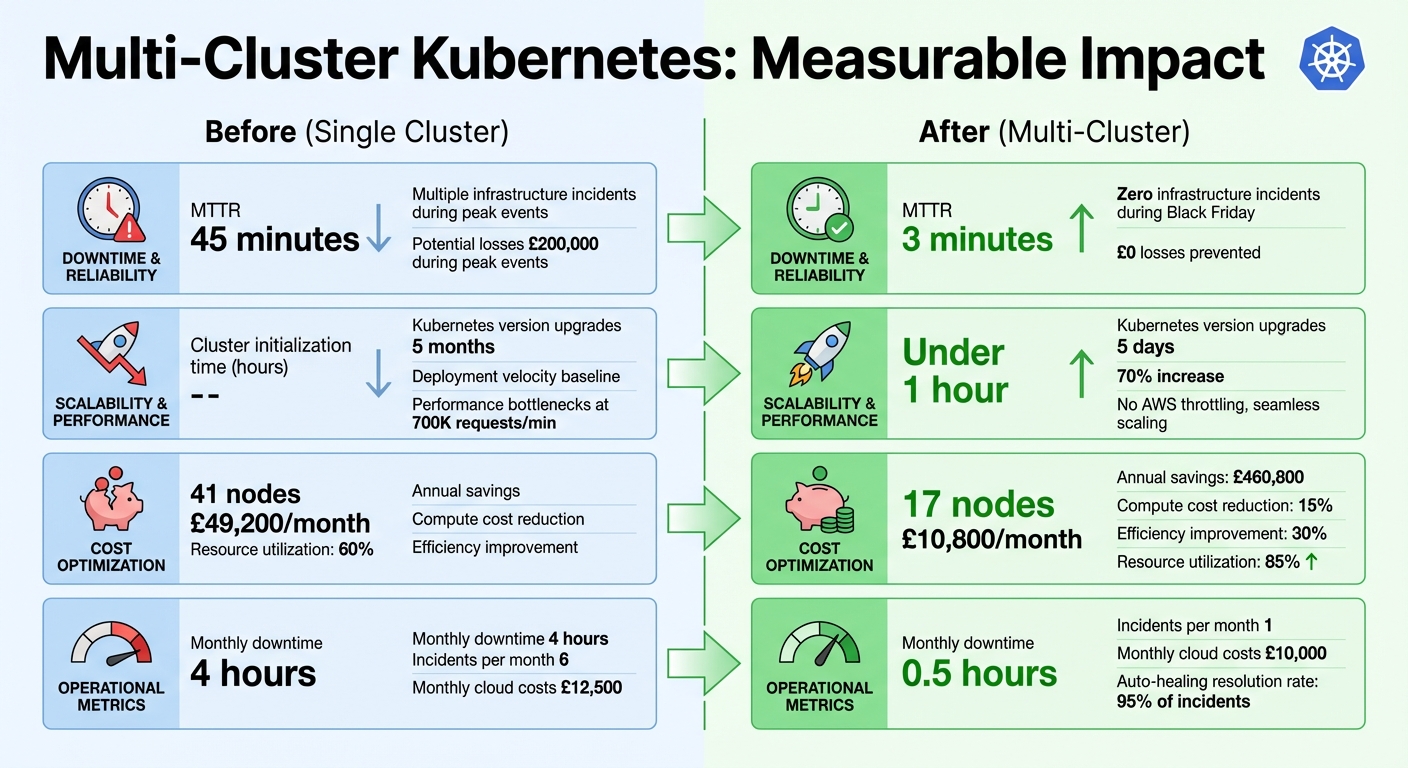 {Multi-Cluster Kubernetes Results: Before vs After Implementation}
:::
{Multi-Cluster Kubernetes Results: Before vs After Implementation}
:::
Zero Downtime During Operations
The multi-cluster architecture tackled the issues of downtime and resource inefficiencies head-on, ensuring uninterrupted service even during critical updates. By employing strategies like kubectl drain and blue-green deployment, the team successfully eliminated downtime, cutting MTTR from 45 minutes to just 3 minutes [12][13][14].
One standout example comes from an e-commerce platform that experienced its first-ever incident-free Black Friday. Their CTO remarked, For the first time in our company's history, we had zero infrastructure incidents during our biggest sale. That's a direct result of this migration
[12]. This achievement not only safeguarded operations but also prevented losses of nearly £200,000 compared to prior peak events [12]. Such results demonstrate how this approach bolstered performance under intense demand.
Better Scalability and Performance
The upgraded architecture proved its strength by managing heavy traffic without triggering AWS throttling. This eliminated bottlenecks and ensured seamless scalability [3].
Ada Support Inc. experienced similar benefits when migrating seven clusters to Amazon EKS between 2022 and 2024. Deployment velocity surged by 70%, while Kubernetes version upgrades, which once took 5 months, were completed in just 5 days [14]. Mike Gozzo, CPTO of Ada Support Inc., highlighted this transformation:
Using Amazon EKS, we have much more time to develop and improve product capabilities to deliver a high-quality customer experience[14].
Cost Savings Through Optimisation
With scalability improvements came notable cost reductions. Ada Support Inc.'s multi-cluster model cut compute costs by 15% and boosted efficiency by 30%. By right-sizing their clusters from 41 nodes to 17, they reduced monthly expenses from £49,200 to £10,800, saving approximately £460,800 annually [14][15].
Automated scaling and resource optimisation also played a key role, ensuring businesses only paid for what they used. One platform reported that 95% of incidents were resolved automatically through effective auto-healing configurations [12].
These financial gains aligned perfectly with broader objectives, supporting enhanced customer experiences and operational efficiency.
Conclusion: Lessons Learned and Best Practices
Key Lessons from the Implementation
The journey towards achieving zero downtime highlighted one thing above all: solid architectural planning is non-negotiable. While stateless workloads can be migrated relatively easily, stateful systems like databases require more advanced strategies, such as replication using tools like PostgreSQL or Velero [2][9]. This shift in mindset - from treating infrastructure as delicate pets
to viewing it as replaceable cattle
- was transformative. As Kay James from Gravitee.io aptly put it:
Organizations now talk of 'treating clusters as cattle, not pets.' This approach results in improved operational readiness and increased availability[5].
The choice of architecture also played a pivotal role. Replicated architectures proved ideal for ensuring high availability and scaling globally, while split-by-service architectures excelled in scenarios demanding strict isolation and compliance [5]. Ultimately, the decision boils down to your specific priorities - whether that’s seamless failover or independent scaling for services.
Best Practices for Zero Downtime
To safeguard against failures, it’s crucial to replicate control plane components - such as the API server, scheduler, and etcd - across at least three failure zones [16]. This redundancy ensures your infrastructure can withstand outages without disruption. Distributing workloads geographically also reduces latency for users in distant regions [4][1], enhancing performance across the board.
The numbers speak for themselves. Organisations that implemented multi-zone architectures reported significant improvements: monthly downtime dropped from 4 hours to just 0.5 hours, resource utilisation increased from 60% to 85%, and monthly cloud expenses fell from £12,500 to £10,000. Incident rates also plummeted from 6 to just 1 per month [5].
By following these practices, companies can set a strong foundation for operational reliability and efficiency.
How Hokstad Consulting Can Help

Achieving these outcomes requires expertise in DevOps and cloud optimisation. Hokstad Consulting offers tailored solutions for seamless cloud migrations with zero downtime. Their approach focuses on reducing cloud costs by 30–50% through automated CI/CD pipelines and resource efficiency. Beyond deployment, they provide continuous infrastructure monitoring to maintain performance over time. Whether you’re exploring public, private, or hybrid cloud options, Hokstad’s customised strategies ensure measurable results. Plus, their pricing model means you only pay based on the savings they deliver.
FAQs
How does using multi-cluster Kubernetes improve reliability and minimise downtime?
Multi-cluster Kubernetes helps improve reliability by distributing workloads across several clusters. This reduces the chances of a single point of failure disrupting services. If one cluster encounters an issue, the others continue functioning, keeping services available without interruption.
With tools like automated failover and workload redistribution, businesses can significantly cut downtime during unexpected problems. This setup also strengthens disaster recovery efforts, allowing for quicker and automated responses to failures. It’s particularly useful for organisations managing complex systems or operating in multiple locations.
This kind of infrastructure is well-suited for mission-critical applications, where maintaining uptime is non-negotiable. By spreading workloads and preparing for potential issues, multi-cluster Kubernetes ensures operations run smoothly, even under challenging circumstances.
What are the key tools for effectively managing a multi-cluster Kubernetes setup?
Managing a multi-cluster Kubernetes environment comes with its own set of challenges. To handle coordination, resilience, and visibility effectively, specialised tools play a key role. Kubernetes Federation stands out for centralised management, allowing unified deployments and robust failover strategies across clusters.
When it comes to disaster recovery, Velero proves invaluable by automating processes, ensuring swift data restoration, and maintaining consistency across clusters.
For monitoring and observability, tools like Prometheus and Grafana offer in-depth insights into system performance and resource usage, helping teams stay on top of their infrastructure. Meanwhile, service mesh solutions like Linkerd ensure secure communication between clusters, and networking tools such as Consul with Mesh Gateways simplify secure traffic flow and network connections.
By combining these tools, organisations can streamline operations, boost reliability, and maintain efficiency in managing multi-cluster Kubernetes setups.
How does using multi-cluster Kubernetes help lower operational costs?
Multi-cluster Kubernetes helps businesses save on operational costs by ensuring efficient resource use. By distributing workloads across clusters, it minimises waste and ensures resources are used where they're needed most. This approach not only optimises performance but also avoids unnecessary over-provisioning.
Automation plays a big role here too. It simplifies infrastructure management, cutting down on the time and effort required for manual tasks. This means teams can focus on more strategic work while the system handles routine operations.
Another key benefit is the ability to consolidate resources across different environments. By eliminating redundancies, businesses can cut extra expenses and streamline their operations. Real-world examples highlight how this method can lead to noticeable cost savings, all while boosting reliability and reducing downtime.
