DevOps teams often struggle to balance rapid software delivery with strict regulatory compliance. This guide explains how to integrate automated compliance scanning into CI/CD pipelines for containerised environments, ensuring security and adherence to standards like GDPR, SOC 2, ISO 27001, and PCI-DSS without slowing down development.
Key Takeaways:
- Why Compliance Matters: Avoid fines and protect reputation by meeting regulatory demands for secure software practices and breach reporting.
- Challenges in CI/CD: Balancing speed with security, managing false positives, and maintaining audit logs amidst frequent changes.
- Step-by-Step Guide:
- Build-Stage Scanning: Use tools like Trivy to catch vulnerabilities early.
- Security Gates: Automate policy enforcement to block non-compliant code.
- Pre-Deployment Validation: Validate compliance with runtime checks and image signing.
- Audit Logging: Centralise logs for traceability and meet retention rules with secure storage.
By automating scans, enforcing policies, and maintaining detailed logs, you can secure your pipeline while staying compliant. Tools like Trivy, Clair, and AWS Inspector can simplify this process.
DevSecOps Governance: Automate Compliance Checks in Your CI/CD Pipeline
Prerequisites for Adding Compliance Scanning
Before integrating compliance scanning into your workflow, it's essential to have a fully automated CI/CD pipeline in place. Platforms like GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, Jenkins, or Azure DevOps should already be managing your build, test, and deployment processes. Your pipeline must efficiently handle containerised workflows, relying on tools like Docker or BuildKit for container builds, and a source code repository for version control. You'll also need a container registry - such as Docker Hub, Amazon ECR, GitHub Container Registry, or GitLab Registry - that supports API access for automated scanning and image tagging. The following sections outline the necessary tools, compliance standards, and scanning options to get started.
Required CI/CD Setup and Tools
Your CI/CD setup should allow for automation through CLI commands or YAML configuration files, ensuring scanning tools can run seamlessly without manual input. For containerised workflows, this means integrating with a registry that supports both access controls and image scanning. For instance, Amazon ECR can automatically trigger vulnerability scans via AWS Inspector, while GitHub Container Registry works effortlessly with GitHub Actions workflows. Make sure your pipeline can perform the following tasks without interruption:
- Pull container images.
- Execute scans.
- Enforce security checks at critical stages like build, test, and pre-deployment.
This ensures compliance checks are embedded into your pipeline, maintaining security without slowing down development.
Compliance Standards to Address
Compliance requirements vary depending on your industry, so it's important to align your pipeline controls with the relevant standards. Here are some examples:
- SOC 2: Focuses on security, availability, and automated vulnerability management.
- ISO 27001: Requires secure development practices and robust logging mechanisms.
- GDPR: Emphasises privacy-by-design principles and breach detection.
- PCI DSS: Mandates regular vulnerability scanning and configuration baselines.
Many organisations now adopt automated checks that align with multiple frameworks simultaneously, such as SOC 2, ISO 27001, NIST, and CIS Benchmarks. This approach avoids redundant work and supports compliance across various standards.
Scanning Tools to Consider
The choice of scanning tools depends on your specific environment and compliance needs. Below are some popular options:
- Trivy: An open-source scanner that covers containers, file systems, infrastructure-as-code, and SBOMs. It integrates easily into pipelines via its CLI and supports a wide range of use cases.
- Clair: Specialises in static analysis for container vulnerabilities and works well with registries like Docker Hub and Quay.
- AWS Inspector: Automates vulnerability scans for EC2 instances and ECR images, focusing on CVEs and compliance checks within AWS ecosystems.
Unlike traditional SAST or DAST tools, container scanners like Trivy and Clair analyse image layers to uncover vulnerabilities, secrets, and malware. When selecting a tool, prioritise those that offer machine-readable outputs (e.g., JSON) for easy automation and that integrate with your registry, orchestrator, and ticketing systems. This ensures a streamlined workflow while meeting your compliance goals.
Step-by-Step Guide to Adding Compliance Scanning
::: @figure 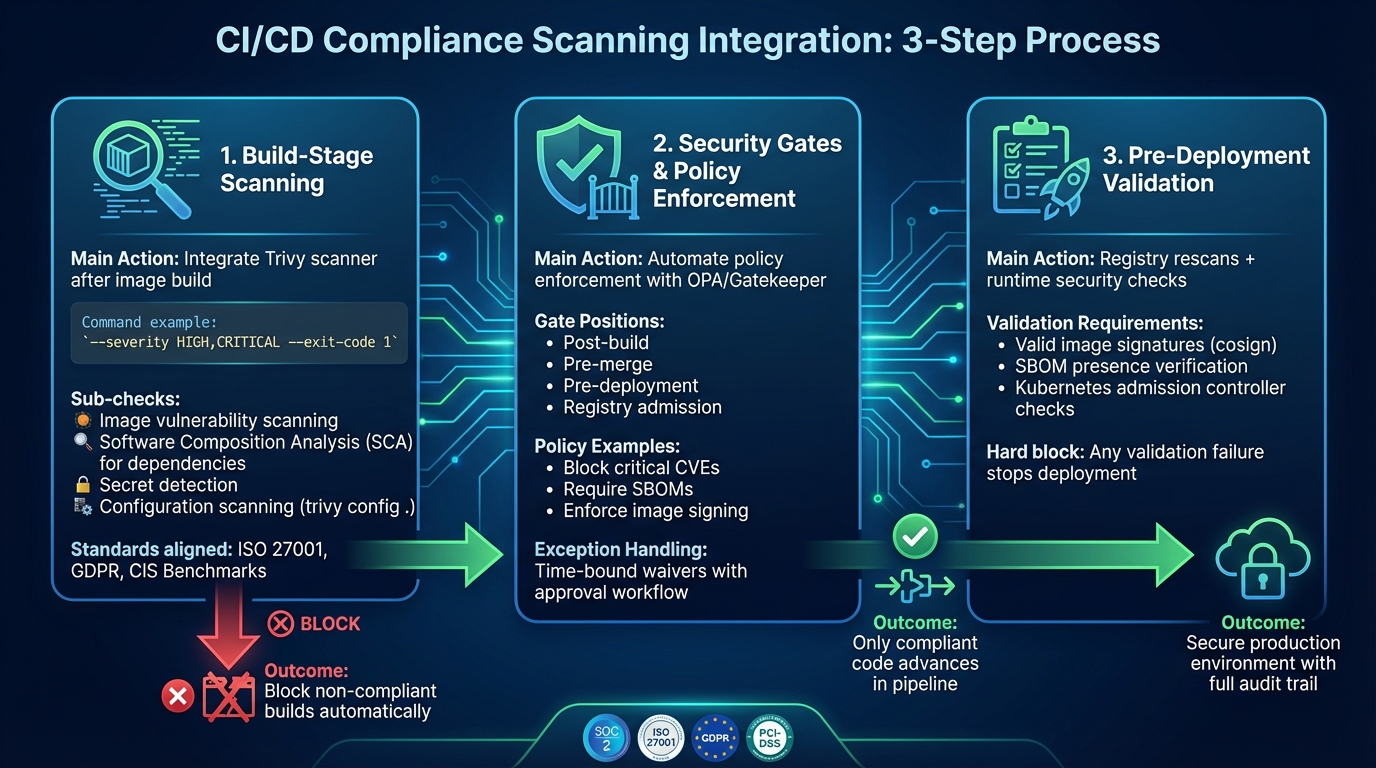 {3-Step Process for Adding Compliance Scanning to CI/CD Pipelines}
:::
{3-Step Process for Adding Compliance Scanning to CI/CD Pipelines}
:::
Incorporating compliance scanning into your workflow involves three key stages: build-stage scanning, security gate enforcement, and pre-deployment validation. These checkpoints help catch vulnerabilities and policy violations before they reach production. By following these steps, you can establish a secure and compliant pipeline that aligns with regulatory requirements.
Step 1: Add Scanning to the Build Stage
Start by integrating a command-line scanner like Trivy immediately after building your image. Configure your CI tool - whether it's GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, Jenkins, or Azure DevOps - to run Trivy with the command --severity HIGH,CRITICAL --exit-code 1. This setup ensures that any build failing to meet policy conditions is automatically blocked, halting the pipeline.
Go beyond image scanning by adding Software Composition Analysis (SCA) for dependency files like package-lock.json and secret detection tools to prevent committing sensitive credentials. Trivy also includes a configuration scanner (trivy config .) to validate Dockerfiles and Kubernetes manifests against CIS Benchmarks. This helps spot issues such as containers running as root or using untrusted registries. These checks align with standards like ISO 27001 and GDPR, making them especially relevant for UK organisations with strict regulatory requirements. Combining these scans ensures your build stage addresses a broad range of compliance needs.
Step 2: Configure Security Gates and Policies
Security gates provide automated policy enforcement with severity-based thresholds, ensuring compliance issues are flagged without unnecessarily disrupting development. Tools like Open Policy Agent (OPA) or OPA Gatekeeper allow you to define machine-readable rules, such as blocking deployments with critical CVEs or images missing SBOMs and signed provenance. These gates can be positioned at critical points in your pipeline - post-build, pre-merge, pre-deployment, and registry admission - to maintain compliance throughout.
To balance security with usability, implement exceptions like time-bound waivers or change tickets for overriding blocks. For instance, if a gate fails due to 3 critical CVEs over policy threshold
, the system can provide detailed remediation steps, such as upgrade paths or configuration fixes. Overrides should require approval from security or compliance teams, ensuring accountability. Regularly review and update policies to reflect evolving threats, and use metrics like failure rates and mean time to remediation to fine-tune your approach. With these gates in place, only compliant code advances further in the pipeline, setting the stage for final validation.
Step 3: Validate Compliance Before Deployment
Before deploying, conduct registry rescans and runtime security checks. Admission controllers, such as Kubernetes ValidatingAdmissionWebhook, can enforce requirements like valid image signatures and the presence of SBOMs. Treat any validation failure as a hard block, providing clear remediation steps to resolve the issue.
Incorporate image signing tools like cosign after successful builds and scans, storing signatures in your container registry. Ensuring that every image is signed and accompanied by a valid SBOM creates an auditable trail from commit to production. This is especially critical for regulated industries like finance and healthcare in the UK, where quick identification of affected services during a vulnerability disclosure is essential. By completing these steps, you secure your production environment and maintain compliance with industry regulations.
Need help optimizing your cloud costs?
Get expert advice on how to reduce your cloud expenses without sacrificing performance.
Setting Up Audit Logging and Reporting
Once compliance scanning is in place, the next step is to establish thorough audit logging and reporting. This ensures continuous oversight and provides traceability for all processes. A centralised logging and reporting framework is key to demonstrating ongoing compliance. By consolidating data from source control, CI runners, container registries, and Kubernetes into one searchable platform, you can meet auditors' expectations efficiently [3][6]. Without this centralisation, tracking events becomes a cumbersome, manual task.
Critical Events to Log
Your logging system should capture essential data, such as:
- Pipeline trigger details: commit IDs, branches, triggering user, and timestamps.
- Security tool scan results: tool versions, pass/fail statuses, and detailed findings.
- Policy-enforcement actions: for instance, builds blocked due to vulnerabilities or licence issues.
- Approvals or manual interventions: include justifications and associated change tickets.
These logs not only ensure traceability and accountability but also help meet frameworks like ISO 27001, SOC 2, and GDPR [3][4]. To streamline this process, configure your CI platform (e.g., GitLab Audit Events, GitHub Enterprise audit log, or Jenkins Audit Trail plugin) to forward logs to a central collector. Use tools like Fluentd or Filebeat for this purpose, and ensure that pipeline jobs produce structured JSON logs tagged with correlation IDs for seamless end-to-end tracing. These logs will then feed into the broader reporting framework.
Log Retention and Access Controls
Maintain CI/CD and security logs for one to two years, or up to six years if required [3][4]. Implement tiered storage for efficiency:
- Hot Storage: Keep logs readily accessible for 30 to 90 days for active operations.
- Warm Storage: Retain logs for 6 to 12 months for cost-effective access.
- Cold Storage: Use this for long-term retention needs.
Apply role-based access control (RBAC) to ensure that developers can only access their own pipeline logs, while security and compliance teams have broader visibility. Limit write access to automated log collectors and use append-only indices or WORM (Write Once, Read Many) storage to prevent tampering. This ensures logs remain admissible as evidence. Additionally, under GDPR, document and justify retention schedules in your Record of Processing Activities, avoiding the unnecessary storage of personal data.
Creating Compliance Dashboards
Dashboards are an excellent way to visualise and monitor compliance metrics. Track key indicators such as:
- Pass rates for compliance gates.
- Vulnerability severity distribution across services and environments.
- Time taken to resolve issues.
- Frequency of exceptions or overrides.
Use tools like Kibana, Grafana, or cloud-native platforms to query structured logs, organising metrics by pipeline, service, and team. Dashboards should provide engineers with actionable insights while offering executives a clear overview of risk levels and progress on remediation. To ensure timely responses, integrate alerting systems (e.g., Slack or Microsoft Teams) so that any breaches of compliance thresholds are flagged immediately, rather than being discovered during periodic reviews.
Best Practices for Maintaining Compliance
Automate Scans and Updates
Automating scans and updates is a crucial step in maintaining compliance. Set your CI/CD pipelines to automatically run scans on every merge, nightly, and before deployment [1][2]. Instead of relying on ad-hoc scripts, use CI job templates or pipeline-as-code. This ensures consistency across projects and simplifies rolling out updates.
Keep your scanning tools and vulnerability databases current by updating scanner images and signatures weekly, especially for production workloads [1][2]. Automate dependency updates by scheduling CI jobs that refresh base images and test new versions in staging before moving them to production. This proactive approach helps catch newly discovered CVEs without waiting for manual checks and demonstrates a commitment to continuous improvement to auditors [4].
Set up health checks to alert you if scans fail to run within a 24-hour window or if critical vulnerabilities are detected. For critical or high-severity vulnerabilities, block the pipeline; for medium or low-severity findings in non-production branches, issue warnings instead of hard failures [1][4]. This strategy reduces alert fatigue while ensuring stricter control over production releases. Once your automation is in place, keep refining your controls to address emerging risks.
Review Policies Regularly
Compliance is not a one-time effort. Regulations, threats, and organisational priorities change over time. Conduct quarterly reviews with key stakeholders to ensure your policies remain effective [3][4]. Before each review, analyse data from dashboards and audit logs to identify frequent policy violations, recurring false positives, or missed risks. This analysis will help you adjust policies that are too strict, too lenient, or misaligned with actual usage [3].
Update policies to reflect changes in regulations. For instance, new ICO guidance on data minimisation could necessitate additional checks for microservices handling personal data. Similarly, FCA rules for financial services may require tighter approval workflows for production changes [4][5]. Document all policy changes in version control, providing clear explanations for adjustments. This transparency makes it easier for auditors to understand why thresholds or controls were updated [3][4]. By aligning your compliance framework with your CI/CD pipeline, you ensure it evolves alongside your organisation's needs.
How Hokstad Consulting Can Help

Hokstad Consulting offers tailored solutions to help organisations integrate automated compliance scanning into their CI/CD pipelines efficiently. Their expertise in cloud cost engineering enables them to optimise scan frequency, job parallelism, and cache usage, reducing unnecessary build times and cloud costs - all while meeting regulatory requirements [1][3]. For UK-based organisations managing hybrid cloud environments, they design scanning systems that keep sensitive data within the region, meeting UK and European data sovereignty standards [1].
In addition to automation, Hokstad Consulting helps establish governance frameworks that clarify ownership of CI/CD compliance controls, aligning them with UK regulations like GDPR accountability principles [3][4]. They organise regular policy review workshops to translate new regulatory guidelines into actionable pipeline rules and create custom reporting dashboards. These dashboards consolidate scan results, exceptions, and remediation statuses, making it easier to prepare for audits and report risks at the board level [1][3].
Their AI-driven solutions further enhance compliance efforts by automating the triage of scan findings, suggesting remediation steps, and prioritising issues based on their impact. This approach helps teams manage the increasing complexity of systems and regulations [1][2]. With Hokstad Consulting’s guidance, you can maintain the integrity and compliance of your CI/CD pipelines while staying ahead of evolving challenges.
Conclusion
Summary of Steps
Adding compliance scanning to your CI/CD pipeline boils down to four main steps, as outlined earlier. First, incorporate tools like Trivy or Clair at the build stage using CLI or YAML configurations. Next, introduce security gates to halt pipelines if critical vulnerabilities or misconfigurations are detected. Third, ensure compliance validation is completed prior to deployment. Finally, set up audit logging for critical events, including retention policies and dashboards for monitoring.
Detecting vulnerabilities early not only enhances security but also speeds up development cycles. By addressing issues before they reach production and adhering to standards like SOC 2, ISO 27001, GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS through automated logs and policy enforcement, you can save costs and meet stringent regulatory requirements effectively.
Maintaining Compliance Over Time
To maintain compliance, an ongoing strategy is essential. Regular automated scans, continuous policy reviews, and active monitoring ensure your systems remain secure as threats evolve. Using policy-as-code is a great way to maintain consistency and scale as your organisation grows.
This proactive approach bolsters security, keeps operations efficient, and ensures regulatory alignment. Tools like SonarQube for static application security testing (SAST), HashiCorp Vault for secrets management, and real-time compliance dashboards can help maintain these standards. Early detection and automated fixes minimise costs while ensuring deployments stay on schedule.
Next Steps
With a solid implementation plan in place, the next phase involves optimisation and continuous improvement. Audit your pipelines to identify any scanning gaps, paying close attention to high-risk stages. Start by prioritising these areas and piloting scanning integrations before rolling them out across the organisation. Embed policy-as-code into your pipelines, schedule regular scans, and encourage collaboration with DevSecOps teams to share responsibility for compliance.
If you’re looking for expert guidance in designing compliant CI/CD architectures, Hokstad Consulting can assist. They specialise in DevOps transformation, compliance scanning integration, cloud cost optimisation, and custom automation. Their expertise is particularly valuable for organisations managing containerised environments, helping to implement security gates, establish audit systems, and streamline deployment cycles while meeting UK and European regulatory requirements efficiently.
FAQs
How can I maintain a fast CI/CD pipeline while adding compliance scanning?
To maintain an efficient CI/CD pipeline while incorporating compliance scanning, consider using incremental scans. These focus only on changes since the last scan, saving time. Alternatively, run scans in parallel with other pipeline stages to keep delays to a minimum. It's also wise to configure scans to target high-risk areas, avoiding unnecessary checks that could slow things down.
Automating these scans and applying caching techniques can help eliminate redundant processes and boost speed. Make it a habit to review and adjust your scanning tools regularly. This ensures you achieve the right balance between being thorough and maintaining performance, so you stay compliant without dragging down your deployment workflow.
What compliance standards should my business prioritise?
When it comes to compliance, the standards your business needs to prioritise will largely depend on your industry and the regulations governing it. Some of the widely recognised frameworks include ISO/IEC 27001 for managing information security, GDPR for safeguarding personal data, PCI DSS for securing payment processes, and the NIST Cybersecurity Framework for overseeing risk management.
Focusing on the standards that align most closely with your organisation's needs helps you meet key legal and operational obligations, all while reinforcing trust with both your customers and stakeholders.
What are the best tools to automate compliance checks in containerised environments?
When it comes to automating compliance checks in containerised environments, tools like Aqua Security, Prisma Cloud, and Sysdig Secure stand out. These solutions integrate seamlessly into CI/CD pipelines, performing automated vulnerability scans and enforcing compliance standards to help maintain security and meet regulatory requirements.
For those looking for an open-source alternative, OpenSCAP offers a reliable option for compliance scanning and reporting. By incorporating these tools into your processes, you can simplify compliance management while concentrating on delivering secure, high-quality software.
