AI is transforming compliance auditing by automating repetitive tasks, enabling real-time monitoring, and improving accuracy. Unlike manual methods, which are time-consuming and prone to errors, AI tools continuously scan data, detect anomalies, and ensure regulatory compliance more efficiently. This shift allows auditors to focus on addressing risks rather than gathering evidence.
However, AI introduces challenges such as data privacy concerns, cybersecurity risks, and potential bias in algorithms. To manage these, organisations must implement strong governance, validate AI models regularly, and ensure transparency.
Key points:
- Efficiency: AI reduces audit time and costs by automating data collection and monitoring.
- Accuracy: AI identifies risks across large datasets, but depends on high-quality data.
- Scalability: AI systems handle complex, multi-jurisdictional operations without extra staff.
- Risks: Privacy, cybersecurity, and bias in AI models require careful oversight.
Blending AI with human judgement offers the best results, enabling organisations to stay compliant while managing risks effectively.
1. AI-Driven Compliance Auditing
Efficiency
AI-powered auditing has revolutionised the way compliance teams handle repetitive tasks, slashing the time needed to complete audit cycles. Instead of manually gathering and consolidating data from various systems, AI tools take on these responsibilities, streamlining the process. This allows teams to conduct more audits without the need for overtime or hiring extra consultants.
For example, AI systems can process logs from multiple access management platforms daily. They swiftly identify unusual patterns, such as unexpected privilege escalations or repeated failed login attempts, enabling compliance teams in the UK to shift from manual sampling to focusing on exceptions. For organisations operating in cloud-native environments, companies like Hokstad Consulting offer solutions that integrate AI-driven compliance checks directly into CI/CD pipelines. This means misconfigurations in infrastructure-as-code can be detected and resolved before deployment.
The results? Fewer audit hours, lower costs, and early identification of issues that can prevent hefty regulatory fines or service disruptions. This level of efficiency leads to audits that are not only faster but also more reliable.
Accuracy
AI brings a new level of precision to compliance auditing by consistently applying standard rules and processing data without human error. In access control, this means correlating user accounts across platforms, spotting dormant or orphaned accounts, and identifying risky role combinations that could violate segregation of duties. Machine learning models, trained on past incidents, can even flag high-risk transactions for deeper examination - going beyond basic rule-based checks.
Automated tools also generate reports that align with regulatory frameworks like UK GDPR and FCA rules, ensuring consistency and minimising errors often seen in manual documentation. Every action is logged in detail, creating a clear evidence trail for UK regulators and external auditors. However, to maintain accuracy, organisations must ensure high-quality input data and regularly validate AI models to avoid amplifying existing biases or errors.
Scalability
AI-driven compliance platforms are designed to scale effortlessly, extending their oversight across vast amounts of data. Once the necessary data connectors and models are set up, a single AI system can monitor controls across multiple UK and international operations, from on-premises systems to complex multi-cloud setups. The results are then consolidated into unified dashboards, giving teams a clear and continuous view of compliance performance. This is especially useful for businesses navigating multiple regulatory requirements, as it allows for ongoing monitoring rather than relying solely on annual audits.
Specialist providers like Hokstad Consulting can further enhance scalability by designing systems that seamlessly integrate AI monitoring into cloud-native and hybrid environments. This ensures that as businesses grow, their compliance oversight keeps pace - without spiralling costs.
Risks
While AI offers numerous advantages, it also introduces risks that need careful management. For instance, many AI tools handle sensitive personal and access-control data, raising concerns about compliance with UK GDPR. The increased use of AI systems, APIs, and data pipelines can also expand an organisation’s attack surface, introducing new cybersecurity vulnerabilities.
Bias in AI models is another concern. Poor-quality training data could lead to unfair or inconsistent outcomes, such as misflagging activities or creating potential discrimination issues. Additionally, the evolving landscape of AI-specific regulations in the UK and globally adds complexity for compliance teams trying to stay ahead.
To address these challenges, organisations should start with formal data protection impact assessments before deploying AI tools. Strong access controls and encryption must be enforced, and human oversight should be included for critical decisions. Regular validation and retraining of AI models, along with detailed documentation of their use, are essential. Finally, establishing governance frameworks that align AI practices with both UK regulatory expectations and internal risk strategies is key to managing these risks effectively.
Artificial Intelligence in Audit | Efficiency, Risk & Governance.
2. Manual Compliance Auditing
Even with advancements in AI, traditional manual auditing still holds its ground, though it comes with clear limitations.
Efficiency
Manual auditing is a resource-heavy and time-consuming process. In the UK, companies often dedicate between 200–500 auditor hours per quarter, with full audits costing anywhere from £50,000 to £100,000. These efforts can divert attention away from more strategic priorities. According to White & Case's 2025 Global Compliance Risk Benchmarking Survey, 74% of respondents have moved away from manual processes due to constraints on efficiency and resources [7].
Accuracy
Human-driven audits are prone to errors caused by fatigue, oversight, or inconsistent judgment. Unlike AI systems that apply rules consistently, manual reviews often miss critical anomalies. For example, when auditors sample transactions or access logs manually, anomalies outside the sample can easily go unnoticed. This is particularly problematic in environments that handle thousands of events daily.
Manual processes also fall short when it comes to identifying emerging risks. ISACA highlights that traditional audit functions, which rely on fragmented and siloed data, struggle to detect risks promptly. This can leave organisations exposed to regulatory fines. For instance, UK GDPR penalties average £4.2 million, with many fines linked to issues that manual reviews failed to identify.
Scalability
Scaling manual audits is another significant challenge. As businesses grow and expand into new jurisdictions, the need for more auditors makes manual processes increasingly impractical. In the financial sector, for instance, adhering to new EU regulations like DORA often requires hiring additional staff, which can slow down compliance efforts. Similarly, healthcare providers experience backlogs when manual audits can’t keep up with the sheer volume of electronic health records.
The UK compliance sector is also grappling with a 25% vacancy rate in compliance roles, further straining resources. Because manual audits are typically conducted at set intervals, they can leave gaps in compliance coverage, amplifying operational risks.
Risks
While manual audits avoid some risks tied to technology - like AI bias or concerns over data privacy when using external tools - they introduce their own set of challenges. Human error is a major issue, often leading to missed obligations, inconsistent processes, and delayed fraud detection. Sample-based testing inherently limits the scope of audits, meaning organisations must accept that some exceptions will go unnoticed.
Handling sensitive data manually also poses privacy and cybersecurity risks. Spreadsheets and manual sampling are particularly vulnerable to errors, especially in complex IT environments or when managing access controls. For UK organisations under the scrutiny of regulators like the FCA or ICO, these vulnerabilities can result in regulatory penalties and reputational harm.
Need help optimizing your cloud costs?
Get expert advice on how to reduce your cloud expenses without sacrificing performance.
Advantages and Disadvantages
::: @figure 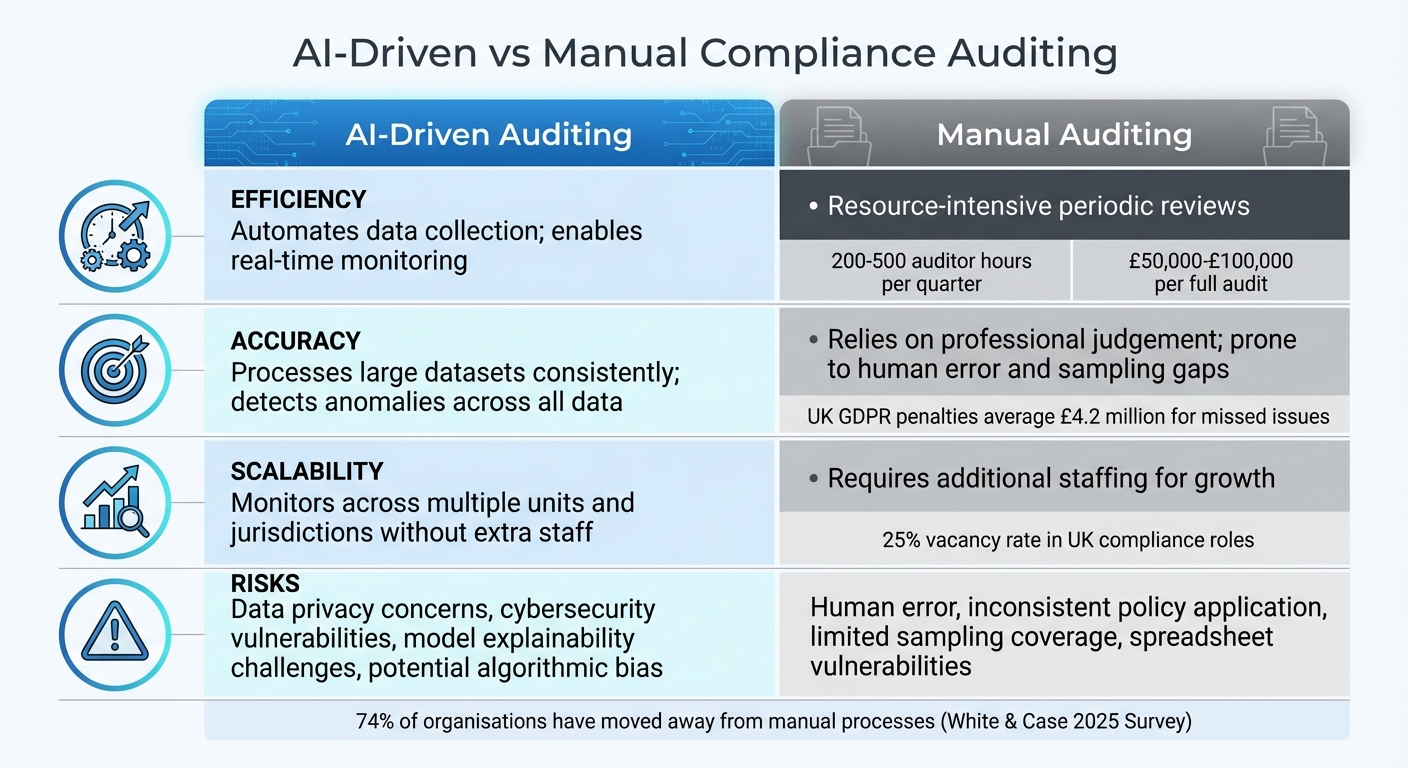 {AI vs Manual Compliance Auditing: Efficiency, Accuracy, Scalability and Risks Compared}
:::
{AI vs Manual Compliance Auditing: Efficiency, Accuracy, Scalability and Risks Compared}
:::
This section dives into the strengths and challenges of AI and manual compliance auditing, highlighting how each approach serves distinct purposes.
AI stands out for its ability to automate tasks, delivering continuous, real-time monitoring to catch issues as they arise. On the other hand, manual auditing offers the benefit of human judgement and contextual insight - essential for interpreting ambiguous regulations, understanding organisational culture, and navigating grey areas where rules may be unclear.
When it comes to accuracy, the difference becomes even more apparent. AI excels at processing massive datasets, identifying anomalies that manual methods might overlook. However, its effectiveness hinges on the quality of its data and model design. Flawed or incomplete training data can lead to blind spots. Manual audits, while prone to human error, bring professional scepticism into play, allowing auditors to challenge and interpret findings with nuance.
Scalability is another area where AI has a clear edge. AI systems can monitor controls across multiple units and jurisdictions without the need for additional staff. For UK organisations managing intricate multi-cloud environments or adapting to shifting regulatory frameworks, AI-driven auditing can handle the complexity with ease. In contrast, manual auditing relies on narrower sampling and requires more staff, making it harder to keep up with growing data volumes and intricate systems.
The discussion wouldn’t be complete without addressing risks. AI introduces concerns around data privacy - especially if input data is used for training - cybersecurity vulnerabilities from integration points, and the challenge of explaining complex model decisions to regulators [3][6][8]. Manual auditing avoids these tech-specific risks but is more prone to oversights caused by limited sampling, inconsistent application of policies, and the pressure of tight deadlines [1][2]. For UK organisations leveraging advanced DevOps and cloud-native technologies, firms like Hokstad Consulting recommend creating secure AI-based monitoring pipelines. These pipelines can integrate with CI/CD workflows and access-control systems, helping to meet both technical and governance requirements.
| Aspect | AI-Driven Auditing | Manual Auditing |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Automates data collection; enables real-time monitoring [1][2] | Resource-intensive periodic reviews |
| Accuracy | Processes large datasets consistently; detects anomalies [1][4] | Relies on professional judgement; prone to human error |
| Scalability | Monitors across units and jurisdictions without extra staff [1][2][5] | Requires additional staffing for growth |
| Risks | Data privacy, cybersecurity, and model explainability concerns [3][6][8] | Human error, inconsistent policies, limited sampling [1][2] |
Conclusion
AI-powered compliance auditing offers a practical way for organisations to improve efficiency, precision, and scalability by enabling continuous, real-time oversight. By automating tasks like data collection and validation, audit teams can focus more on strategic risk analysis, all while ensuring transparency and compliance with UK regulations such as GDPR.
The most effective approach blends AI's processing capabilities with human judgement. Organisations can start by piloting automated solutions for routine compliance checks, gradually expanding their use while maintaining strong governance frameworks. To ensure these systems remain reliable, regular audits should prioritise areas like data quality, model transparency, and security measures.
For organisations navigating complex, multi-cloud environments and evolving regulatory requirements, partnering with experts can simplify the journey to fully integrated AI auditing. Hokstad Consulting offers AI strategy services, cloud security audits, DevOps transformation, and cloud cost optimisation. Their expertise in automated CI/CD pipelines and Infrastructure as Code provides the technical foundation needed to securely implement AI-driven compliance tools.
FAQs
How can AI make compliance auditing more efficient?
AI has transformed compliance auditing by automating the analysis of complex data. This capability allows organisations to handle massive amounts of information both quickly and accurately, cutting down the need for laborious manual reviews. It also enhances the ability to spot anomalies or risks with much greater precision.
By simplifying these tasks, AI not only speeds up the auditing process but also reduces the likelihood of human error, ensuring compliance standards are met more reliably. Plus, it frees up valuable team resources, letting them concentrate on resolving critical challenges instead of being tied up with repetitive, routine tasks.
What risks should organisations consider when using AI in compliance auditing?
AI undoubtedly has the potential to improve compliance auditing, but it's not without its challenges. One major concern is the possibility of bias or inaccuracies in algorithms. If the data or models are flawed, this could result in unfair or incorrect evaluations. Another issue is the lack of transparency in how AI systems make decisions, which can make it hard to trace how specific conclusions are reached - raising questions about accountability.
There's also the danger of becoming too reliant on automation. While AI can handle many tasks efficiently, human judgement is often needed to navigate complex or nuanced situations that algorithms might not fully grasp. Additionally, data privacy concerns come into play, especially when sensitive information is involved. Errors in AI systems could lead to serious consequences, potentially undermining compliance efforts.
To address these risks, organisations must focus on careful implementation of AI tools and ensure they undergo regular auditing. This helps maintain accuracy, fairness, and accountability in compliance processes.
How can organisations maintain accuracy and fairness in AI-powered compliance audits?
To ensure AI-powered compliance audits remain accurate and impartial, organisations need to focus on rigorous validation of their AI models. This includes making sure these models are trained on diverse and representative datasets. Regularly reviewing the outputs generated by AI is equally important to spot and address any biases or inconsistencies that may arise.
Human oversight is an essential counterpart to AI systems, helping to ensure decisions are not only dependable but also make sense within their specific context. By implementing transparent and explainable AI processes, organisations can foster trust and accountability. This approach makes it easier to pinpoint potential problems and take corrective measures when necessary.
