AI is reshaping Kubernetes monitoring, making it more efficient and predictive. While traditional methods rely on static rules, they struggle with Kubernetes' dynamic nature, leading to false alerts and missed issues. AI-driven systems, however, analyse historical data to detect anomalies, predict failures, and optimise resources in real time.
Key Takeaways:
- AI Advantages: Reduces downtime, improves detection rates (92%), and cuts response times by 67%.
- Challenges: Requires more processing power and specialised skills for implementation.
- Traditional Monitoring: Easier to set up but less effective in handling Kubernetes' complexities, often leading to alert fatigue and inefficiencies.
Quick Comparison:
| Feature | Traditional Monitoring | AI-Driven Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Anomaly Detection | Static rules, prone to false alerts | Learns behaviour, detects subtle issues |
| Scalability | Struggles with large clusters | Handles vast data streams easily |
| Resource Management | Reactive, less efficient | Predictive, optimises resources |
| Risk Mitigation | Reactive, slower response | Proactive, faster resolution |
Conclusion: AI-driven monitoring is a game-changer for Kubernetes, offering faster issue detection, better resource use, and reduced downtime. Combining AI with existing tools like Prometheus can balance simplicity with advanced capabilities.
::: @figure 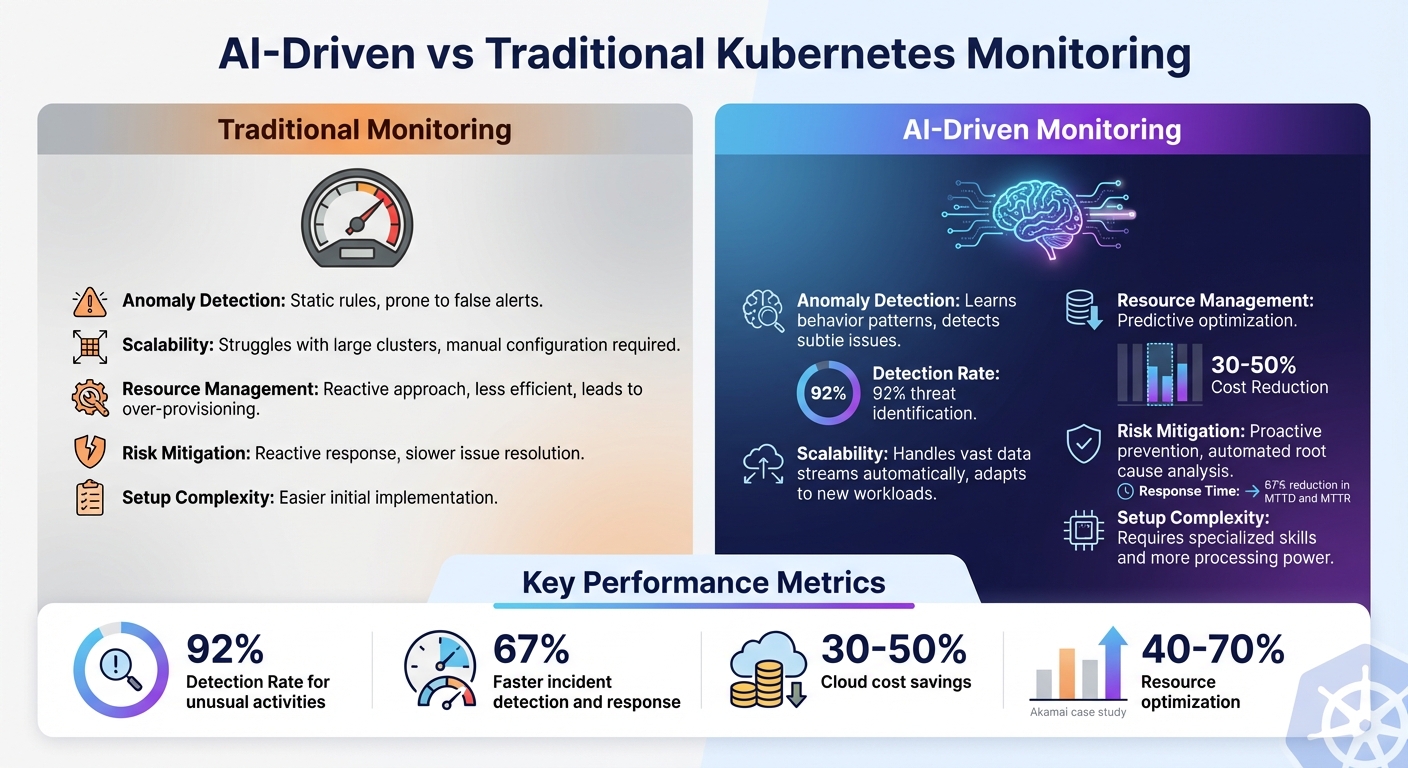 {AI-Driven vs Traditional Kubernetes Monitoring: Key Differences and Performance Metrics}
:::
{AI-Driven vs Traditional Kubernetes Monitoring: Key Differences and Performance Metrics}
:::
My Kubernetes Workflow: How AI Detects & Fixes Issues Faster
1. AI-Driven Kubernetes Monitoring
AI is changing the game for Kubernetes management by learning and adapting to workload behaviour in real time. Instead of relying on static rules - like alerting when CPU usage passes 90% - AI creates dynamic baselines tailored to each workload. By analysing historical data, it recognises patterns, such as traffic spikes on Monday mornings or memory surges during batch jobs, and adjusts its monitoring thresholds accordingly [1].
Anomaly Detection
The true power of AI lies in its ability to analyse multiple data streams simultaneously. By correlating logs, metrics, and traces, it can uncover complex issues that traditional single-metric monitoring might miss. For example, AI might flag a pod communicating with an unexpected external IP address while making unusual API calls - an anomaly that signature-based tools would likely overlook [9]. In fact, this approach has achieved detection rates of over 92% for identifying unusual activities in Kubernetes environments [9].
Traditional security tools struggle in Kubernetes because workloads are constantly starting, stopping, and shifting. Static rules or signature-based scanners can't keep pace with ephemeral containers.
– Plural.sh [9]
This advanced anomaly detection is essential for managing Kubernetes' vast and ever-changing data streams.
Scalability
Kubernetes clusters produce an overwhelming amount of telemetry data - far too much for manual analysis. AI is built to process this deluge, handling logs, metrics, traces, and audit events from thousands of ephemeral pods that may only exist for seconds [9]. Organisations using AI-driven alerts have reported a 67% reduction in Mean Time to Detect (MTTD), allowing teams to catch issues early and prevent outages [9].
Resource Efficiency
AI also brings a smarter approach to resource management. By using time-series models, it predicts future capacity needs, enabling proactive scaling rather than reactive adjustments. Instead of waiting for CPU usage to spike, AI anticipates demand and scales resources accordingly. This predictive scaling ensures workloads are consolidated onto the most efficient nodes, with some organisations cutting cluster costs by 30–50% [10]. It also identifies unused capacity in real time, helping avoid both overprovisioning and performance bottlenecks [5][10].
These resource optimisation capabilities go hand in hand with improved operational efficiency.
Risk Mitigation
AI significantly reduces the noise of excessive alerts by combining related signals into a single, actionable incident. Rather than overwhelming teams with hundreds of individual notifications, it provides clear, automated root cause analysis. This has allowed organisations to cut Mean Time to Respond (MTTR) by 67%, freeing teams to focus on innovation rather than constant firefighting [9].
At Hokstad Consulting (https://hokstadconsulting.com), we specialise in helping businesses adopt these AI-driven monitoring strategies. By integrating them into DevOps workflows and cloud infrastructure, we ensure teams can work smarter, not harder, and dedicate more time to driving progress.
2. Traditional Kubernetes Monitoring
Traditional Kubernetes monitoring relies heavily on static, rule-based alerts. For instance, it might trigger an alert if CPU usage exceeds 90% or if the number of pods falls below a set threshold. While these methods can catch some issues, they often struggle to keep up with Kubernetes' dynamic and ever-changing nature [4][9].
Anomaly Detection
Conventional approaches to anomaly detection typically involve signature-based scanners and simple rule triggers. For example, an alert might be configured to activate if the number of ingress requests surpasses a predefined value [4]. However, this reactive method tends to identify problems only after thresholds are breached. It also struggles with normal fluctuations, leading to frequent false positives that can overwhelm teams [4][9].
Traditional monitoring tools often fail to account for the multi-dimensional correlations between these components.
– Caitlin Halla and Laiba Siddiqui, Splunk [3]
Scalability
As Kubernetes clusters expand, the shortcomings of static alerts become glaringly apparent. Manually configuring and continuously adjusting these alerts is not feasible at scale [3][4]. Kubernetes' ephemeral nature - where pods can disappear quickly - adds to the difficulty, as logs or states may be lost before they can be captured. Yuval Dror from Anodot highlights this challenge, pointing out the impracticality of managing static alerts across multiple clusters [4].
Resource Efficiency
Traditional monitoring tools, such as metrics-server, focus on lightweight tracking of CPU and memory usage, often combined with log rotation strategies [13][12]. However, these systems remain reactive, flagging issues only after they occur. This not only increases the likelihood of false positives but can also result in missed critical events. As infrastructure grows, manually managing countless alert rules becomes an overwhelming task [11][1].
Risk Mitigation
One major drawback of traditional monitoring is the generation of siloed data. Teams often have to juggle multiple tools to piece together a complete picture, which significantly increases the mean time to resolution (MTTR) [3]. The manual triage of scattered logs and metrics can leave teams spending more time firefighting alerts than addressing root causes. This reactive approach underscores the limitations of traditional methods in handling the complexities of modern Kubernetes environments [11][9].
Advantages and Disadvantages
When it comes to monitoring Kubernetes environments, both AI-driven and traditional approaches come with their own set of trade-offs. Traditional monitoring methods are simpler to implement and consume fewer resources upfront, but they can lead to alert fatigue, especially in dynamic environments. On the other hand, AI-driven solutions excel at delivering proactive insights and reducing response times, though they demand more processing power and specialised skills.
For instance, AI-driven alerts have been shown to reduce Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) and Mean Time to Resolve (MTTR) by 67%, while identifying over 92% of simulated threats [9].
Traditional monitoring is no longer sufficient for the scale and dynamic nature of Kubernetes. AI-powered systems are essential for moving from a reactive to a proactive posture.
– Plural.sh [9]
Resource Efficiency
Resource management highlights another key difference. Traditional monitoring may consume fewer resources initially but often leads to inefficiencies, such as over-provisioning. In contrast, AI-driven solutions can optimise resource allocation. For example, Akamai's implementation of AI-driven monitoring resulted in 40–70% savings on cloud costs while also improving engineer productivity through automated Kubernetes optimisation [14].
| Criterion | Traditional Kubernetes Monitoring | AI-Driven Kubernetes Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Anomaly Detection | Relies on static rules and signatures; struggles with unknown zero-daythreats or subtle behavioural shifts [9][7]. |
Uses machine learning to detect deviations from learned baselines; identifies both known and unknown (zero-day) attack patterns [9][1]. |
| Scalability | Becomes harder to manage as clusters grow; requires manual updates to rules and thresholds for new services [9][8]. | Scales automatically by processing large telemetry streams and adapting to new workloads without manual intervention [9][8]. |
| Resource Efficiency | Often leads to inefficient resource use due to over-provisioning or static, inaccurate resource limits [14][9]. | Enhances efficiency with predictive analytics, automated bin packing, and real-time adjustments to resource usage [14][1]. |
| Risk Mitigation | Reactive approach; alerts trigger only after an issue arises, increasing the potential for impact [1][7]. | Proactive approach; identifies risks, such as persistent volume exhaustion, before they cause outages, enabling automated remediation [9][1]. |
These comparisons underline that the right choice depends heavily on the scale and complexity of your Kubernetes environment. As these environments grow, adapting your monitoring strategy to meet operational demands becomes increasingly important - a theme that has been central throughout this discussion.
Conclusion
AI-powered Kubernetes monitoring is transforming infrastructure management by moving beyond reactive responses to enable proactive oversight. Many organisations have already reported improvements in incident response times and operational efficiency, highlighting the potential of AI in this space.
That said, this evolution doesn’t mean abandoning traditional monitoring tools. A combined approach - leveraging familiar tools like Prometheus and Grafana for core metrics alongside AI solutions - has proven to be the most effective strategy. Experts agree on the value of this hybrid model.
If you are already managing Kubernetes you are on the right track with your organisation's progress towards IT automation... AI monitoring and anomaly detection will become a standard tool.– Yuval Dror, Director of Engineering and Head of DevOps, Anodot [4]
To successfully integrate AI into your monitoring framework, start with high-level indicators such as API latency and error rates. Gradually expand to more complex, multi-dimensional analysis. At the same time, monitor the performance of AI models by tracking metrics like accuracy, false-positive rates, and feature distribution drift. This ensures the insights provided by AI remain dependable as your system evolves [1][4][5]. Tools like OpenTelemetry can standardise data collection, helping you avoid vendor lock-in while ensuring consistent telemetry streams for machine learning models [15][2].
Security and privacy are equally critical for effective monitoring. When using external AI backends, prioritise data anonymisation, encrypt telemetry both in transit and at rest, and enforce strict access controls [1][6]. For organisations handling sensitive workloads, deploying local AI backends can ensure complete data sovereignty. The aim is to harness AI’s predictive capabilities without compromising the security of your monitoring infrastructure.
For organisations looking to refine their approach to Kubernetes monitoring and integrate AI-driven solutions, expert guidance can make all the difference. Hokstad Consulting (https://hokstadconsulting.com) offers tailored support to optimise DevOps and cloud infrastructure, helping you stay ahead in this rapidly evolving landscape.
FAQs
How does AI enhance anomaly detection in Kubernetes monitoring?
AI brings a new level of precision to anomaly detection in Kubernetes monitoring by using machine learning to process telemetry and time-series data in real time. This approach makes it possible to spot complex, multi-dimensional patterns and trends that might otherwise slip under the radar.
By automating the detection process, AI improves accuracy while cutting down on false positives, freeing up teams to concentrate on actual issues. On top of that, AI-driven systems offer predictive alerts, enabling teams to tackle potential problems before they affect system performance or uptime.
What challenges come with using AI for Kubernetes monitoring?
Using AI to monitor Kubernetes environments comes with its own set of hurdles. For starters, the sheer volume of data generated by dynamic and short-lived clusters can make both data processing and training AI models a daunting and costly task. On top of that, AI systems can sometimes misinterpret normal workload fluctuations as anomalies, leading to false-positive alerts. This not only causes unnecessary disruptions but can also result in alert fatigue, ultimately eroding confidence in the monitoring system.
Keeping AI models accurate over time is another significant challenge. As workloads evolve or cluster configurations change, frequent retraining becomes necessary, piling on operational complexity. The infrastructure required for AI - such as GPU-enabled nodes - only adds to the expenses. And let’s not forget the need for specialised expertise. Implementing and managing AI tools isn’t straightforward, and the lack of skilled professionals can make integration, governance, and addressing data privacy concerns even tougher.
Hokstad Consulting offers tailored solutions for UK-based organisations to navigate these challenges. They focus on building cost-effective AI pipelines, streamlining model updates through automation, and ensuring governance practices that prioritise security and compliance. By addressing these obstacles head-on, businesses can leverage predictive analytics without compromising the reliability or security of their Kubernetes setups.
Can AI be integrated with traditional monitoring methods for Kubernetes?
AI can work alongside traditional monitoring tools to make them even more effective. Traditional methods often depend on fixed thresholds and manual setups, which can sometimes miss subtle issues or generate unnecessary alerts. AI, on the other hand, brings in machine learning-based anomaly detection and predictive analytics. This means potential problems can be spotted earlier, and the number of false alarms can be reduced.
By blending these two approaches, organisations can create a stronger Kubernetes monitoring system. They get the dependability of tried-and-tested methods along with the flexibility and foresight that AI brings to the table.
