Cybersecurity threats are faster than ever, leaving organisations struggling to keep up. Attackers exploit vulnerabilities within 5 days, while most businesses take 60–150 days to patch them. Real-time vulnerability detection powered by AI changes this by continuously monitoring systems and identifying risks immediately. Here's how AI is transforming cybersecurity:
- Continuous Monitoring: AI scans systems 24/7, spotting vulnerabilities as they emerge, unlike periodic scans.
- Improved Accuracy: AI reduces false positives by focusing on behavioural anomalies, cutting unnecessary work for security teams.
- Faster Responses: Critical vulnerabilities that once took months to fix are now resolved in hours.
- Risk Prioritisation: AI predicts which vulnerabilities are most likely to be exploited, helping teams focus on critical issues.
While AI speeds up detection and remediation, it still struggles with context-specific vulnerabilities and depends on high-quality training data. Combining AI with human oversight ensures better decision-making and smoother integration into existing workflows.
For businesses in the UK, firms like Hokstad Consulting offer tailored AI solutions to secure systems while meeting regulatory requirements like GDPR and ISO/IEC 27001. This blend of automation and human expertise is key to staying ahead of cyber threats.
Key Benefits of AI in Real-Time Vulnerability Detection
Better Detection Accuracy and Fewer False Positives
AI has significantly boosted detection accuracy by analysing the deeper semantic relationships within code, rather than treating it as mere static text. Many systems now incorporate large language models (LLMs) as a secondary layer to validate alerts, achieving an impressive 80% precision rate. This falls well within the 20% false-positive threshold that security professionals find acceptable [8].
The transition from traditional, signature-based detection methods to pattern recognition is a game-changer. Signature-based systems depend on recognising known threats, often failing to detect zero-day exploits. In contrast, AI processes vast datasets to uncover complex anomalies that static rule-based systems would miss [7]. Researchers Malek Malkawi and Reda Alhajj highlight this shift:
AI methods substantially improve the precision of detection, scalability, and response speed compared with human-driven and rule-based approaches
[7]. This enhanced precision is particularly valuable for continuous monitoring, where speed and accuracy are critical.
Continuous Monitoring and Faster Response Times
AI's ability to continuously monitor systems has revolutionised response times. With cloud attacks capable of unfolding in as little as 10 minutes [6], speed is paramount. Unlike traditional methods that rely on periodic snapshots, AI systems operate autonomously, scanning environments 24/7 [2]. This constant vigilance allows organisations to move from reactive containment to proactive prevention.
Take NVIDIA’s deployment of Agent Morpheus in May 2024 as an example. This AI-driven workflow automates CVE analysis using the Morpheus cybersecurity framework and LLMs, enabling parallel processing of vulnerabilities. A container with 20 CVEs that once took nearly 2,843 seconds to process manually was handled in just 305 seconds by Agent Morpheus - a 9.3× improvement [9]. Moreover, this system can handle hundreds of vulnerabilities across thousands of nodes simultaneously, a feat beyond human capacity [5][9]. Organisations using AI-powered remediation have seen their mean time to remediate drop by 87% to 90% [5][6], turning months-long processes into tasks completed within hours.
Risk Prioritisation and Mitigation
AI doesn't just respond quickly - it also helps focus efforts where they matter most. Traditional CVSS scoring often categorises around 60% of vulnerabilities as High
or Critical
[11][12][13], which can overwhelm security teams. AI narrows this focus by predicting which vulnerabilities are most likely to be exploited, using real-world threat intelligence and data on exploit availability. In reality, only about 1.6% of vulnerabilities demand immediate attention, reducing remediation workloads by up to 98.4% [12].
As Shantanu Gattani from Sysdig aptly puts it:
Vulnerability management isn't about fixing everything - it's about fixing what counts
[6]. AI further streamlines mitigation efforts by assessing asset criticality. Using firmographic and behavioural data, it categorises systems into tiers, ensuring critical business infrastructure receives top priority. Tools like CrowdStrike's ExPRT.AI engine predict which vulnerabilities are most likely to be exploited [10], while Tenable’s Vulnerability Priority Rating (VPR) dynamically recalculates risk daily for every CVE, factoring in over 150 elements, including discussions on the dark web [11][13]. This targeted, dynamic approach ensures security teams focus on genuine threats, strengthening modern cybersecurity strategies.
Risks and Limitations of AI in Vulnerability Detection
Dependence on High-Quality Training Data
AI might improve vulnerability detection, but its effectiveness heavily depends on the quality of the training data. A closer look at BigVul, a widely used dataset, revealed that only about 25% of its labels were accurate[16]. That leaves a staggering 75% of examples potentially misleading. Other datasets, like ReVeal, also show similar inconsistencies. For instance, the same code snippet can be marked as both vulnerable and secure. In ReVeal, around 15% of vulnerable samples are incorrectly classified as uncertain
or even non-vulnerable elsewhere[15][16]. BigVul further complicates matters with a label duplication rate exceeding 12.7%[16].
When AI models trained on these curated datasets were tested on more realistic, real-world data, their performance plummeted. Precision dropped by as much as 95 percentage points, and F1 scores fell by up to 91 percentage points[15]. This drastic decline highlights a troubling issue: these models often rely on superficial patterns, like word counts or variable names, rather than genuinely understanding vulnerabilities. Niklas Risse, a researcher in the field, put it succinctly:
High scores can be achieved even when only word counts are available. This shows that these datasets can be exploited to achieve high scores without actually detecting any security vulnerabilities
[14].
Challenges with Context-Specific Vulnerabilities
AI also struggles to assess vulnerabilities that depend on a broader context. Most models analyse code at the function level in isolation, but over 90% of functions cannot be accurately evaluated without understanding how they interact with the rest of the system[14]. A function may seem secure on its own but could become vulnerable depending on how it’s called, the parameters it receives, or whether proper input validation is handled elsewhere. Niklas Risse explains this limitation:
Vulnerable functions are often vulnerable only because a corresponding vulnerability-inducing calling context exists whilst non-vulnerable functions would often be vulnerable if a corresponding context existed
[14].
This challenge becomes even more apparent in real-world scenarios. In December 2024, Microsoft researchers conducted a study involving 17 professional developers who used an AI-powered tool to analyse 24 projects, totalling over 1.7 million lines of code. The tool flagged 170 potential issues, but many turned out to be false positives due to its inability to consider inter-procedural context. Moreover, 75% of the 50 fixes it suggested required significant manual adjustments because the AI failed to account for existing sanitisation libraries in the developers' codebases[8].
AI Agents for Cybersecurity: Enhancing Automation & Threat Detection
AI-Driven vs Manual Vulnerability Detection
::: @figure 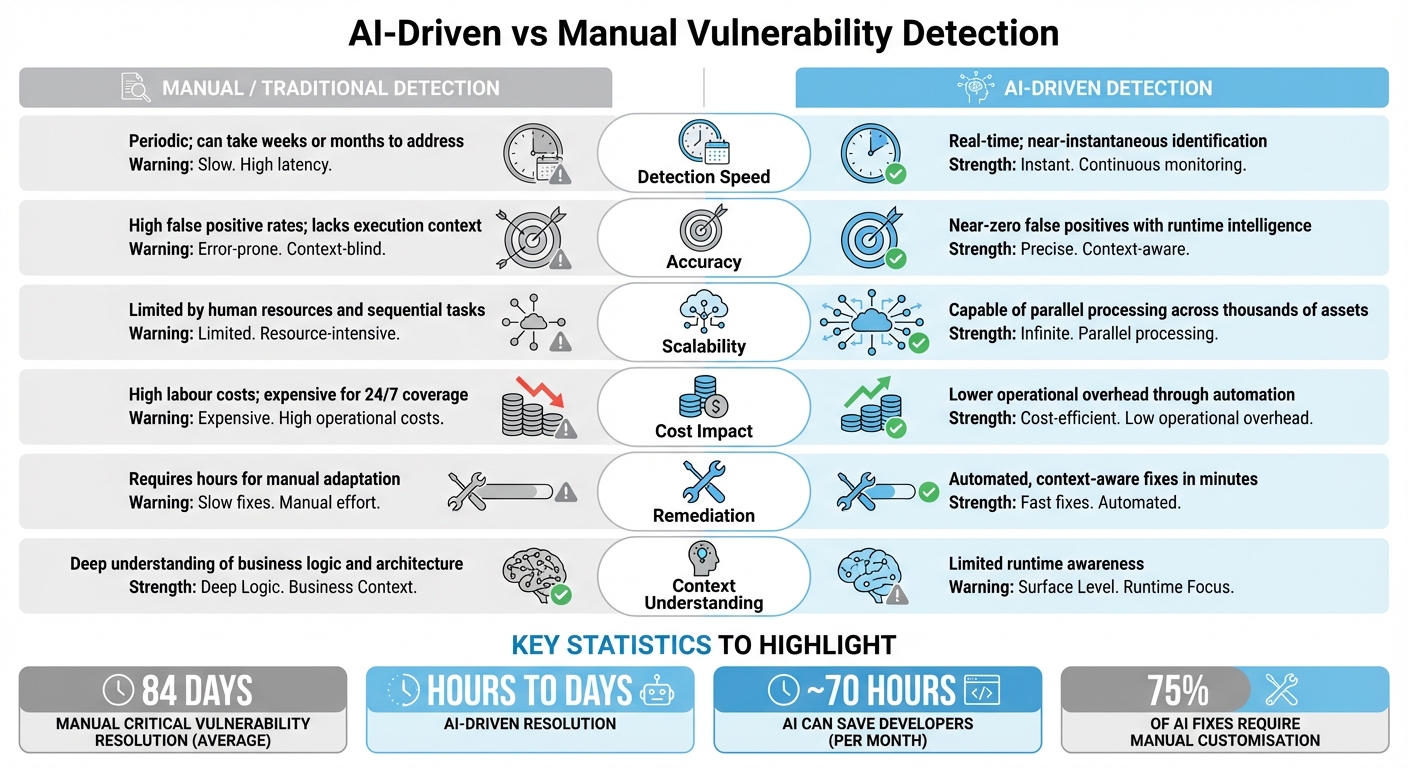 {AI-Driven vs Manual Vulnerability Detection: Speed, Accuracy and Cost Comparison}
:::
{AI-Driven vs Manual Vulnerability Detection: Speed, Accuracy and Cost Comparison}
:::
As cyber threats evolve and demand faster responses, comparing AI-driven and manual vulnerability detection highlights their distinct strengths and limitations. Manual detection relies heavily on human expertise and a deep understanding of business logic. While this approach can be thorough, it is inherently slow and sequential. On the other hand, AI-driven systems operate at machine speed, offering continuous monitoring across thousands of assets simultaneously. However, these systems often lack the nuanced contextual awareness that experienced security professionals bring to the table[17]. The shift toward AI-driven detection reflects a move from reactive, human-led processes to proactive, automated solutions.
For example, addressing critical vulnerabilities manually takes an average of 84 days, while AI-driven systems can reduce this to just hours or days[18]. Despite these advantages, AI tools sometimes struggle to generate fixes that account for specific runtime contexts, such as existing sanitisation libraries or environment-specific requirements. AI tools can produce production-ready code and even pull requests in mere minutes, potentially saving developers around 70 hours per month[18]. Yet, a study involving 17 professional developers found that 75% of AI-generated fixes required manual customisation to align with specific environments[8]. This underscores that while AI excels in speed and initial triage, human oversight is still essential to ensure that fixes integrate smoothly into production systems.
Comparison Table
| Metric | Manual/Traditional Detection | AI-Driven Detection |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Speed | Periodic; can take weeks or months to address[18] | Real-time; near-instantaneous identification[19] |
| Accuracy | High false positive rates; lacks execution context[18] | Near-zero false positives with runtime intelligence[18] |
| Scalability | Limited by human resources and sequential tasks[18] | Capable of parallel processing across thousands of assets[18] |
| Cost Impact | High labour costs; expensive for 24/7 coverage[17] | Lower operational overhead through automation[19] |
| Remediation | Requires hours for manual adaptation[18] | Automated, context-aware fixes in minutes[17][18] |
| Context Understanding | Deep understanding of business logic and architecture[5] | Limited runtime awareness[5] |
Need help optimizing your cloud costs?
Get expert advice on how to reduce your cloud expenses without sacrificing performance.
Best Practices for Implementing AI in Real-Time Vulnerability Detection
Integrating with Existing Security Systems
To make the most of AI in vulnerability detection, it's crucial to centralise and standardise data from endpoints, networks, and cloud environments. This ensures AI models receive high-quality training inputs[20]. Lightweight CI/CD sensors can be deployed to monitor real-time application behaviour and data flows without interfering with the application's core logic[5].
For a streamlined workflow, connect AI detection tools directly to Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems and Extended Detection and Response (XDR) platforms. This integration creates a unified security framework, allowing AI to prioritise alerts and feed them into existing processes. It can even assign issues to the right teams via ticketing systems, complete with contextual explanations for why fixes are necessary. This added clarity helps reduce friction between security and development teams, especially in handling rapidly evolving cloud threats[20][6].
Take Intermex (International Money Express) as an example. In October 2025, they used CrowdStrike's ExPRT.AI and Falcon Exposure Management to overhaul their patching workflow. By combining AI-driven exploit prediction with an assessment of asset criticality, the company managed to cut critical vulnerabilities in its DMZ by 98%[23].
This kind of integration creates a seamless flow of data that supports human oversight, which is explored in the next section.
Combining AI with Human Oversight
Even with advanced automation, human expertise is indispensable for validating context and making strategic decisions. AI excels at processing massive datasets quickly, but it’s the human touch that ensures alerts are meaningful and actionable. A human-in-the-loop (HITL) approach is key. In this setup, security analysts review AI alerts and provide feedback that can refine model training over time[20][1]. This feedback loop ensures defences stay relevant as threats evolve.
The goal isn't to slow things down – it's to make sure automation is informed, contextual, and accountable.- Rapid7[21]
To maintain flexibility, configure AI systems to flag uncertain events as maybe
rather than forcing binary decisions[4]. This lets analysts step in to make nuanced calls on ambiguous threats. For high-stakes automated actions, such as isolating devices or locking accounts, it's wise to route decisions through human review layers. This prevents unnecessary disruptions to business operations[21].
When implemented effectively, AI can dramatically cut investigation times - from over 30 minutes to less than 2 minutes in a Security Operations Centre[22]. However, this efficiency should always complement, not replace, human judgement, especially for critical decisions.
AI Strategy in DevOps Security at Hokstad Consulting

Hokstad Consulting's Expertise in AI and DevOps Integration
Hokstad Consulting helps organisations shift from reactive to proactive security by embedding AI into their DevOps workflows. By using pre-trained models within CI/CD pipelines, they enhance anomaly detection and automate testing to identify vulnerabilities early on [3]. Their approach focuses on behavioural anomaly detection, applying machine learning to logs, metrics, and traces. This enables detection capabilities that go beyond the limitations of traditional rule-based systems, improving accuracy and speeding up response times.
AI improves CI/CD tool security through real-time code and log analysis, automated vulnerability scanning and remediation, fewer false positives and automated compliance.- Hokstad Consulting [3]
Rather than just identifying issues, Hokstad takes it a step further with predictive alerts and self-healing systems, which help prevent recurring incidents from escalating. They emphasise integrating security measures early in the development pipeline [3]. For organisations managing multi-cloud environments, Hokstad offers tailored risk mitigation, automating security across platforms like AWS, Azure, and GCP. For example, a financial services client successfully reduced privilege sprawl across eight Kubernetes clusters by implementing a GitOps strategy with least-privilege RBAC and automated audits [3]. This demonstrates how their proactive measures seamlessly integrate into the DevOps ecosystem.
Tailored Solutions for Businesses
Hokstad Consulting provides AI-driven CI/CD pipelines customised to meet each organisation's regulatory and operational needs. For UK-based businesses, this includes ensuring compliance with standards like GDPR, ISO/IEC 27001, and PCI DSS. They achieve this through automated audit trails that maintain clear decision records.
Their integrations include tools like Snyk and Mend for automated dependency scans at every build, commit, and pull request stage. Security dashboards built in platforms like Grafana or Datadog are customised to UK-specific requirements, such as using £ for currency and dd/mm/yyyy date formats, offering unified visibility into logs, metrics, and traces. Hokstad's rollout strategy begins with non-critical workloads, gradually building trust before scaling to production environments. This phased approach ensures human oversight remains active while introducing agentic remediation, where AI suggests code changes for human review [24][25]. Additionally, their cost-aware AI autoscaling can cut GPU expenses for AI workloads by 30–50% [3], making these solutions accessible even for smaller businesses. These tailored measures reinforce their proactive and integrated approach to security.
Conclusion
AI is reshaping vulnerability detection, shifting the focus from reactive patching to proactive defence. Consider this: attackers can exploit vulnerabilities within just five days[6] and move laterally through networks in under 51 minutes[23][26]. Yet, traditional patching processes often drag on for 60 to 150 days[6]. AI-driven systems bridge this gap by automating triage and prioritising genuine threats, making security measures far more efficient.
One key advancement is context-aware remediation, which can reduce the mean time to remediate by up to 87%[5]. Unlike generic fixes that might disrupt production systems, this approach targets the most pressing issues without unnecessary risk.
Vulnerability management isn't about fixing everything - it's about fixing what counts.
[6]
For AI to deliver on its potential, it requires high-quality training data, accurate runtime sensors, and clear insights. While AI excels at handling repetitive analysis, human oversight remains critical for strategic decision-making. Together, this partnership ensures a well-rounded, effective security framework.
UK organisations operating under GDPR, ISO/IEC 27001, and PCI DSS must also consider regulatory compliance when integrating AI into their security systems. Hokstad Consulting offers a phased approach, starting with non-critical workloads and scaling gradually. This method ensures smooth adoption without disrupting operations. Their work with financial services clients highlights how tailored AI solutions can provide both cost savings and stronger security, delivering rapid, precise responses to evolving threats.
FAQs
How does AI enhance the accuracy of detecting vulnerabilities compared to traditional methods?
AI brings a new level of precision to vulnerability detection through techniques like graph-based models, runtime analysis, and analysis of real-world behavioural data. These approaches allow AI to spot intricate patterns that traditional methods, such as static analysis or rule-based systems, often miss. Plus, they help cut down on false positives, making the detection process much more accurate.
What sets AI apart is its ability to adjust to changing environments. It learns from evolving threats and application behaviours, ensuring vulnerabilities are identified more quickly and accurately. This dynamic approach allows organisations to tackle potential risks as they emerge, rather than after the fact.
What challenges does AI face in detecting vulnerabilities specific to unique contexts?
AI faces challenges with context-specific vulnerabilities because it struggles to grasp the subtle details of a system's environment, architecture, or operational setup. This limitation can affect its ability to accurately analyse codebases that are unfamiliar or heavily customised.
Another hurdle is that AI models depend on patterns from past data, which don't always translate effectively to new or complex situations. Because of this, human expertise is still essential to ensure vulnerabilities are correctly identified and resolved across various scenarios.
How can businesses incorporate AI-driven vulnerability detection into their existing security systems?
Businesses can weave AI-powered vulnerability detection into their existing security setups by implementing AI tools that align effortlessly with their current frameworks. These tools leverage real-time insights to pinpoint weaknesses, automate fixes, and rank threats based on their relevance and seriousness.
By integrating AI into day-to-day operations, organisations can strengthen their capacity to spot and address vulnerabilities without interfering with established systems. This approach boosts efficiency while also minimising risks through quicker and more precise decision-making.
