Cloud costs for CI/CD pipelines can spiral quickly, especially for large teams. This article explores how companies like Rippling and ITV tackled this issue by shifting their pipelines to spot instances, achieving up to 60% savings on compute costs and improving efficiency.
Key Takeaways:
- Spot Instances: Unused cloud capacity available at discounted rates, offering savings of 60–90% compared to on-demand instances.
- Success Stories:
- Rippling reduced EC2 costs by 60% and overall cloud spend by 50%.
- ITV saved £115,000 annually and cut deployment times from 40 minutes to 4 minutes.
- Migration Strategy: Start with 10% spot instances, monitor performance, and gradually increase usage while managing interruptions.
- Challenges: Spot interruptions can cause delays, but automated retries and fallback mechanisms ensure smooth workflows.
Bottom Line: Migrating to spot instances can dramatically cut costs while maintaining performance, but success relies on a phased approach and robust fault tolerance mechanisms.
::: @figure 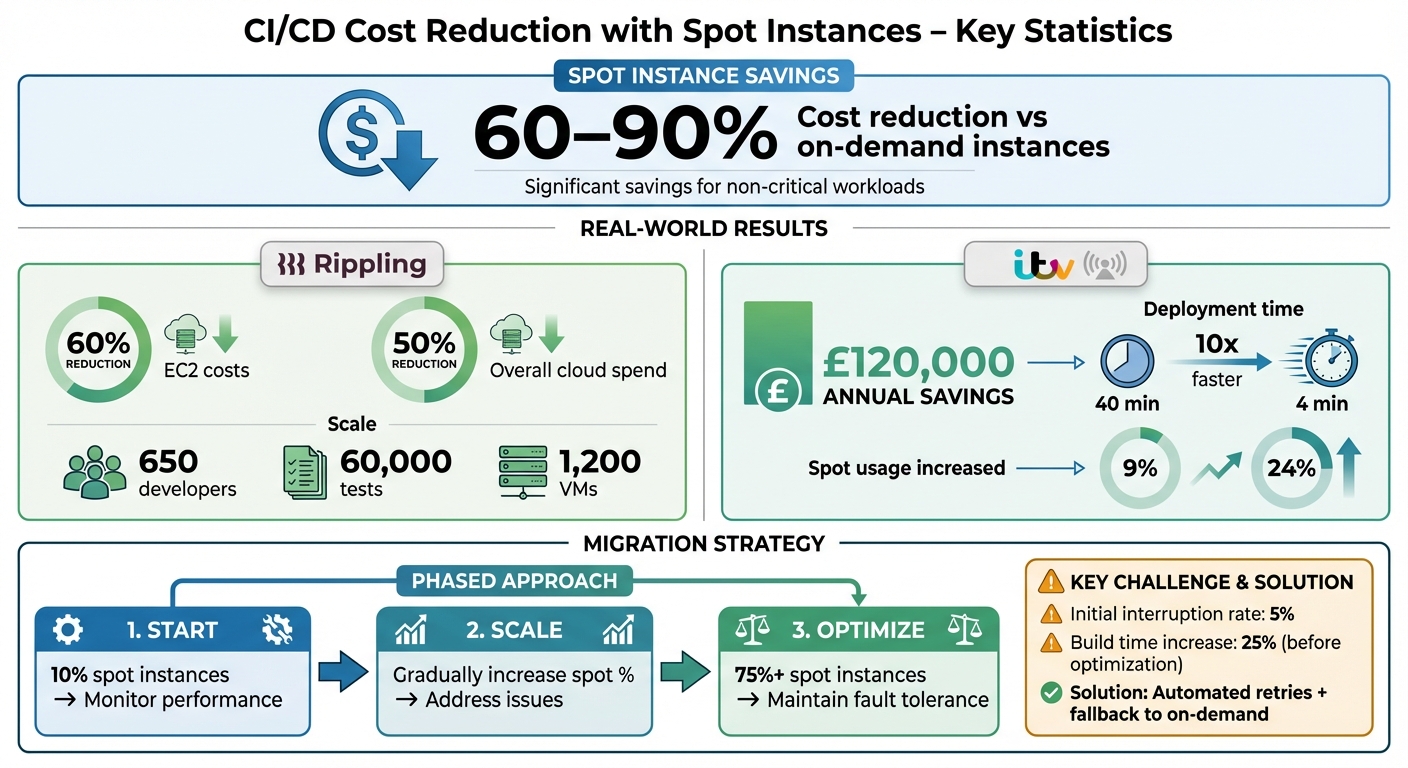 {CI/CD Cost Savings with Spot Instances: Key Statistics and Results}
:::
{CI/CD Cost Savings with Spot Instances: Key Statistics and Results}
:::
The Problem: High CI/CD Pipeline Costs
The Original Setup
The client's CI/CD system was built entirely on on-demand instances, but this approach quickly became unmanageable. With over 650 developers running more than 60,000 tests, the pipeline required a massive amount of compute power. At peak usage, the system needed upwards of 1,200 large virtual machines - translating to 50,000 CPUs and 100,000 GB of RAM. These compute resources alone made up nearly 90% of the total infrastructure costs, resulting in what Rippling's engineering team referred to as a million-dollar cloud bill
[2]. Remy DeWolf, Staff Engineer at Rippling, highlighted the situation:
At this scale, when we get a million-dollar cloud bill, we view it as an opportunity to reduce our cost. But, we also see it as an engineering challenge to do so without compromising performance or efficiency [2].
This overwhelming expense made it clear that their current setup wasn't sustainable, prompting a search for more efficient CI/CD solutions.
Problems in the CI/CD Workflow
The reliance on on-demand instances created a vicious cycle of escalating costs. Every new pipeline, additional test suite, or increase in team size pushed the infrastructure expenses even higher. Attempts to manage costs by reducing the number of build agents only led to longer build queues during peak hours. This, in turn, slowed down development cycles and decreased overall productivity, leaving the team stuck between rising costs and reduced efficiency.
Cost Savings Analysis with Spot Instances
Price Comparison: On-Demand vs Spot Instances
Spot instances can slash compute costs by 60–90%, which is a game-changer for large-scale CI/CD environments where compute often represents around 90% of the total bill [2].
The amount you save depends on several factors. Pipelines that are adaptable enough to use different instance types can tap into larger, cheaper spot capacity pools, unlocking more savings. Choosing the right allocation strategy is equally important. For example, a capacity-optimised strategy reduces the risk of interruptions, while a lowest-price strategy prioritises cost savings [2][4].
Finding High-Cost Pipelines
Once you've compared costs, the next step is identifying the pipelines that are eating up the most budget. The classic 80/20 rule applies here: around 20% of your pipelines are likely responsible for 80% of your compute costs. These high-cost pipelines often include the main monolithic CI pipeline [2].
Start by digging into your historical cloud billing data. Look for pipelines that run the most frequently, use the largest instance types, or take the longest to execute. These are your prime candidates for optimisation.
Rippling's engineering team offers a great example. Between August 2023 and April 2024, they zeroed in on their monolithic CI pipeline, which was responsible for running over 60,000 tests and driving their £1m cloud bill. By shifting this single, high-cost pipeline to AWS Spot Instances using the lowest-price allocation strategy, they managed to cut their EC2 compute costs by 60% and their overall cloud bill by 50% [2]. This targeted approach delivered immediate results without requiring a complete revamp of their infrastructure.
Cloud provider portals also make it easier to evaluate potential savings by comparing on-demand spending against historical spot pricing for equivalent instance types [1].
Migration: Moving CI/CD Pipelines to Spot Instances
Phased Migration Approach
Start your migration gradually by examining your cloud bills and historical spot pricing data. This helps establish a baseline for potential savings before making any changes [1][2].
Begin with a cautious setup: 90% on-demand instances and 10% spot instances [1][2]. This initial configuration allows you to test the waters without jeopardising critical operations. As your confidence grows and the pipeline shows stable performance, you can incrementally reduce the on-demand percentage. At each stage, monitor the process closely to catch and address any issues before they disrupt your team.
Lyft offers a great example of how manageable this process can be. The company transitioned its entire Jenkins CI/CD pipeline to EC2 Spot Instances by tweaking just four lines of deployment code. Thanks to their stateless and fault-tolerant architecture, they achieved a seamless migration and slashed their monthly compute costs by 75% [4][6].
This step-by-step approach ensures your CI/CD system is equipped to handle the unique challenges of spot instance interruptions.
Handling Spot Instance Interruptions
Spot instance interruptions are inevitable, but you can minimise their impact with the right strategies. Automated retries and dynamic fallback mechanisms are key here. Configure your CI/CD tools to retry jobs automatically if an agent disconnects or is stopped. For instance, Buildkite users can set up retries triggered by signals like exit_status: -1 or agent_stop [5].
Dynamic fallback mechanisms are another crucial component. These systems detect when spot capacity is unavailable and automatically switch pipelines to on-demand instances [2]. This prevents build queues from piling up and keeps developers from facing frustrating delays.
Rippling's engineering team tackled this challenge during their migration of a monolithic CI pipeline in August 2023. Initially, they encountered a 5% interruption rate that extended build times by 25%. To counter this, they introduced a custom persistence layer using Pytest, which skipped already-completed tests during retries. Additionally, they developed a service to detect spot outages and fall back to on-demand capacity. These measures resulted in a 60% reduction in EC2 compute costs and a 50% overall cloud savings, all while maintaining a smooth developer experience [2].
By implementing these strategies, you can ensure that interruptions don’t derail your workflows, and you can still achieve the cost efficiencies that make spot instances attractive.
Maintaining Fault Tolerance and Performance
Once you've addressed interruptions, the next step is to ensure fault tolerance and consistent performance.
Start with the capacity-optimised allocation strategy, which selects spot instance pools with the lowest interruption risk [4][2]. Only consider switching to the lowest-price strategy once your pipeline has demonstrated fault tolerance through rigorous testing and monitoring.
Another critical factor is right-sizing your hardware. Match executor counts to the available vCPU and RAM to avoid bottlenecks and ensure smooth operations [4].
For Jenkins users, an important tip is to externalise your JENKINS_HOME directory to persistent storage, such as Amazon EFS [4]. This ensures that if the master instance is reclaimed, a replacement instance can mount the same EFS volume and resume operations without losing configurations or job history. The EC2 Fleet Jenkins Plugin can further streamline your workflow by elastically scaling build agents. It automatically requests spot capacity when needed and scales down to zero during idle periods, optimising both performance and costs [4][6].
Results: Cost Reductions and Efficiency Gains
Cost Savings Achieved
The financial benefits of migrating to spot instances are clear from the experiences of two organisations. In 2021, ITV successfully shifted 75% of its workloads to Amazon EKS with Spot Instances, resulting in annual savings of approximately £120,000. This move also increased their spot instance usage from 9% to 24% [3]. Similarly, Rippling achieved a 60% reduction in EC2 costs and slashed their overall cloud spending by 50% following their migration [2].
These substantial cost reductions also paved the way for meaningful workflow improvements, as detailed below.
CI/CD Performance Improvements
The operational benefits of these migrations extended far beyond cost. ITV's transition brought a remarkable improvement in deployment times, cutting them down from 40 minutes to just 4 minutes - a tenfold increase in speed [3]. This dramatic boost in efficiency allowed their team to scale operations, increasing the number of hosted microservices by 30%. Without spot instances, achieving such scalability would have been prohibitively expensive [3].
Amazon EKS gives us the flexibility to optimise scaling and takes much of the pain out of cluster management.- Jonathan Harvey, Head of the Common Platform, ITV [3]
The ability to stretch budgets further has also unlocked new possibilities for parallelisation and scalability. Teams can now run more parallel builds, manage larger test suites, and handle traffic spikes without worrying about runaway costs. For example, Rippling's system processes over 60,000 tests across 1,200 VMs during peak periods. Such a level of parallelisation would be financially unsustainable using traditional on-demand instances [2].
This combination of cost efficiency and operational performance highlights the strategic value of incorporating spot instances into CI/CD workflows. By enabling organisations to do more with less, spot instances create a win-win scenario for both budgets and productivity.
Lessons Learned: Spot Instance Best Practices for CI/CD
Best Practices for Spot Instances
To make the most of spot instances in your CI/CD pipelines, diversify your instance pool. Instead of relying on a single instance type, expand your options to include multiple types. This increases the likelihood of finding available capacity and reduces the risk of interruptions [1][2]. For example, an initial strategy that relied on 90% spot instances caused outages. These were resolved by diversifying the instance pool and adopting a lowest-price
strategy [2]. This approach helps create a more resilient CI/CD workflow.
Another key practice is to take a phased approach when introducing spot instances. Start small, using 10–20% spot instances, and gradually increase the percentage as your system’s fault tolerance improves [1][2]. This step-by-step migration allows teams to identify and address recovery gaps before scaling up. Rippling demonstrated the success of this method, showing how a gradual transition can optimise cost savings while maintaining reliability [2].
Automating retries is another critical tactic. Configure your CI tools to automatically retry jobs if agents disconnect or are terminated [5]. Adding features like skipping already completed tests during retries, as Rippling did, can turn potential pipeline failures into manageable delays. This ensures that interruptions from spot instance terminations don’t derail your workflow.
The Benefits of Expert Cloud Cost Optimisation
While these strategies can be highly effective, implementing them correctly often requires specialised knowledge. This is where cloud cost optimisation experts can provide immense value. For example, Hokstad Consulting offers expertise in cloud cost engineering and DevOps transformation. Their services aim to reduce cloud costs by 30–50% while maintaining system reliability and improving deployment cycles.
Their offerings range from initial cloud cost audits to ongoing infrastructure optimisation and monitoring. For organisations considering a move to spot instances, expert guidance can ensure a smooth transition that delivers immediate savings. Without this expertise, a poorly executed rollout could undermine confidence in the approach.
Hokstad Consulting even offers flexible engagement models, including a no savings, no fee
option. This structure caps fees to a percentage of the savings achieved, making it a low-risk way for businesses to access the expertise needed to replicate successes like those seen with Rippling - all without significant upfront investment.
Age of Learning: Highly Scalable Continuous Integration Platform with Amazon EKS and Amazon EC2-Spot
Conclusion
Shifting CI/CD pipelines to spot instances can lead to major cost savings while maintaining performance levels. Success depends on a phased migration strategy, broadening the range of instance types, and automating fault-tolerance mechanisms. For instance, Rippling achieved a 60% reduction in EC2 compute costs alongside a 50% decrease in total cloud expenses [2]. Similarly, FundGuard managed to cut CI/CD costs by 70% while reducing testing times by half [7].
However, achieving these outcomes requires careful execution. Starting with a small portion of spot instances and gradually scaling up helps teams identify and iron out recovery issues before they affect production. This approach not only minimises risks but also bolsters resilience against spot instance interruptions. For example, Rippling initially faced a 25% increase in build times but overcame this challenge by refining their strategy [2]. Without such precautions, organisations may face disruptions or slower build processes.
To streamline the transition, expert guidance can make a world of difference. Hokstad Consulting specialises in cloud cost optimisation and DevOps transformation, helping businesses cut cloud expenses by 30–50%. Their offerings include cloud cost audits, infrastructure monitoring, and ongoing support, ensuring spot instance migrations yield immediate savings without sacrificing reliability. Plus, their no savings, no fee
model - where fees are capped as a percentage of savings - makes their expertise both accessible and risk-free. With this kind of support, your CI/CD pipelines can maintain high performance while delivering significant cost reductions.
FAQs
What are the key differences between spot instances and on-demand instances in terms of cost and reliability?
Spot instances can slash costs by as much as 90% compared to on-demand instances, making them a budget-friendly option for workloads that are flexible or not time-sensitive. The trade-off? They come with a level of unpredictability, as they can be interrupted with just two minutes' warning.
On the other hand, on-demand instances, though far pricier, provide steady availability. This makes them ideal for tasks that demand high reliability or consistent uptime without compromise.
How can I prevent interruptions when using spot instances in CI/CD pipelines?
To reduce the chances of disruptions when using spot instances in CI/CD pipelines, it's a good idea to set up automated recovery processes. Tools like Auto Scaling Groups or Kubernetes can help manage this effectively. Make sure to store essential data externally so it stays safe and accessible, even if interruptions occur. Structuring your pipelines to be stateless and idempotent allows them to restart smoothly without issues.
It's important to regularly test how your system handles interruptions. This helps you spot any weaknesses and improve your processes. For certain workloads, using techniques like checkpointing can be useful to save progress and lessen the impact of interruptions. By planning for resilience, you can keep your CI/CD pipelines dependable and cost-efficient.
How can I start using spot instances to reduce CI/CD pipeline costs?
To start using spot instances in your CI/CD pipeline, the first step is to confirm that your workloads are a good fit. Tasks like automated testing or batch processing, which can handle interruptions without major issues, are perfect candidates.
Next, make use of tools that can automatically manage the provisioning and replacement of spot instances. This ensures you maintain the necessary capacity, even when spot instances are interrupted. It's equally important to set up safeguards for handling interruptions - this might include automatic retries or mechanisms to resume jobs if a spot instance is terminated.
You’ll also need to adapt your CI/CD pipeline to support dynamic scaling. This means ensuring it can adjust as spot instance availability fluctuates. Once these adjustments are in place, run small-scale tests to evaluate performance. These tests will help you fine-tune your setup and squeeze the most savings out of your configuration while keeping the pipeline reliable.
