In today's fast-paced DevOps environments, balancing rapid delivery with compliance requirements is critical - especially for regulated industries like finance and healthcare. Traditional manual audits often slow teams down, but integrating compliance into CI/CD pipelines can eliminate inefficiencies and reduce risks.
Key Takeaways:
- Policy as Code (PaC): Automate compliance by encoding rules into machine-readable policies, ensuring consistency across environments.
- Shift-Left Security: Detect compliance issues early in development to prevent costly fixes later.
- Automated Tools: Use tools like Open Policy Agent (OPA) for real-time policy enforcement and Conftest for Infrastructure as Code (IaC) validation.
- Security Scanning: Implement SAST, SCA, and IaC scanning in CI/CD pipelines to catch vulnerabilities early.
- Continuous Monitoring: Use AWS Config and Cloud Custodian to enforce compliance throughout the lifecycle.
- Audit Trails: Maintain immutable logs for clear evidence of compliance, stored securely in tamper-proof locations.
::: @figure 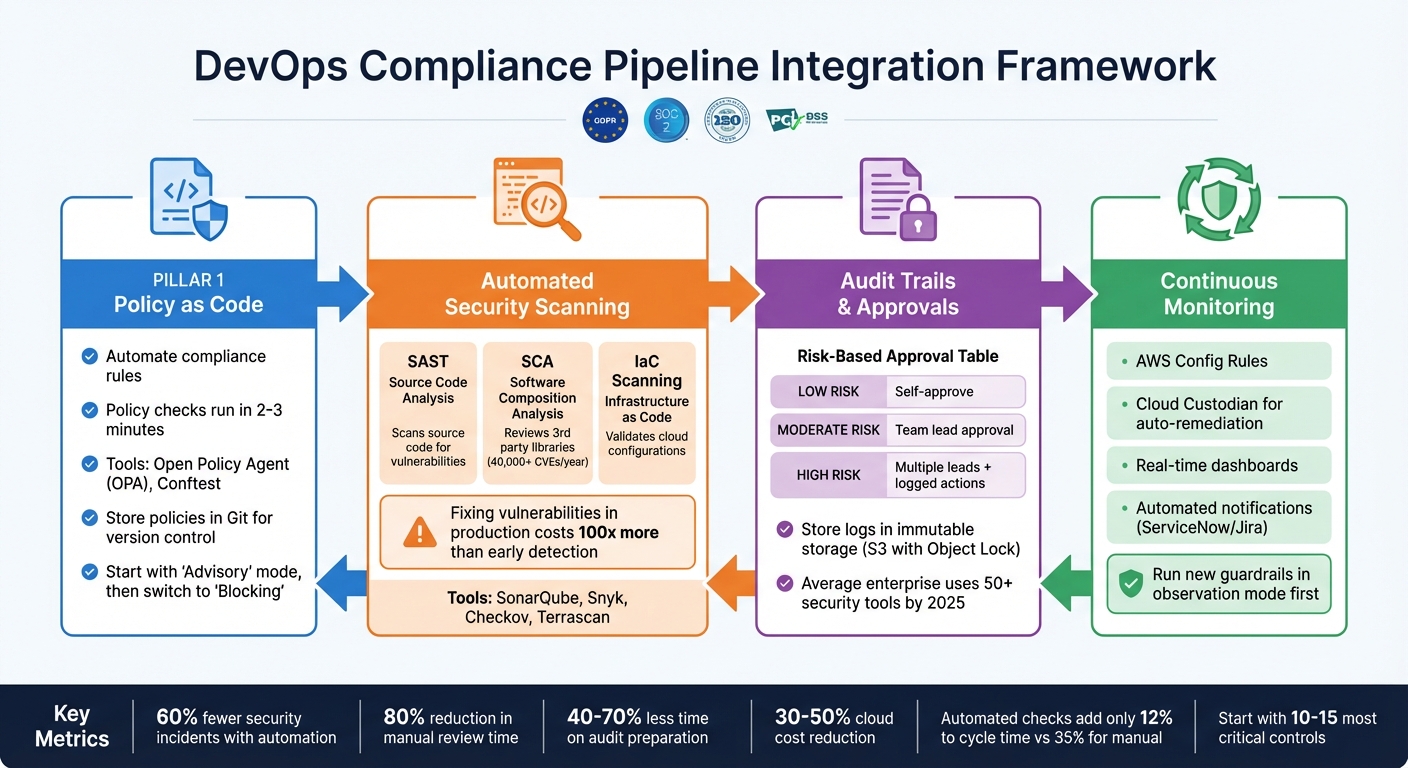 {DevOps Compliance Pipeline Integration Framework}
:::
{DevOps Compliance Pipeline Integration Framework}
:::
Achieving Compliance through DevOps Pipelines | DevOps & Data Impact 2024
Policy as Code for Automated Compliance
Policy as Code (PaC) takes the guesswork out of compliance by turning regulatory requirements into automated rules. Instead of relying on manual reviews, PaC allows compliance teams to manage policies independently of the infrastructure itself [5]. This approach ensures that Infrastructure as Code (IaC), written by different teams, consistently aligns with organisational standards for security, cost control, and compliance [5].
One of the biggest benefits of PaC is the shift from reactive to proactive governance. By integrating policy checks directly into the CI/CD pipeline, teams can catch misconfigurations in minutes rather than weeks [7]. As policyascode.dev explains:
Integrating policy checks directly into your CI/CD pipeline transforms governance from a reactive, after-the-fact process into a proactive, automated part of development.– policyascode.dev [7]
For developers, speed is key. Policy checks need to run in under 2–3 minutes to avoid slowing down workflows [7]. Tools like Open Policy Agent (OPA), which became a CNCF incubation project in April 2019, act as automated gatekeepers. They can block non-compliant deployments, such as unencrypted S3 buckets or unauthorised IAM roles, before these issues reach production [5][8]. This proactive enforcement is where tools like OPA shine.
Open Policy Agent (OPA) for Real-Time Enforcement
OPA uses Rego, a declarative language, to enforce compliance rules in real time. By separating policy decision-making from the software stack, it offers consistent enforcement across microservices, Kubernetes, and CI/CD pipelines [9][10]. For organisations using Infrastructure as Code, Conftest - a utility built on OPA - is often the tool of choice for validating configuration files like HCL, JSON, and YAML stored in Git repositories [6][7].
For Terraform users, the process is straightforward: convert plans to JSON using terraform show -json and run OPA with the --fail flag to block non-compliant deployments [5][11]. This ensures that non-compliant infrastructure never gets deployed in the first place.
OPA also generates detailed audit trails for every decision, which is invaluable for both compliance and debugging [10]. These logs can be replayed to analyse past decisions or identify issues. To maintain data integrity for auditing purposes, evidence logs - such as policy decision logs - should be stored in immutable, write-once locations like S3 buckets with Object Lock enabled [3].
Version Control for Compliance Policies
Real-time enforcement is only part of the equation; version control is equally crucial for maintaining regulatory traceability. Storing policies in Git provides a clear, auditable history of changes [3][7]. This history creates a direct link between policy updates and specific regulatory requirements. Teams should name or comment policy files to match the relevant regulations - such as pci_dss_3_4_1.rego - to make these connections explicit [3].
OPA's built-in testing framework allows teams to unit-test policies before deployment, ensuring they work as intended and don’t introduce new problems [5]. When rolling out new policies, it’s a good idea to start with an Advisory
mode. This mode alerts developers to issues without blocking the pipeline, giving teams time to adjust. Once everyone is aligned, the policy can be switched to Blocking
mode to enforce compliance [7].
Automated Security Scanning in CI/CD Pipelines
Automated security scanning has become a cornerstone of maintaining secure CI/CD pipelines. By embedding these scans directly into the development process, teams can catch vulnerabilities early without slowing down deployments. Security, after all, should enhance workflows, not hinder them [12].
The most effective strategies combine multiple scanning methods - SAST, SCA, and IaC scanning - at different pipeline stages. Each approach targets specific vulnerabilities:
- Static Application Security Testing (SAST) examines source code for issues like SQL injection and hardcoded credentials, catching them early in development [19].
- Software Composition Analysis (SCA) reviews third-party libraries for known vulnerabilities, a crucial step considering over 40,000 new CVEs were reported last year [17].
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) scanning evaluates cloud configuration templates for potential misconfigurations before deployment [18].
Addressing security flaws during development isn't just faster - it's far cheaper. Fixing a vulnerability in production can cost up to 100 times more than addressing it early [19]. This is why many organisations now adopt a break-the-build
approach, where pipelines are halted if high or medium-risk vulnerabilities are detected [15]. As Srinivas Manepalli, DevSecOps Solutions Architect at AWS, explains:
Identifying the vulnerabilities during the initial stages of the software development process can significantly help reduce the overall cost of developing application changes, but doing it in an automated fashion can accelerate the delivery of these changes as well.[12]
SAST and Software Composition Analysis
SAST tools, like SonarQube, Bandit (for Python), and PHPStan, scan source code line-by-line to detect security flaws before the application is executed. These tools are often run during nightly builds or as part of the CI process to ensure continuous monitoring. While SAST can sometimes produce false positives, its precision in pinpointing vulnerabilities - down to the exact line of code - makes it invaluable for remediation [13].
SCA tools, such as OWASP Dependency-Check and Snyk Open Source, focus on third-party libraries. They identify known vulnerabilities not just in direct dependencies but also in transitive ones - those buried several layers deep in the dependency chain [14]. This is vital, as vulnerabilities in these hidden layers can easily go unnoticed.
A robust approach combines both SAST and SCA during the build process. For example, lightweight SAST and secret scanning can run on every commit, while full dependency analysis is reserved for daily builds [19]. Tools like git-secrets can catch over 750 types of hardcoded secrets, such as API keys and cloud tokens, before they even make it into the repository [19]. For better oversight, platforms like AWS Security Hub consolidate findings from multiple tools into a single dashboard, categorising vulnerabilities by severity from 0 (Informational) to 100 (Critical) [12].
Infrastructure as Code Scanning
IaC scanning is key to preventing misconfigurations in cloud environments. Tools like Checkov, Terrascan, and AWS CloudFormation Guard analyse templates for issues such as unencrypted storage, overly permissive firewall rules, or insecure default settings [18]. By integrating these scans into the CI/CD pipeline, teams can enforce security policies before infrastructure is deployed. Many organisations start with soft-fail
alerts to flag issues, gradually moving to hard-fail
mechanisms that block deployments until problems are resolved [18].
To maintain consistency, custom scanning policies can be stored in a central repository, ensuring uniform enforcement across all pipelines [18]. Beyond the initial scans, IaC tools also support continuous compliance. For instance, AWS Config monitors resource configurations over time, comparing them against predefined baselines to detect and address any drift that might reintroduce risks [16][17]. This level of automation ensures ongoing compliance and reduces risks throughout the lifecycle of cloud deployments.
Automated Audit Trails and Approval Processes
Meeting compliance standards means having clear proof that your processes function as intended. Automated audit trails and risk-based approval systems provide this evidence, ensuring that high-risk changes are reviewed carefully before they go live.
Immutable Audit Logs
Securing audit trails is a key step in proactive compliance. Immutable logs create a tamper-proof record of every action within your pipeline, capturing critical events to track changes from start to finish [21]. AWS DevOps Guidance highlights:
Comprehensive audit trails involve capturing, recording, and storing every action taken across your environment. This provides a log of evidence that can offer insights for security and audit teams.[21]
To maintain the integrity of these logs, store them in a secure, isolated environment accessible only to authorised auditors. Implement controls to prevent tampering or deletion, and use automated tools to extract data from resource APIs, reducing the need for manual input [21]. For organisations juggling numerous security tools - an average of 50 in enterprise setups by 2025 [22] - centralised logging offers real-time insights into compliance issues, helping to minimise risks [20].
Risk-Based Deployment Approvals
To complement immutable logs, a tiered approval system ensures that high-risk changes get the attention they require. By tailoring approval workflows to the level of risk, organisations can ensure proper oversight. Risk-based approval gates route changes through specific workflows depending on their potential impact [24]. This system also supports segregation of duties, ensuring no single individual handles development, testing, and deployment without independent oversight [4].
| Resource Risk Category | Recommended Approval Process |
|---|---|
| Low Risk | No formal approval needed; developers can self-approve deployments [25] |
| Moderate Risk | Team leads must approve each commit and deployment [25] |
| High Risk | Multiple leads must approve; all actions are logged; privileged access management systems are required [25] |
Risk assessments should take place at the start of each project using standardised questionnaires, with approval checkpoints assigned automatically [24]. For high-risk changes, manual gates remain crucial for complex evaluations, such as reviewing exceptions for specific Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs). Meanwhile, automated checks like port scans can streamline simpler tasks [23][24]. Storing compliance policies and threat models as versioned artifacts in source control ensures they evolve alongside your application code [24]. These automated workflows integrate seamlessly with DevOps practices, strengthening continuous compliance efforts.
Need help optimizing your cloud costs?
Get expert advice on how to reduce your cloud expenses without sacrificing performance.
Continuous Compliance Monitoring and Feedback
Ensuring compliance doesn't stop once deployment is complete. It requires constant vigilance through runtime monitoring to address any manual changes or configuration drifts. By combining pre-deployment checks with runtime monitoring, organisations can maintain compliance throughout the entire lifecycle [2][8]. This continuous oversight helps bridge the gap between development and operations, ensuring that compliance standards are upheld at all times.
AWS Config Rules and Cloud Custodian for Compliance Enforcement
AWS Config plays a key role in monitoring configurations against industry standards like SOC, PCI, and HIPAA across all accounts and regions [26][28]. When paired with Cloud Custodian, it takes things a step further by automatically remediating non-compliant changes, reducing the time vulnerabilities remain unaddressed [8][27].
A great example of this in action is Truist Financial Corporation’s implementation of a continuous compliance workflow in December 2019. Following the merger of BB&T and SunTrust Banks, Gary Smith (Group Vice President Digital Enablement) and David Jankowski (SVP Digital Application Support) led the initiative to scale security checks across development teams using an observation mode. This approach provided early insights into workload compliance before enforcement began, supporting key standards like CIS, PCI, and NIST while also improving audit readiness [2].
The continuous compliance workflow provided us with a framework over which we are able to roll out any industry standard compliance sets - CIS, PCI, NIST, etc. It provided centralised visibility around policy adherence to these standards, which helped us with our audits.- David Jankowski, SVP Digital Application Support Services, Truist Financial Corporation [2]
Feedback Loops for Continuous Improvement
Maintaining compliance isn't just about enforcement - it’s about learning and improving. Feedback mechanisms play a vital role in turning compliance into a continuous improvement process. A good starting point is running new guardrails in observation mode. This allows security teams to identify violations and notify developers, giving them time to fix issues before enforcement kicks in [2]. Once flagged issues are resolved within the grace period, the guardrail can then be moved to active enforcement mode, blocking non-compliant deployments [2].
Centralised dashboards are invaluable here, offering real-time insights into compliance status. These dashboards enable teams to act quickly, while aggregated reports help organisations spot recurring non-compliance patterns and share solutions across teams [2]. Automated notifications, integrated with tools like ServiceNow or Jira, can help track remediation progress by triggering alerts as soon as violations are detected [30]. By combining preventive, detective, and responsive controls, organisations can better handle unexpected compliance issues that may arise [27][29].
Hokstad Consulting's Approach to DevOps Compliance

Hokstad Consulting takes established best practices a step further by weaving compliance seamlessly into DevOps processes. Instead of treating compliance as an afterthought, they embed it directly into DevOps pipelines, combining security with operational efficiency. By integrating policy enforcement, automated scanning, and continuous monitoring into CI/CD workflows, Hokstad Consulting ensures compliance becomes a natural part of the development process. This approach is particularly crucial for UK businesses navigating the evolving regulatory landscape in a post-Brexit environment. Their tailored automation solutions address the specific demands of modern DevOps operations.
Custom CI/CD Automation with Built-In Compliance
Incorporating compliance into automated pipelines removes the delays caused by manual reviews. While traditional manual compliance checks can increase cycle times by over 35%, automated guardrails typically only add about 12% to median cycle times [31]. Hokstad Consulting employs tools like Open Policy Agent (OPA) and Kyverno to enforce compliance rules in real time. Vulnerability scanning is handled through tools such as Trivy, Snyk, and SonarQube, while secrets are managed securely using HashiCorp Vault and AWS Secrets Manager. This setup ensures every deployment aligns with standards like GDPR, SOC 2, ISO 27001, and PCI-DSS, all without slowing down release cycles.
Security Audits and Process Optimisation
Automated deployment checks are just one part of Hokstad's compliance strategy. Continuous security audits enhance compliance further by replacing lengthy manual reviews with automated systems that provide real-time alerts and simplify audit preparation. Their cloud cost engineering approach integrates compliance with cost-saving measures, aiming to cut cloud expenses by 30-50% while maintaining security and performance. Quarterly reviews, combined with AI-driven threat detection, ensure policies stay aligned with changing requirements and help mitigate risks. This combination of automation and expertise has enabled clients to reduce audit preparation times by up to 60%.
Compliance Solutions for Hybrid and Managed Cloud
Hokstad Consulting also extends its compliance strategies to complex multi-environment setups, including hybrid and multi-cloud operations. These environments often face challenges like data residency and varying regulatory standards. Hokstad designs frameworks for public, private, and managed hosting environments, implementing Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) across platforms. This approach has been shown to reduce security incidents by up to 30%. Their policy-as-code solutions maintain consistency across AWS, Azure, private infrastructure, and managed hosting environments. For organisations bound by UK-specific regulations, such as the Data Protection Act 2018 or NHS Digital standards, Hokstad delivers tailored solutions that ensure compliance while optimising infrastructure costs and performance.
Conclusion
Bringing compliance into DevOps pipelines is essential for organisations striving to balance fast delivery with meeting regulatory requirements. Automated methods, such as Policy as Code and continuous monitoring, allow teams to maintain audit-level accountability without slowing down workflows. In fact, organisations using automated compliance checks have seen 60% fewer security incidents, while cutting manual review times by up to 80% [1].
The move towards automation is also reshaping how compliance is handled, shifting from periodic audits to continuous frameworks. By storing, reviewing, and enforcing compliance policies automatically, teams can maintain clear audit trails and reduce the time spent on manual audit preparation by 40–70% [1]. Tools like Open Policy Agent and Kyverno provide developers with real-time feedback, helping to catch vulnerabilities early - long before they reach production, where fixing them becomes far more expensive.
For organisations in the UK, where regulatory requirements are constantly evolving, this approach is particularly important. Hokstad Consulting offers expertise in embedding compliance directly into DevOps workflows while optimising cloud costs. Their solutions not only ensure security but also help reduce costs by 30–50%. This approach transforms compliance from a costly obligation into a seamless safeguard integrated into daily operations.
To get started, it’s best to take a phased approach. Begin by automating the 10–15 most critical controls for a single framework, and then expand the process across the organisation [1][3]. Explicitly mapping policy files to regulatory controls (e.g., pci_dss_3_4_1.rego) ensures clear, auditable links for regulators. Additionally, storing policy decision logs in immutable storage like S3 with Object Lock guarantees the integrity of your evidence.
FAQs
What are the benefits of using Policy as Code for compliance in DevOps pipelines?
Policy as Code strengthens compliance within DevOps pipelines by integrating automated policy checks directly into development processes. This method enables ongoing monitoring, identifies compliance issues early, and reduces the need for manual interventions.
By moving compliance checks to the earlier stages of development, teams can tackle potential risks head-on, avoiding delays and streamlining workflows. Alongside maintaining regulatory requirements, this approach encourages a sense of accountability and teamwork across different groups.
What are the advantages of using automated security scanning in CI/CD pipelines?
Integrating automated security scanning into CI/CD pipelines can make a world of difference for development teams. It helps identify vulnerabilities early in the development cycle, cutting down the chances of security misconfigurations and ensuring compliance with important standards.
By catching issues before they make it to production, businesses can significantly lower the risk of costly breaches and sidestep the hassle of implementing time-intensive fixes down the line. On top of that, automated scanning enhances the security of the entire pipeline, enabling teams to deliver dependable, secure software more efficiently.
Why is continuous compliance monitoring essential in DevOps pipelines?
Continuous compliance monitoring plays a key role in DevOps, ensuring security and regulatory standards are consistently met throughout the development and deployment process. Unlike traditional methods such as manual reviews or periodic audits, which often lag behind the rapid pace of modern DevOps, continuous monitoring aligns seamlessly with automated workflows.
By integrating automated compliance checks directly into CI/CD pipelines, organisations can catch and fix non-compliance issues as they happen. This stops misconfigurations from progressing through the deployment process, minimising the risk of vulnerabilities, data breaches, or regulatory fines. Additionally, it simplifies audits by offering ongoing proof of compliance, which is especially important for industries with strict regulations.
This approach not only strengthens security but also helps teams stay responsive to changing laws and standards. It ensures software is delivered efficiently without cutting corners on compliance.
