CI/CD pipelines are essential for modern software development, but they come with security risks. AI is transforming how these pipelines are secured by detecting vulnerabilities, automating responses, and reducing manual workloads. Key benefits include:
- Faster detection and remediation: AI tools can identify issues in minutes, compared to hours or days with traditional methods.
- Advanced threat detection: AI models like Transformers and Graph Neural Networks analyse code, logs, and configurations to spot vulnerabilities.
- Automated compliance: AI ensures adherence to security policies and generates real-time compliance reports.
- Reduced false positives: By learning from historical data, AI filters out benign anomalies, focusing only on real threats.
For example, in 2025, FineryMarkets.com improved its security by cutting detection times from 4 hours to 15 minutes and remediation times from 2 days to 30 minutes. AI is not just a tool but a proactive measure that ensures security without slowing down development workflows.
Read on to learn how AI strengthens CI/CD pipelines through real-time monitoring, automated scanning, and predictive maintenance.
::: @figure 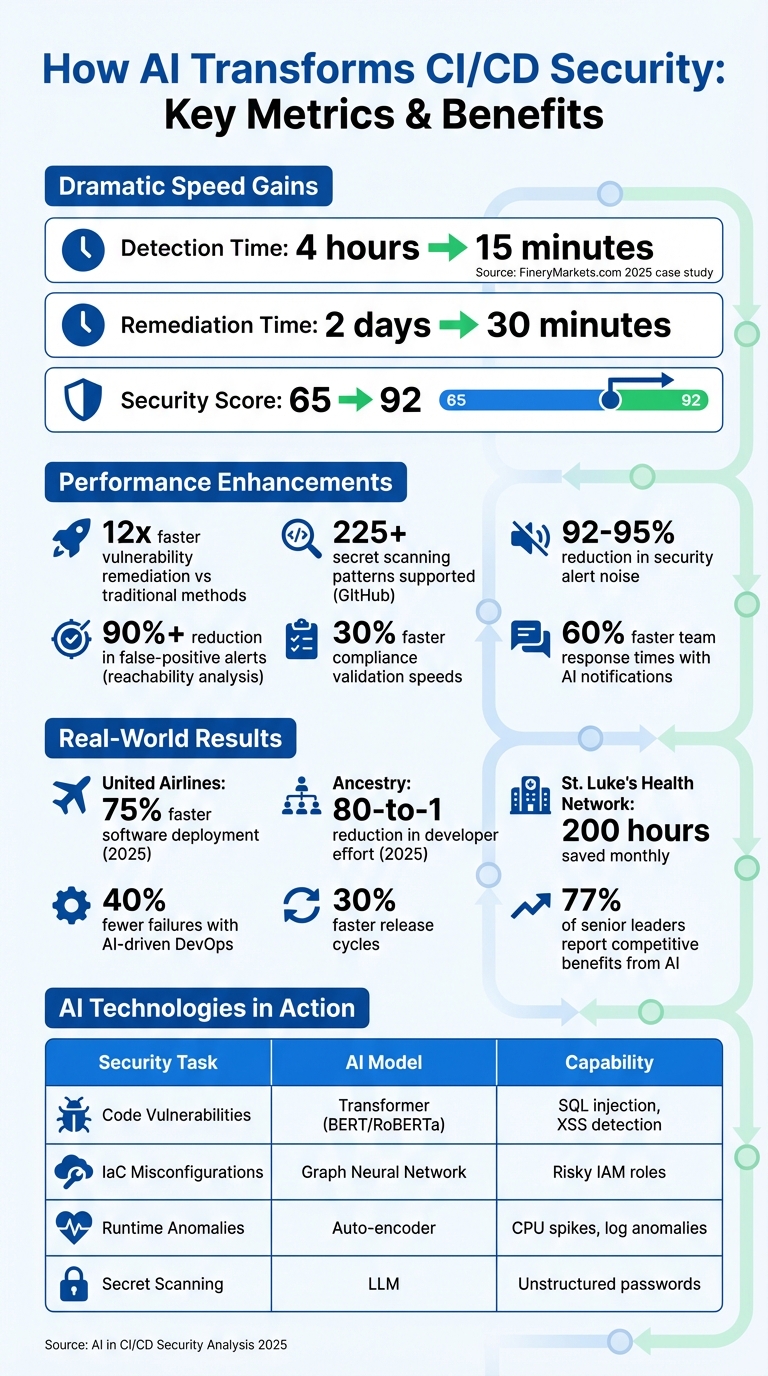 {AI Impact on CI/CD Security: Key Performance Metrics and Benefits}
:::
{AI Impact on CI/CD Security: Key Performance Metrics and Benefits}
:::
Enhancing Quality and Security in CI: Gunjan Patel
AI-Powered Threat Detection and Prevention in CI/CD Pipelines
AI is reshaping how organisations identify and address security threats in CI/CD pipelines by quickly analysing code, dependencies, and configurations. Unlike traditional static tools that rely on rigid rules, AI models such as Transformers (e.g. BERT and RoBERTa) can analyse code commits in real time. This allows them to detect complex vulnerabilities like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and insecure imports [5].
These AI-driven tools can make vulnerability remediation up to 12 times faster than conventional methods [8]. For example, GitHub’s secret scanning programme supports over 225 patterns through a network of 180 partners, showcasing the scale and efficiency AI can bring to security processes [9]. These advancements pave the way for more sophisticated real-time code analysis and automated scanning techniques.
Real-Time Code and Build Log Analysis
AI continuously monitors every code commit and build log as they move through the pipeline, identifying security issues before they can affect production. Large Language Models (LLMs) excel at detecting unstructured secrets, such as leaked passwords, outperforming traditional regex-based methods [9]. At the same time, Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) scrutinise Infrastructure as Code (IaC) files - like Terraform and CloudFormation templates - to identify overly permissive IAM roles or risky configurations that could compromise your infrastructure [5].
Auto-encoders take this a step further by observing build logs and runtime metrics, establishing baselines for normal behaviour and flagging anomalies like CPU spikes or unusual traffic patterns that could signal a breach [5]. AI-enhanced autofix
capabilities amplify this process by suggesting fixes directly in Pull Requests, enabling developers to address vulnerabilities before merging code into the main branch [5].
An example of AI’s dual potential and its risks occurred in December 2025 when Aikido Security uncovered a PromptPwnd
vulnerability in Google’s Gemini CLI repository. The issue arose when untrusted content from an issue was passed into a model prompt, triggering a gh issue edit command that exposed sensitive credentials like GEMINI_API_KEY and GITHUB_TOKEN. Google resolved the vulnerability within four days of its disclosure [7]. This incident underscores both the advantages of AI in CI/CD workflows and the new security challenges it introduces.
Automated Vulnerability Scanning
AI also enhances security by automating the detection of vulnerabilities in third-party dependencies. Software Composition Analysis (SCA) tools, powered by AI, continuously monitor dependencies for risks, such as outdated components, tampered libraries, or impostor packages (e.g. reqeusts
instead of requests
) [10] [3].
This scanning process runs automatically, evaluating each dependency against the latest threat intelligence whenever a developer adds or updates one. By catching vulnerabilities early, AI helps prevent insecure code from entering the codebase, effectively reducing the attack surface. According to Cycode, 63% of security professionals believe more investment is needed in software code security, yet 66% struggle to prioritise findings from multiple security tools [12]. AI addresses this by offering context-aware prioritisation, correlating scan results with runtime context and ownership metadata to focus on the most critical vulnerabilities.
| Security Task | AI Model Type | Detection Capability |
|---|---|---|
| Code Vulnerability Detection | Transformer (BERT, RoBERTa) | Identifies SQL injection, XSS, and unsafe patterns [5] |
| IaC Misconfigurations | Graph Neural Network | Flags risky IAM roles and permissive configurations [5] |
| Runtime Anomaly Detection | Auto-encoder | Detects unusual CPU spikes and log anomalies [5] |
| Secret Scanning | LLM | Finds unstructured passwords and generic secrets [9] |
Automating Security Responses with AI
When a threat is detected in your CI/CD pipeline, AI systems spring into action, triggering containment measures almost instantly. This rapid response eliminates the need to wait for a security analyst to assess the situation and manually intervene. By acting within seconds, AI significantly reduces the time attackers have to exploit vulnerabilities. This proactive approach helps organisations contain threats before they escalate into major breaches.
One example from 2025 demonstrated remarkable improvements in both detection and remediation times [5].
Automatic Rollbacks and Containment
AI doesn't just detect threats quickly - it also handles rollbacks and containment with precision. By monitoring post-deployment metrics like latency spikes, error rates, and unusual network activity, AI can spot anomalies and act accordingly. For instance, it can initiate blue-green or canary rollbacks to prevent disruptions [2]. Beyond this, AI can take more advanced actions, such as adjusting firewall rules, revoking IAM permissions, or isolating compromised service instances when it detects unauthorised API access [2][7].
AI systems also apply smart failure
logic during the CI phase. These agents review code commits for potential issues, such as SQL vulnerabilities or logic errors. If they identify a critical flaw, the system triggers a kill switch
, halting the pipeline with an exit code to ensure the problematic code never reaches the main branch [6].
By embedding the GitHub Copilot CLI directly into a GitHub Action, you can build AI Agents that review your code for security, logic, or product specs. If the Agent detects a critical issue, it triggers a programmatic failure, stopping the merge before a human even reviews it.
This insight comes from Ve Sharma, a Solution Engineer at Microsoft [6].
Instant Notifications and Team Alerts
AI doesn’t just act - it keeps your team in the loop, too. Intelligent notifications summarise root causes and remediation steps, enabling teams to respond up to 60% faster [13].
These systems integrate seamlessly with platforms like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Jira, embedding alerts into developers' daily workflows. They automatically identify application owners and initiate escalation procedures without requiring manual input [15]. For example, Aikido Security's platform reduces security alert noise by 92% to 95% through automated triaging and deduplication [16].
With 92% noise reduction, we got used to 'the quiet' quickly. It's a massive productivity and sanity boost.
This was how one developer from n8n described the impact [16].
For organisations aiming to bolster their CI/CD security with AI-driven automation, Hokstad Consulting offers expert guidance. Their tailored solutions can help integrate these advanced responses into your DevOps pipeline, ensuring your security measures are both effective and aligned with your specific operational needs.
Reducing False Positives and Improving Detection Accuracy
Traditional security tools often overwhelm teams with a flood of alerts, many of which turn out to be harmless. This not only slows down workflows but also wastes valuable time. AI tackles this issue by analysing historical data to differentiate between actual threats and benign anomalies. By studying past build and incident data, machine learning models create a baseline of normal activity, flagging only genuine deviations. To refine detection further, AI employs advanced machine learning techniques, as outlined below.
Machine Learning for Context-Aware Threat Detection
Machine learning models take threat detection to the next level by considering context. For example, Transformers like BERT and RoBERTa analyse code patterns to uncover vulnerabilities such as SQL injection or hard-coded secrets [5]. Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) focus on Infrastructure as Code, pinpointing risky IAM roles while ignoring safe, intentional permissions [5]. Meanwhile, auto-encoders monitor runtime behaviour, identifying true anomalies while filtering out routine fluctuations [5].
A particularly effective approach is function-level reachability analysis, often enhanced by AI. This method determines whether a vulnerable dependency is actually executed within an application, reducing noise and false-positive alerts by over 90% [19]. Additionally, Reinforcement Learning has gained traction for test case prioritisation. It learns which tests are most likely to catch regressions for specific code changes, accounting for 44.64% of research applications in CI/CD testing stages [18].
Continuous Security Monitoring and Compliance Automation
After discussing AI-powered threat detection, let's dive into how continuous security monitoring builds on these capabilities to maintain compliance throughout the pipeline. AI shifts security from being a last-minute hurdle to an integral, ongoing process within the CI/CD pipeline [21]. For example, it evaluates Infrastructure as Code files like Terraform or CloudFormation in real time, identifying risky patterns or misconfigurations before they can make their way into production [5][2]. On top of that, unsupervised learning agents actively monitor logs, metrics, and network traffic, flagging unusual behaviours as they occur [5]. This constant vigilance lays the groundwork for the automated compliance measures we'll explore next.
Automated Compliance Reporting
Real-time monitoring is just the start - AI also streamlines compliance by automating checks across different environments. By converting policies into executable code, AI ensures adherence to frameworks like GDPR, SOC 2, and HIPAA during the build process [4][5]. This approach, called Policy as Code
, uses declarative languages such as Rego or JSON Schema to represent regulatory requirements as software artefacts, ensuring uniformity across systems [13]. Organisations adopting Policy as Code have seen compliance validation speeds improve by 30% compared to traditional manual methods [13]. A real-world example: in 2025, United Airlines boosted software deployment speeds by 75% using the Harness platform. This tool provided automated governance policies and built-in guardrails for developers, transforming their DevOps tools into a secure delivery platform [22]. Additionally, the system generates compliance reports on the fly, offering instant transparency for auditors and leadership - no manual effort required [13].
Policy Violation Alerts
AI's ability to pinpoint policy violations is another game-changer. It analyses code, build logs, and Infrastructure as Code files to predict risky patterns [5]. For instance, when a pull request is submitted, AI-powered tools scan it in real time, flagging hardcoded secrets and explaining the reasons behind the policy breach [20]. Each commit is assigned a risk score, and if that score crosses a set threshold, the pipeline halts automatically to prevent non-compliant code from moving forward [5]. Tools like Gemini in Security Command Centre summarise critical alerts, highlighting misconfigurations, their potential impacts, and recommended fixes for human operators [11]. In 2025, Ancestry experienced an 80-to-1 reduction in developer effort by using Harness to implement new features once and seamlessly apply them across all pipelines. This approach added consistency and governance to their systems while simplifying processes [22].
Continuous security applies policies and testing directly into the CI/CD pipeline, securing infrastructure and applications at each stage in the software development lifecycle.- Jamie Smith, Snyk [21]
Integrating AI Security Tools into CI/CD Pipelines
Integrating AI security tools into your CI/CD pipelines during the pull request stage can help prevent delays while still allowing for thorough scans. These scans typically take a few minutes - longer than traditional linters but essential for detecting deeper vulnerabilities [6][2]. Building on the concept of AI-driven security improvements, this step ensures that security checks are seamlessly embedded into your development process.
To make this work effectively, implement a kill switch
mechanism. Since large language models provide conversational outputs rather than straightforward pass/fail results, configure your AI agent to flag critical vulnerabilities with a specific signal (e.g. THIS ASSESSMENT CONTAINS A CRITICAL VULNERABILITY
). A simple script can then search for this signal and automatically fail the build if necessary. For added security, use limited-permission access tokens, such as GitHub’s Copilot Requests: Read, to manage integrations securely [6].
Integration with Existing CI/CD Platforms
AI security tools can be integrated into CI/CD platforms using command-line tools, offering flexibility as your security requirements evolve [23]. Instead of starting from scratch, take advantage of pre-built configuration packages like CircleCI Orbs or GitHub Actions, which streamline the process of adding scanning features [4][5]. That said, integrating these tools with existing automation frameworks - such as Jenkins, Kubernetes, or Ansible - may require API customisation, especially in environments built around microservices [2].
Different types of AI models are suited to different security tasks. For example, transformer models like BERT and RoBERTa are excellent at identifying code vulnerabilities due to their ability to understand context, outperforming traditional pattern-matching methods [5]. Meanwhile, Graph Neural Networks are particularly adept at spotting risky IAM roles in Infrastructure as Code files [5]. Once the tools are integrated, the next step is to focus on delivering actionable, real-time feedback to developers.
Real-Time Feedback for Developers
Providing real-time feedback directly within developers' workflows is a game-changer. Tools like Snyk, Semgrep, and Aikido can be integrated into popular IDEs like VS Code, IntelliJ, and PyCharm through plugins. These tools offer inline vulnerability detection and remediation suggestions as developers write code, enabling a shift left
approach. This method identifies issues early in the development process, making them quicker and cheaper to fix while maintaining productivity [6][21].
AI agents can also enhance pull requests by automatically commenting on code with context-aware suggestions. In some cases, they can even generate one-click
fixes for developers [25][26]. To avoid overwhelming teams with unnecessary alerts, these tools assess whether a vulnerability is genuinely exploitable by analysing its reachability and the sensitivity of the data it could impact. This ensures that only real risks are flagged [25][26].
For example, St. Luke's University Health Network saw impressive results when they deployed the Phishing Triage Agent within Microsoft Defender. Under the guidance of Associate CISO Krista Arndt, the AI agent autonomously managed thousands of false-positive alerts, saving the security team nearly 200 hours each month [24].
The Phishing Triage Agent is a game changer. It's saving us nearly 200 hours monthly by autonomously handling and closing thousands of false positive alerts.
– Krista Arndt, Associate Chief Information Security Officer, St. Luke's University Health Network [24]
Predictive Issue Detection and Preventative Maintenance
AI doesn't just stop at preventing threats in real time - it also digs into historical build and deployment data to predict potential failures before they happen. By analysing patterns in job outputs, workflow metadata, and past performance, it can spot trends that hint at upcoming problems [27][28]. This is especially handy when dealing with flaky tests that disrupt workflows and cause delays [27]. Unlike traditional linters, which focus on syntax errors, AI goes deeper, identifying more complex issues like logical flaws, security risks, or deviations from product requirements [6]. These predictive capabilities lay the groundwork for a more focused approach to analysing failures, which we'll explore next.
Failure Prediction Based on Historical Data
AI tools can comb through stack traces to locate the exact files and lines responsible for pipeline failures [29]. By linking historical vulnerability data with runtime context, these systems help development teams prioritise fixes for the most urgent threats [12]. This is particularly critical in today’s fast-paced software development environment, where teams have moved from quarterly releases to deploying changes multiple times a day. Automated decision-making has become less of a luxury and more of a necessity [27].
Self-healing CI is a new pattern that uses AI to automatically diagnose failures, apply code changes, re-run the pipeline, and open a pull request.
– Tomas Fernandez, Full-time Writer, Semaphore [28]
On top of predicting failures, AI takes it a step further by scheduling proactive maintenance to prevent issues from escalating.
Scheduling Preventative Maintenance
AI's predictive insights enable teams to address outdated dependencies and insecure cryptography before they lead to breaches [6][12]. It can even take action by applying code fixes and automatically generating pull requests to resolve issues [28][29]. This self-healing capability eases the workload for developers while ensuring pipelines remain stable and reliable. To make the most of this feature, consider configuring your pipeline with Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers. These servers allow AI agents secure access to CI logs and metadata, improving their ability to diagnose and resolve failures [28].
Key Considerations for AI-Driven Security Implementation
When integrating AI into CI/CD security, it's crucial to address governance, data integrity, and task prioritisation. Successfully implementing AI-driven security requires careful planning in these areas.
Governance and Risk Management
Before deploying AI security systems, establish a strong governance framework. The UK-led AI Cyber Security Code of Practice, now the foundation for the ETSI global standard TS 104 223, sets essential security requirements for the AI lifecycle [30][31]. This framework has widespread support, with 80% of stakeholders advocating for government intervention in AI cyber security, and industry respondents backing specific principles with approval rates between 83% and 90% [31].
A comprehensive governance strategy should include AI footprint mapping, documenting all AI assets such as datasets, pre-trained models, pipelines, and endpoints [20][31]. To tackle unique AI risks like data poisoning, model inversion, and indirect prompt injection, use threat modelling frameworks like STRIDE or MITRE ATLAS [20][31][21].
DevOps engineers... are not just builders of infrastructure and pipelines. You are architects of trust.– Eran Kinsbruner, Enterprise Product Marketing Executive, Checkmarx [20]
Adopt Pipeline-Based Access Controls (PBAC) tailored to AI systems to restrict permissions to the minimum necessary for functionality [1][31]. Maintain versioned model registries with tools like MLflow or Kubeflow, ensuring every model in production can be traced back to its training data [20]. Incorporate human-in-the-loop oversight to keep model outputs explainable and auditable for security purposes [31].
With governance in place, the next critical step is ensuring the quality and availability of data.
Data Quality and Availability
AI models depend heavily on high-quality data from historical logs, observability metrics, and telemetry. Poor data quality can lead to unreliable predictions and flawed automation [2]. Organisations using AI-driven DevOps report 40% fewer failures and 30% faster release cycles, but these advantages hinge on robust data foundations [2].
AI models rely on historical log data, observability metrics, and telemetry from distributed systems. Inaccurate outdated or biased datasets lead to poor predictions and unreliable automation.– Gaurav Gupta, Founder and CEO, Squareboat [2]
Combat model drift - where predictions degrade over time due to changing conditions - by continuously validating and retraining models with MLOps tools [2]. Monitor telemetry data to detect performance issues early, and use tools like the Adversarial Robustness Toolbox to test resilience against corrupted inputs [20].
A model registry can provide instant rollbacks if data quality deteriorates [20]. Tools like Git LFS help track large datasets and artefacts, ensuring training data is versioned and reproducible [20]. Additionally, agentic AI tools can autonomously scan codebases and pipeline metadata to maintain accurate inventories, addressing visibility gaps in large-scale pipelines [20].
With governance and data quality secured, teams can shift their focus to tackling the most critical security challenges.
Focus on High-Priority Security Tasks
AI automation allows security teams to concentrate on high-stakes tasks rather than routine operations. Proper deployment not only automates threat management but also enhances human decision-making in critical areas.
| AI Security Task | Human Role (High-Priority) | AI Role (Automated) |
|---|---|---|
| Code Review | Analysing complex logic and architectures | Identifying syntax errors and known CVEs [20][2] |
| Incident Response | Strategic containment and post-mortem analysis | Automated rollbacks and instant alerts [20][5] |
| Threat Detection | Contextualising risks within business processes | Analysing large log volumes for anomalies [11][14] |
| Governance | Developing risk management frameworks | Maintaining asset inventories and compliance reports [20][11] |
Security teams should prioritise threat modelling for AI systems using frameworks like STRIDE or MITRE ATLAS [20]. Conduct adversarial testing and red teaming to simulate attacks such as prompt injection, model inversion, and data poisoning [20]. Update incident response plans to cover scenarios like compromised models, poisoned data pipelines, and unintended model behaviour [20].
Implement measures like prompt sanitisation to block injection attacks and output filtering to prevent harmful content exposure, especially for public-facing AI systems [20]. Use pre-commit hooks and CI/CD gates to detect and block hardcoded secrets or API keys before they are merged [20]. Foster collaboration between data scientists and AppSec teams through training on AI-specific threats [20].
Traditional AppSec tooling doesn't account for risks like adversarial prompts, poisoned datasets, insecure plugins, broken or insecure access controls, emergent model behaviours, or additional supply chain vulnerabilities.– Eran Kinsbruner, Enterprise Product Marketing Executive, Checkmarx [20]
Conclusion
Integrating AI into CI/CD pipelines shifts security from being a reactive hurdle to becoming a proactive shield. With real-time threat detection, AI can scan code, configurations, and logs in mere milliseconds, identifying vulnerabilities well before they reach production [5]. Automated remediation speeds up the process, enabling teams to resolve issues up to twelve times faster compared to manual methods [8]. Meanwhile, continuous monitoring ensures anomalies are caught early, triggering immediate rollbacks when necessary [5].
Take the example of FineryMarkets.com. In September 2025, they managed to slash their Mean Time to Detect from 4 hours to just 15 minutes and reduced their Mean Time to Remediate from 2 days to a swift 30 minutes. These improvements boosted their security score from 65 to 92, all thanks to an AI-enabled DevSecOps pipeline [5]. These gains highlight the power of AI’s ability to process data and recognise patterns rapidly [17].
We are entering an era where CI/CD pipelines don't just compile code - they understand it.– Ve Sharma, Solution Engineer, Microsoft [6]
However, while AI brings immense benefits, it's crucial to strike a balance between automation and human oversight. To maintain robust security, organisations must limit AI agent permissions, sanitise all inputs, and ensure human review for critical decisions [7][17]. As deployment frequencies continue to rise, AI alleviates the burden of repetitive tasks, freeing teams to focus on higher-level priorities like threat modelling and incident response [17].
Beyond operational improvements, adopting AI-driven security in CI/CD workflows offers a strategic advantage. It accelerates deployment cycles, reduces manual workloads, and provides thorough coverage across code, infrastructure, and runtime. With 77% of senior business leaders reporting competitive benefits from AI adoption, the real question isn't whether to embrace AI-driven security, but how quickly and effectively it can be implemented [17].
For more insights on optimising AI-powered CI/CD security, visit Hokstad Consulting.
FAQs
How does AI help reduce false positives in CI/CD tool security?
AI brings a new level of precision to CI/CD tool security by analysing extensive datasets to spot patterns and detect unusual behaviour. This makes it easier to separate actual threats from routine activities, cutting down on false alarms.
Using machine learning models, AI evolves its detection skills over time, staying ahead of emerging threats while reducing unnecessary alerts. This allows DevOps teams to concentrate on tackling real security challenges instead of getting bogged down by irrelevant notifications.
Which AI models are commonly used to detect threats in CI/CD pipelines?
AI models used for spotting threats in CI/CD pipelines often leverage machine learning methods. By analysing historical pipeline data, these models are trained to spot unusual patterns or behaviours in real-time, making it easier to identify and address potential security risks as they arise.
The types of models may differ, but the emphasis is usually on algorithms built for anomaly detection and predictive analysis, specifically adapted to the distinct nature of CI/CD workflows.
How does AI enhance compliance automation in CI/CD processes?
AI takes compliance automation in CI/CD pipelines to the next level by constantly examining code, dependencies, and pipeline setups against established policies and regulatory requirements. It can pinpoint violations, propose or implement corrections, and produce audit-ready documentation, ensuring compliance is upheld throughout the development process.
By cutting down on manual tasks and simplifying enforcement, AI not only speeds things up but also reduces the chances of human mistakes. This helps organisations maintain strong security measures and adhere to regulations effectively within their software delivery workflows.
